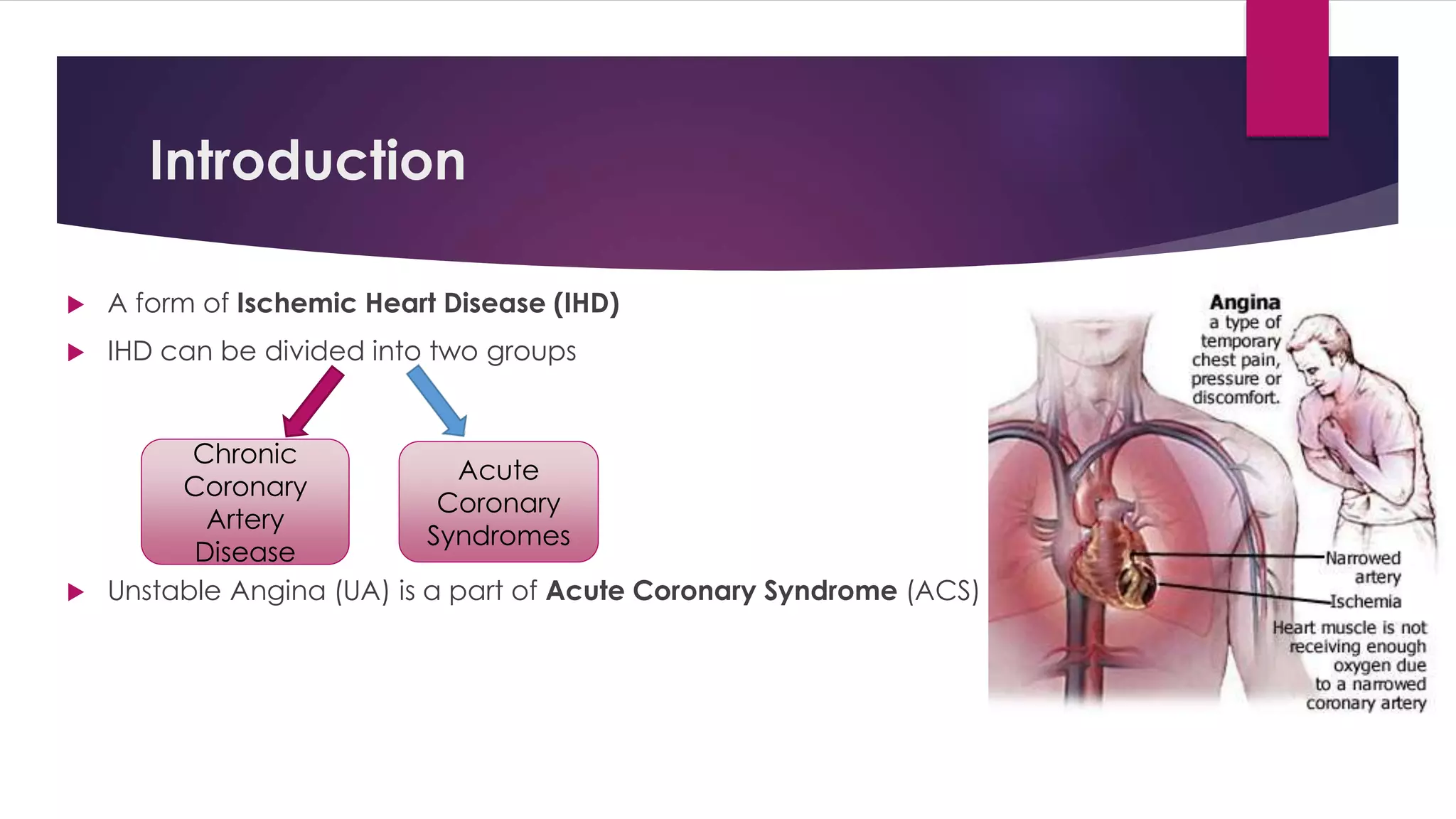
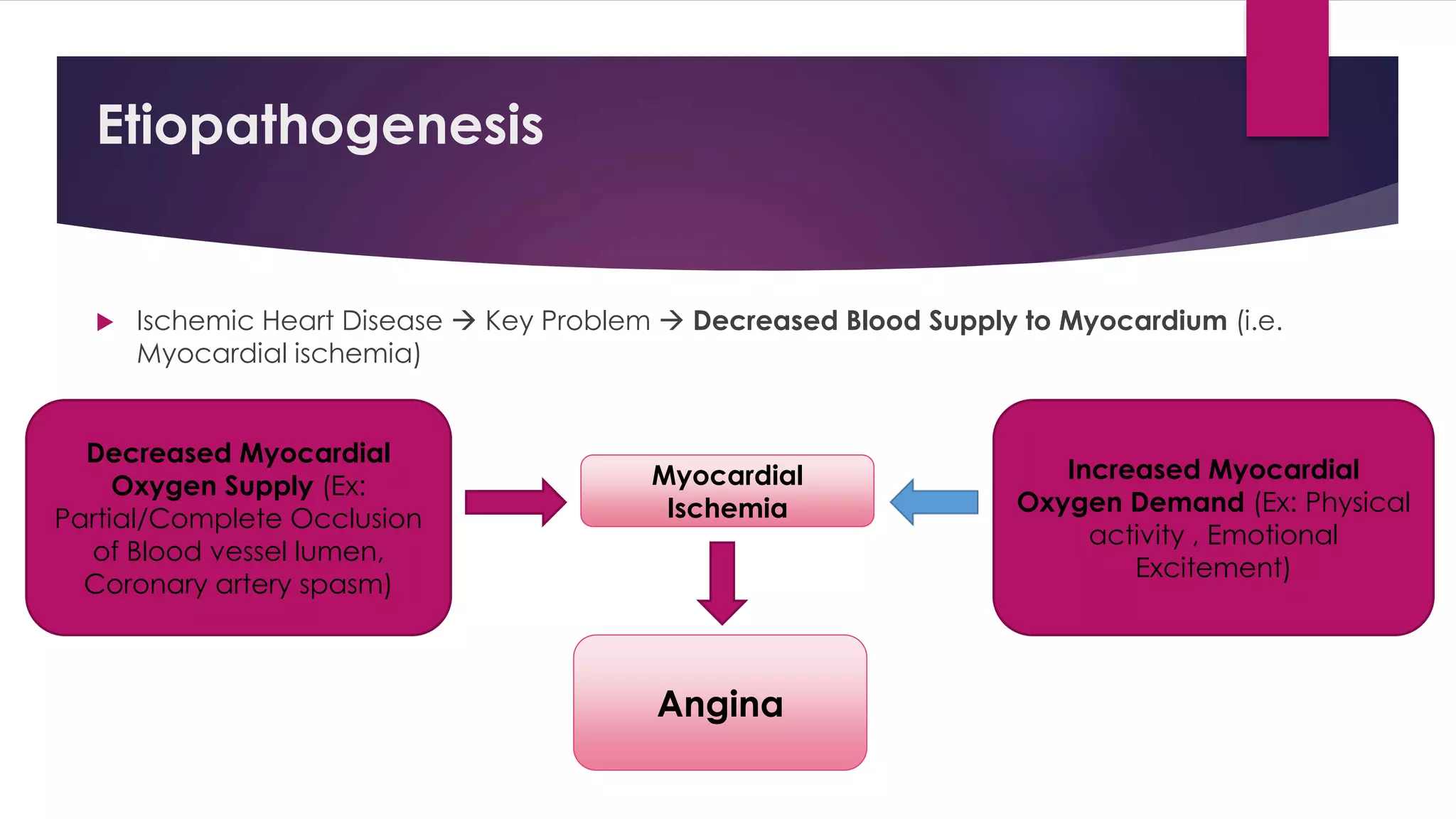
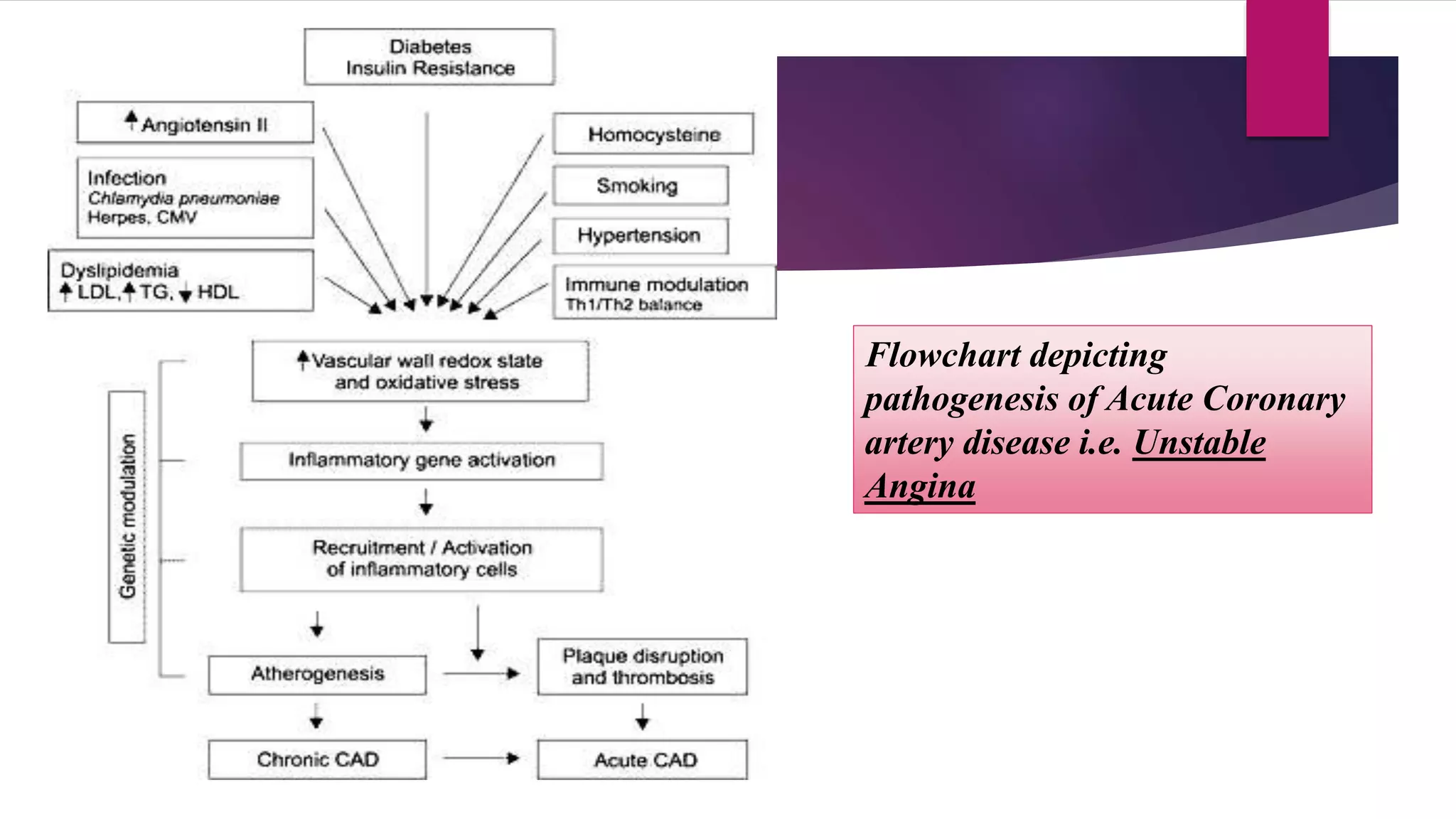
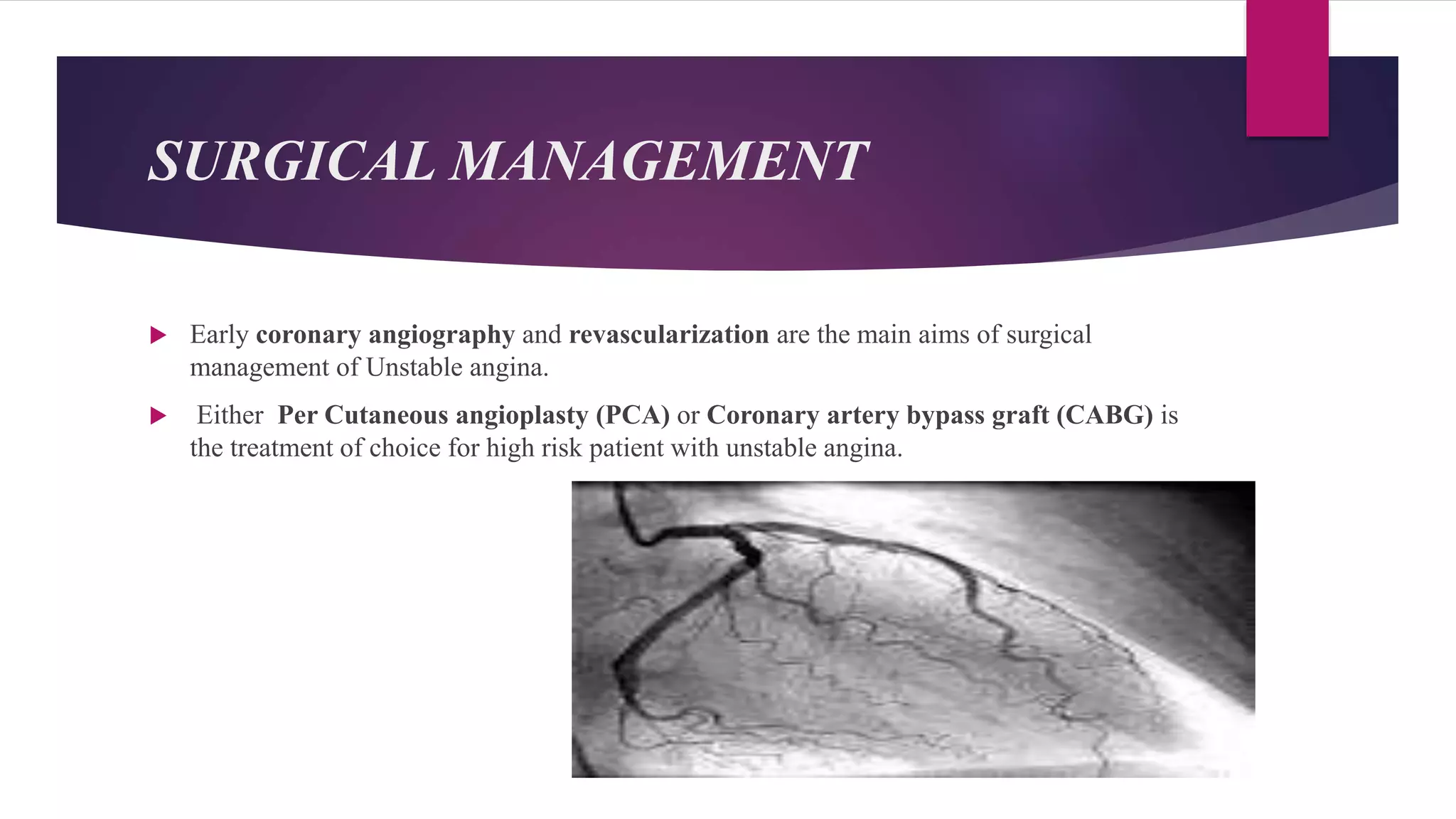
Unstable angina is a form of ischemic heart disease where a person experiences chest pain or discomfort that occurs at rest or with minimal exertion. It is caused by decreased blood supply to the heart muscle due to partial blockage of the coronary arteries. Diagnosis involves taking a medical history, electrocardiogram, cardiac enzyme tests, and stress testing. Treatment consists of blood thinners, nitroglycerin, blood pressure medications, and cholesterol-lowering drugs medically or early cardiac catheterization and angioplasty or bypass surgery if high risk.