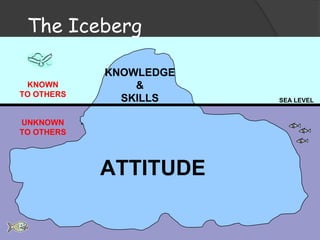
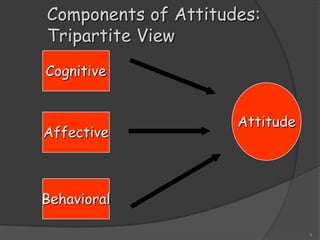
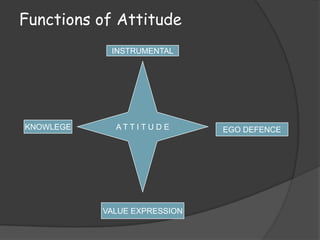
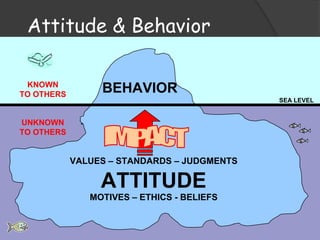
The document discusses the concept of attitude, likening it to an iceberg where only a small portion is visible, with attitudes influencing behavior and perceptions in various ways. It outlines the components of attitudes, functions, and theories of attitude change, particularly cognitive dissonance and self-perception theory. Additionally, it addresses the impact of attitudes in the workplace, emphasizing job involvement, organizational commitment, and job satisfaction.