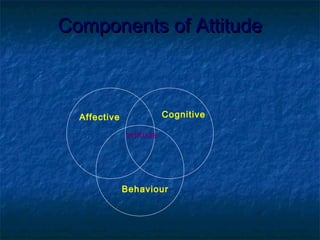
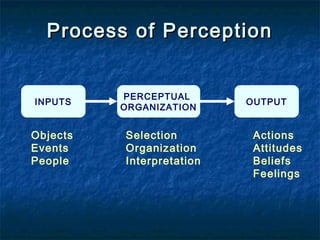
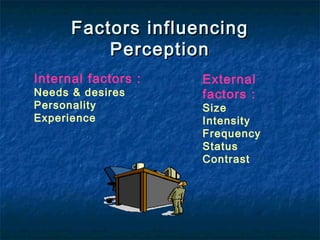
Attitudes, perceptions, and motivation influence individual behavior. Attitudes are learned predispositions that exert influence through three components: affective feelings, cognitive beliefs, and behavioral tendencies. They are formed through experience and associations. Perception is the process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting information from the environment. It is influenced by internal factors like needs and external factors like size and intensity. Motivation is influenced by attitudes and drives human behavior and decision making.