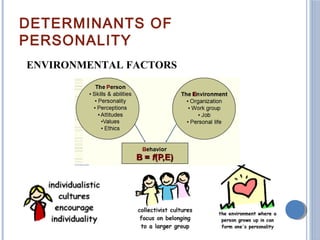
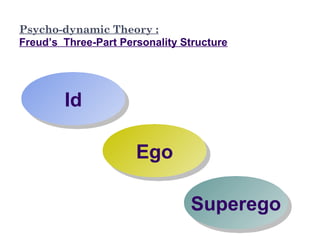
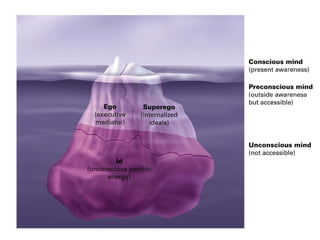
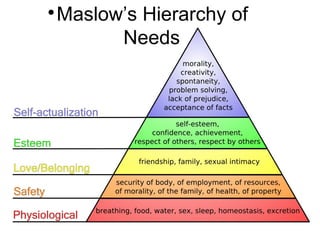
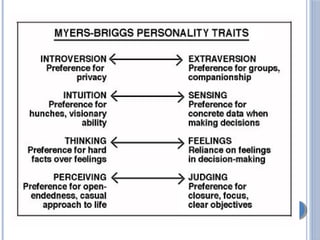
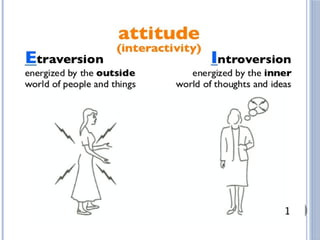
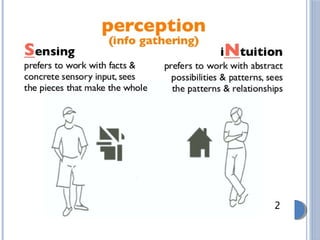
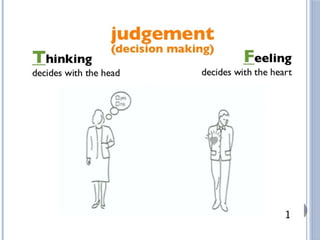
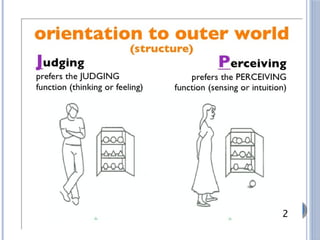
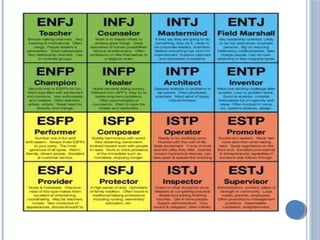
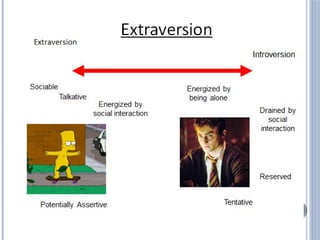
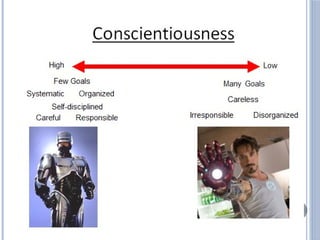
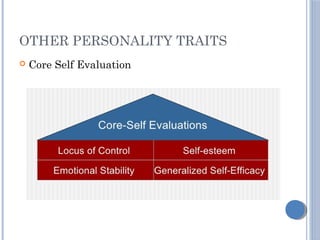
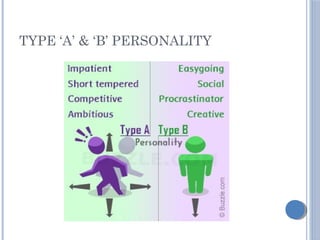
The document discusses personality definitions, determinants, and various theories, including Freud's psycho-dynamic theory that consists of the id, ego, and superego. It also covers humanistic approaches, specifically Maslow's hierarchy of needs, and the social-cognitive approach emphasizing environmental and cognitive influences on personality development. Additionally, it touches on methods of measuring personality traits and profiles of notable individuals related to these concepts.