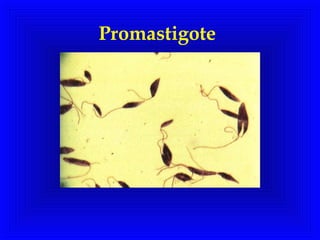
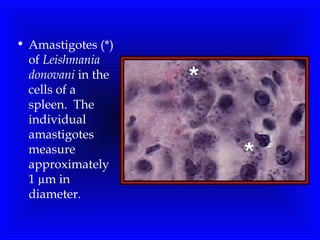
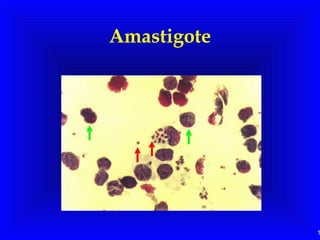
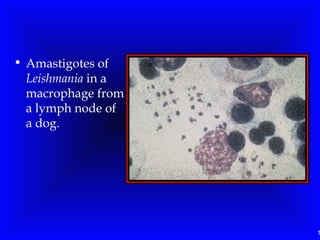
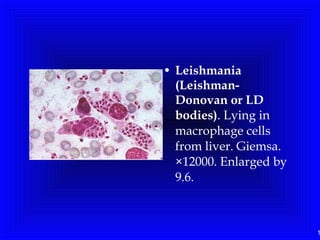
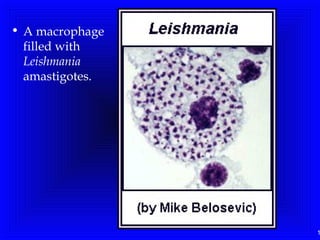
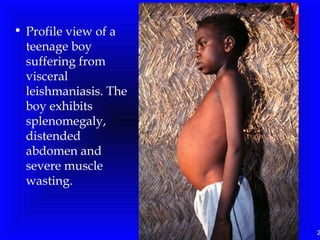
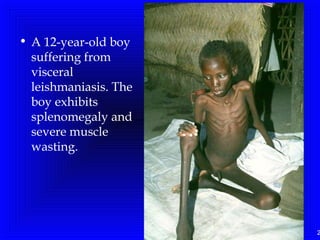
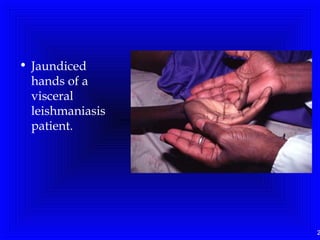
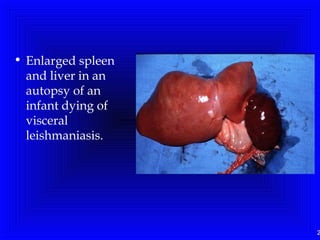
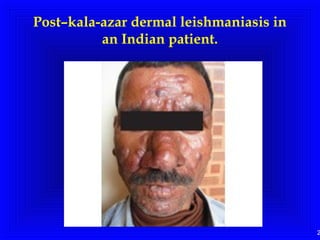
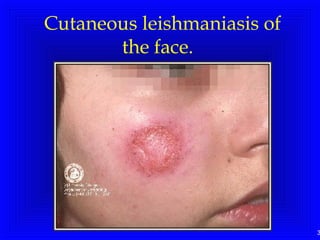
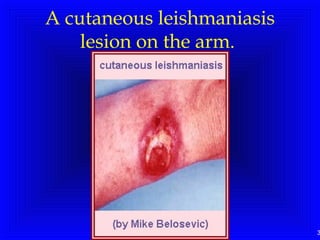
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Leishmania. It is transmitted by sand fly bites and affects the reticuloendothelial system. There are three main clinical forms: visceral leishmaniasis which involves vital organs, cutaneous leishmaniasis causing skin lesions, and mucosal leishmaniasis affecting mucous membranes. Visceral leishmaniasis, if left untreated, can be fatal and involves enlargement of the spleen, liver and lymph nodes with pancytopenia. Diagnosis involves clinical signs, serology, microscopy and culture. Treatment depends on the geographical region but involves pentavalent antimonials, amphotericin B