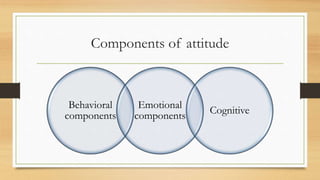
This document discusses organizational attitudes. It defines attitude and identifies its three main components: affective, behavioral, and cognitive. It explains how attitudes can influence behavior but are not always directly related. Causes of employee dissatisfaction and negative attitudes are then outlined. The document also discusses different types of attitudes employees can have, barriers to changing attitudes, and methods for measuring attitudes. Finally, it concludes that attitudes are influenced by both logical beliefs and emotional factors, and shape behavior.