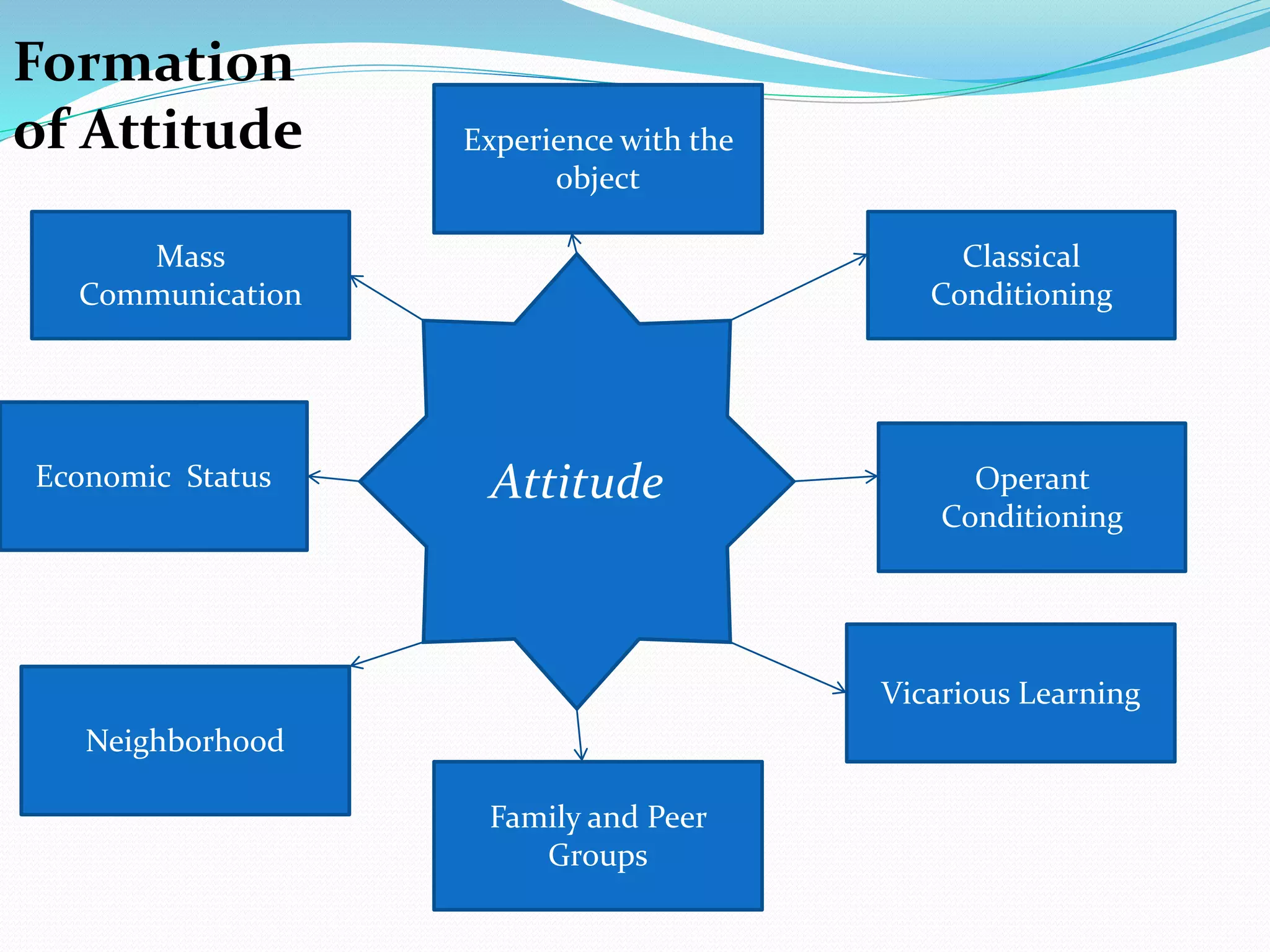
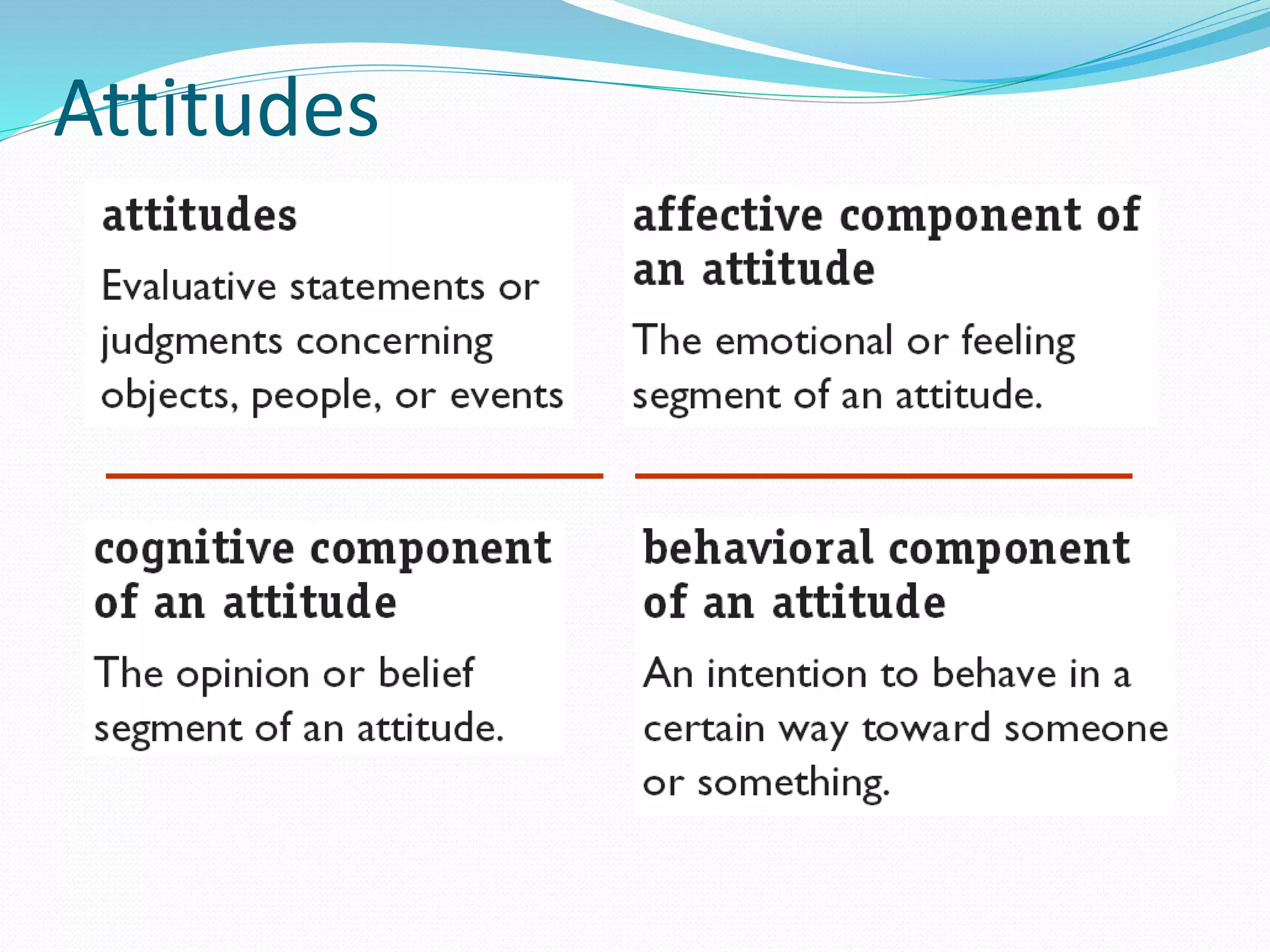
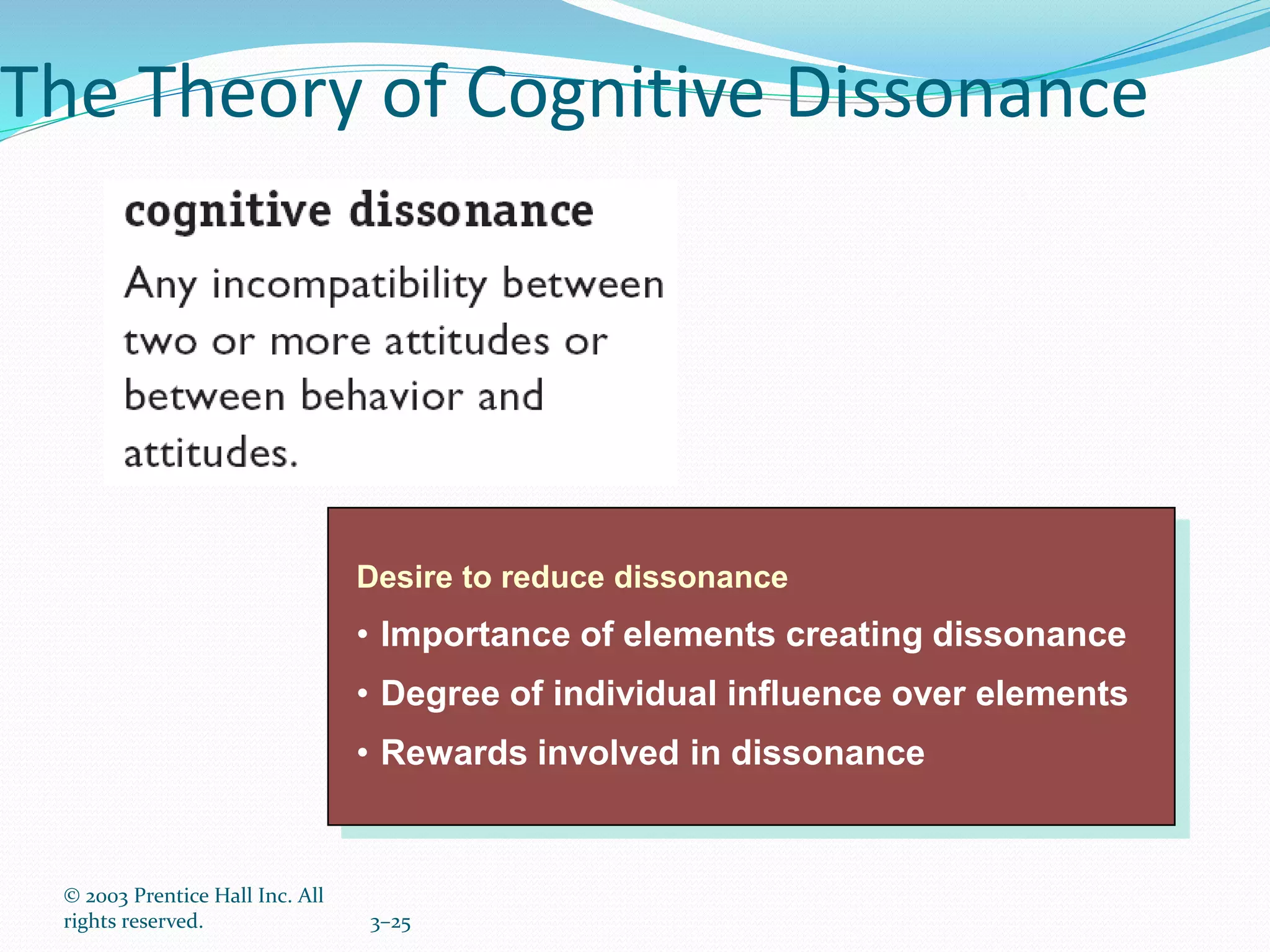
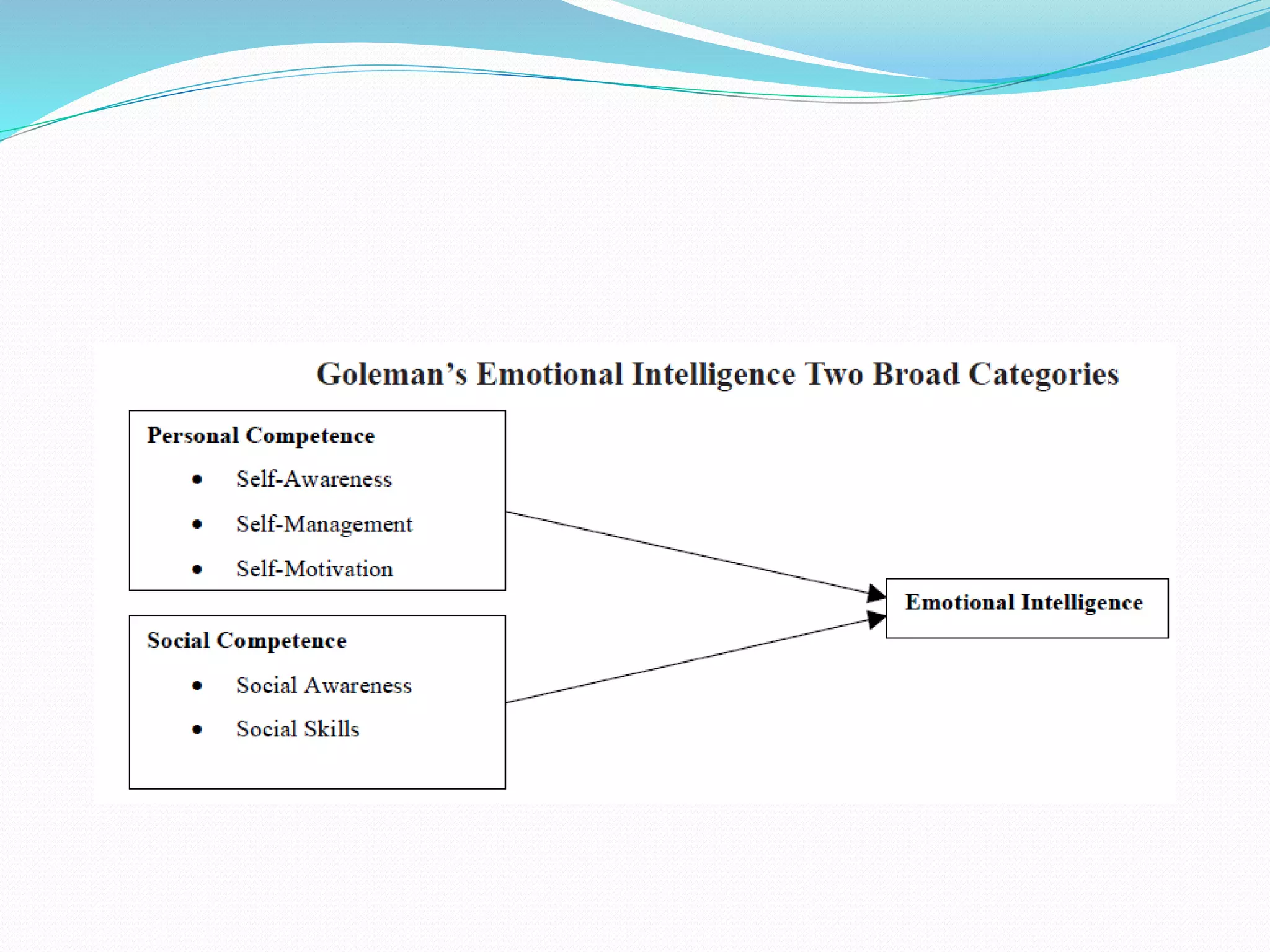
This document discusses attitudes and their importance in organizations. It defines attitudes as mental states that influence responses to people, objects, and situations. Attitudes have three components - affective, cognitive, and behavioral. They serve four functions: adjustment, knowledge, ego-defense, and value expression. In organizations, important job-related attitudes include job involvement, organizational commitment, and job satisfaction. Changing attitudes can be difficult due to barriers like prior commitment and lack of information, but providing new information, using fear appeals, and influencing peers can help overcome these barriers. Measuring the relationship between attitudes and behaviors requires considering moderating variables. The document also discusses self-fulfilling prophecies, cognitive dissonance theory, and emotional intelligence