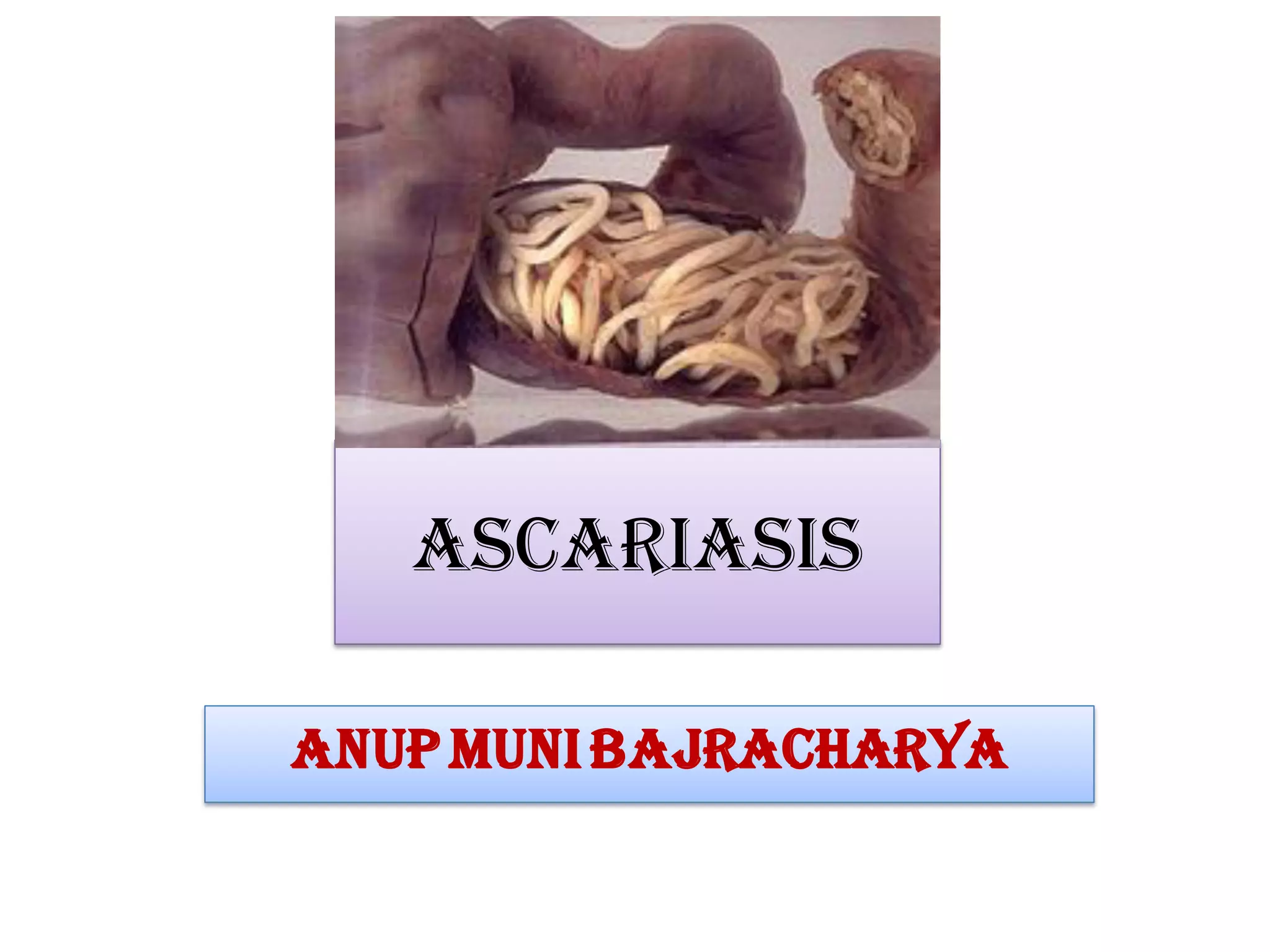
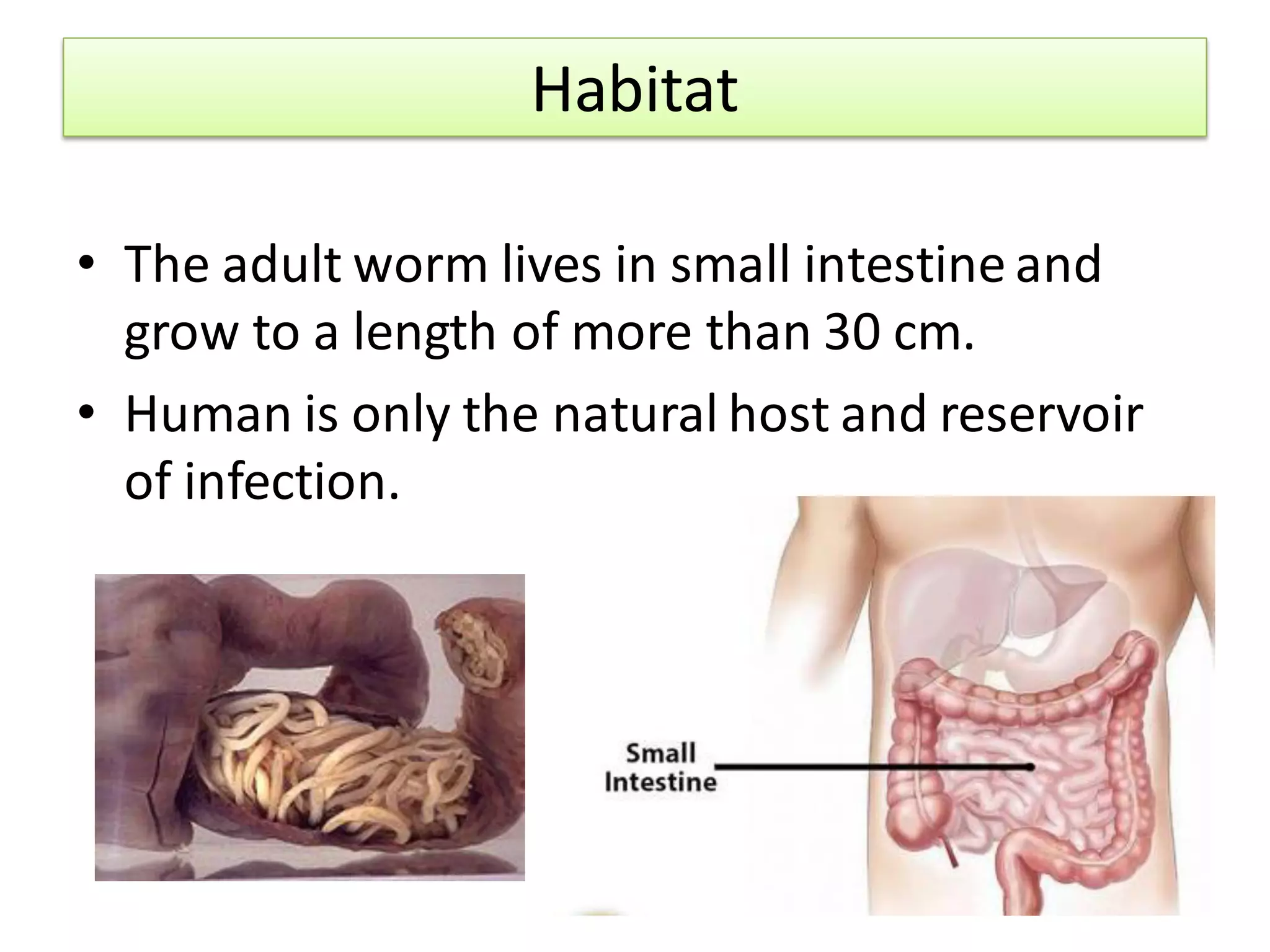
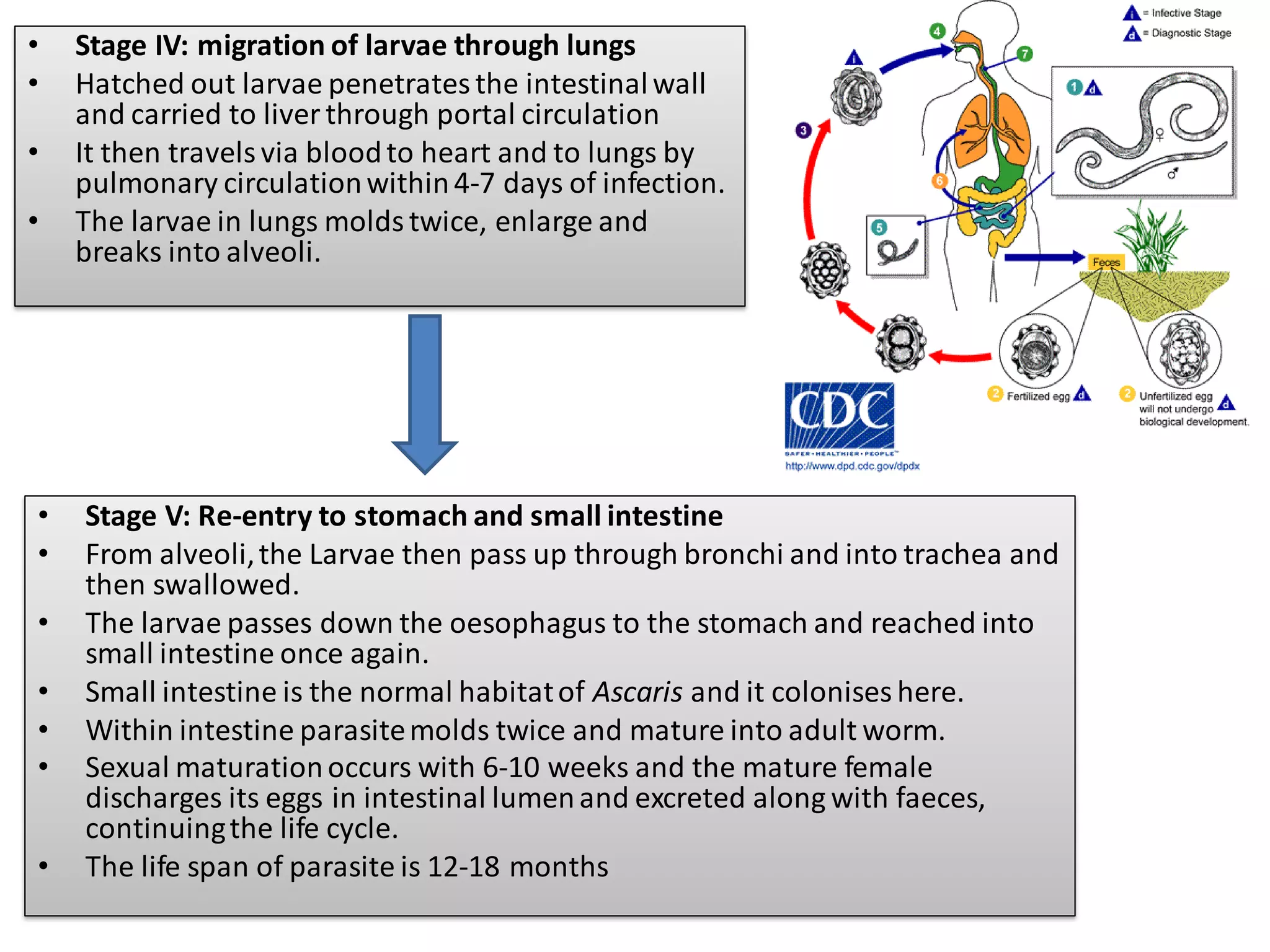
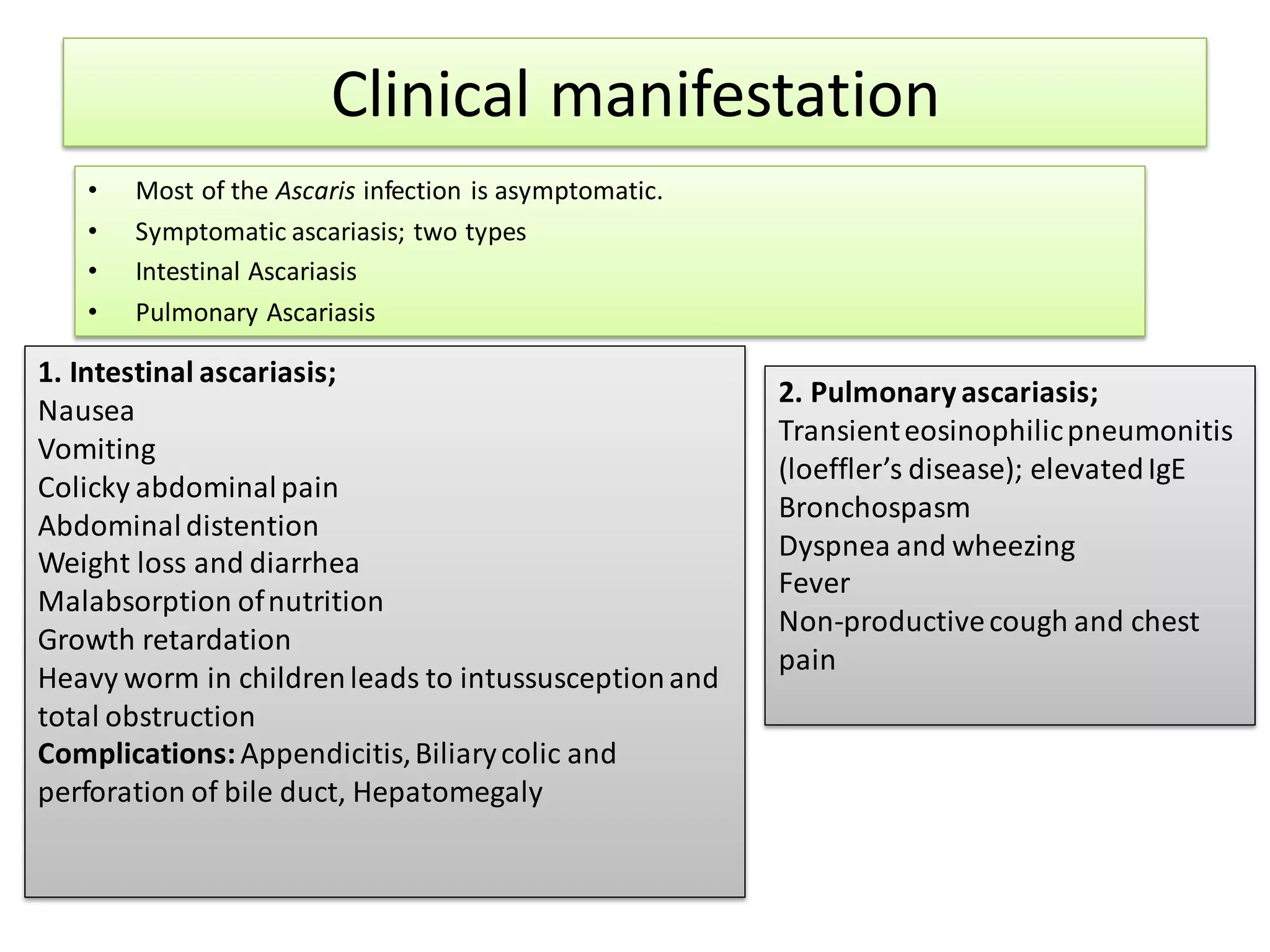
Ascariasis is an infection of the small intestine caused by the Ascaris lumbricoides worm, which is the largest intestinal nematode in humans and primarily found in tropical and subtropical areas with poor sanitation. The life cycle involves the ingestion of embryonated eggs, larval migration through the body, and maturation in the intestine, with various clinical manifestations ranging from asymptomatic to severe complications such as intestinal obstruction. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of stool and treatment options include medications like mebendazole and albendazole, along with preventive measures such as hygiene practices.