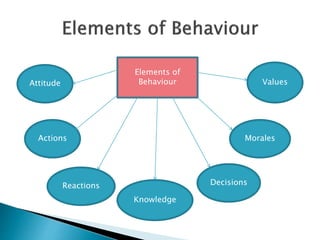
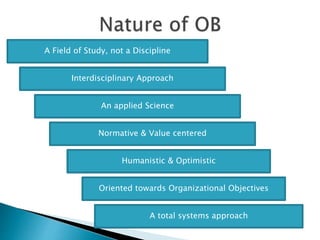
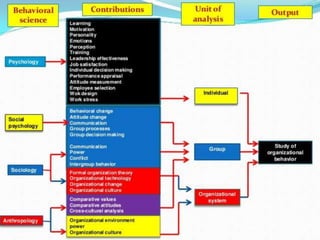
1. Organizational behavior is the study of human behavior, attitudes, and performance within organizational settings, drawing on theories from disciplines like psychology, sociology, and anthropology.
2. It analyzes how the external environment affects organizations and their human resources, objectives, and strategies.
3. Organizational behavior is an interdisciplinary field that uses concepts from multiple reference disciplines like psychology, sociology, social psychology, anthropology, political science, management, and economics to understand, predict, and manage human behavior in organizations.