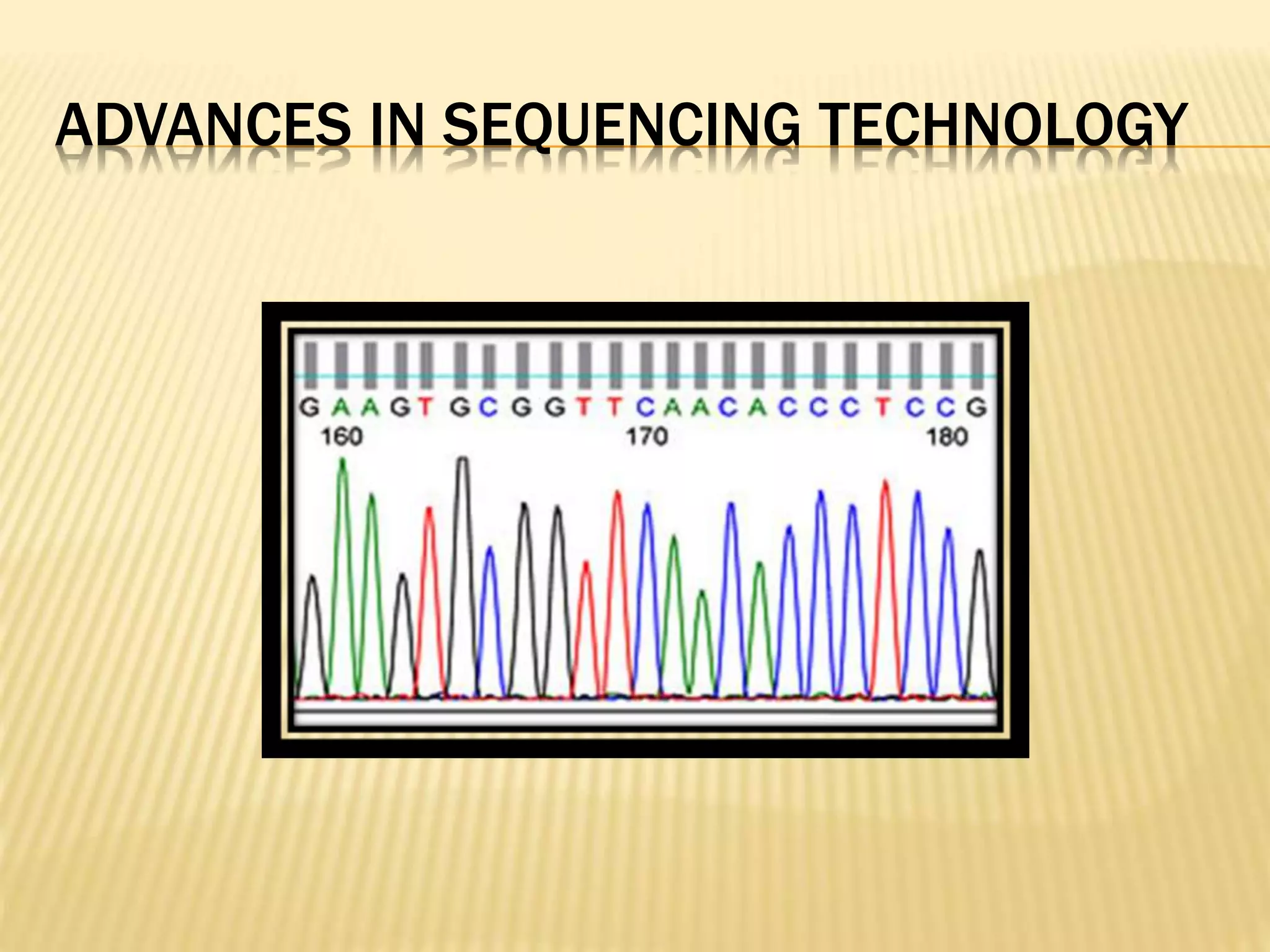
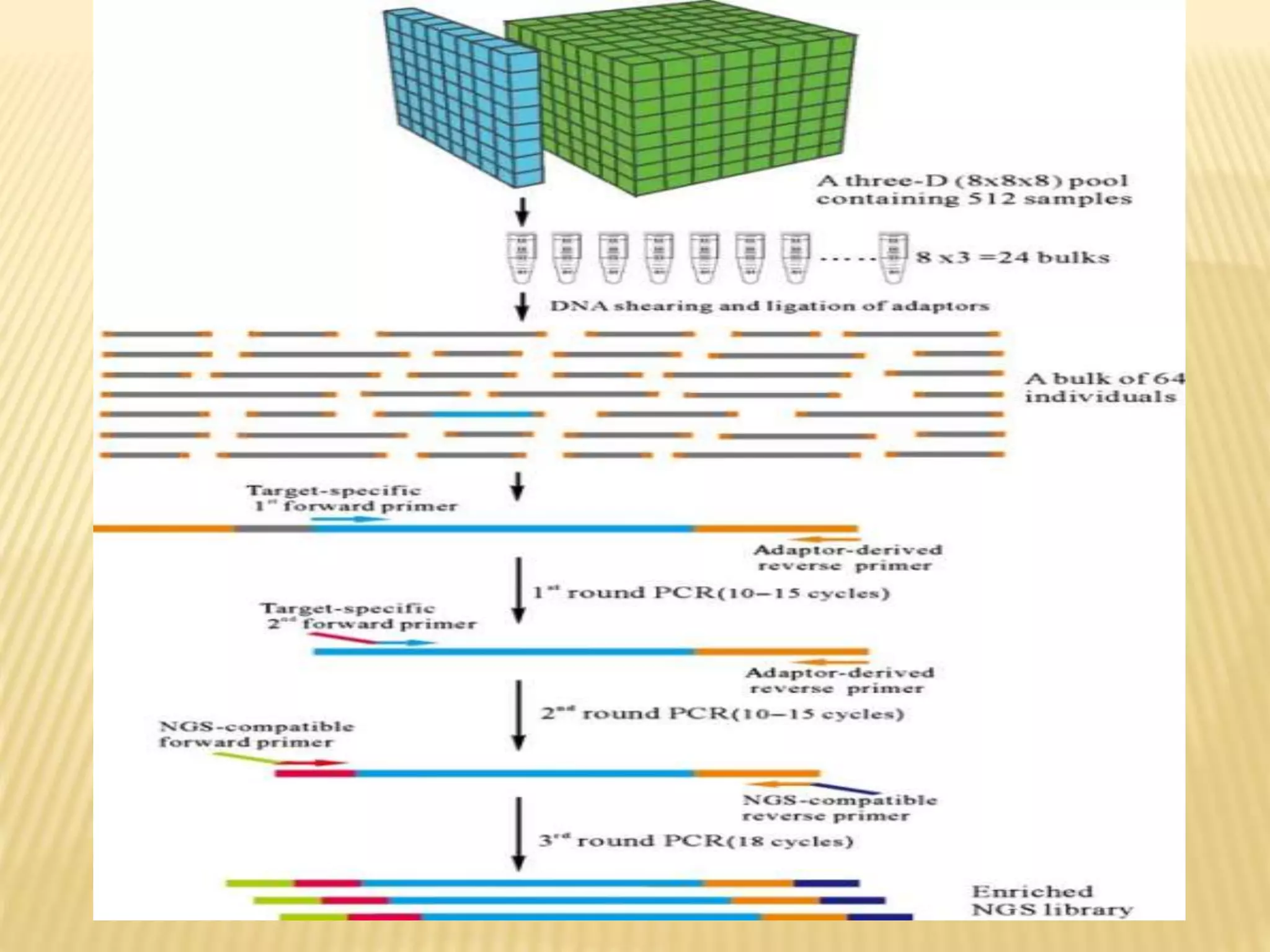
Next generation sequencing (NGS) refers to modern DNA sequencing technologies that allow for high-speed, low-cost sequencing of entire genomes. NGS works by massively parallel sequencing of millions of DNA fragments. The Illumina sequencing by synthesis method is the most commonly used NGS approach. It involves library preparation, cluster generation on a flow cell, sequencing via reversible dye-terminator chemistry, and computational analysis of sequenced reads. Key advantages of NGS include its scalability, unlimited dynamic range, tunable coverage levels, and ability to multiplex many samples simultaneously in a single run.