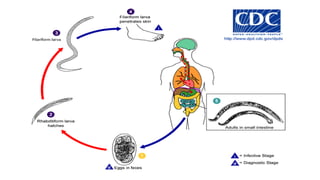
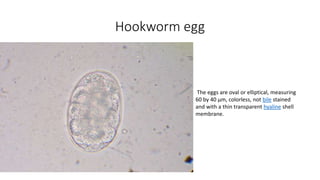
Hookworm is an intestinal parasite spread through contact with contaminated soil. It has a complex lifecycle involving eggs hatching in soil into larvae that penetrate human skin, traveling to the lungs and then intestines where they mature into adult worms, feeding on blood and causing anemia. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and protein deficiency. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of stool samples. Treatment involves anthelmintic drugs like albendazole or mebendazole. Prevention focuses on improved sanitation and not walking barefoot in contaminated areas.



![LIFECYCLE
• The host is infected by larva not by eggs and usual route is skin
• Hookworm need moist soil, above 18c ,in order to hatch, they die if
exposed to direct sunlight or if they become dry
• First stage larva [L1]are noninfective ,feed on soil microorganism until
they moult into second stage larva[L2]
• First and second stage larva are in rhabditiform stage
• After feeding for seven days they moult into Third stage
larva[L3]known as filariform stage .This is nonfeeding ,infective stage`](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hookworm-191204160051/85/Hookworm-5-320.jpg)