1) Hydronephrosis is defined as the dilatation of the pelvi-calyceal system of the kidney due to partial or intermittent blockage of urine flow.
2) Causes include congenital abnormalities, kidney stones, ureteral strictures, or compression from other structures.
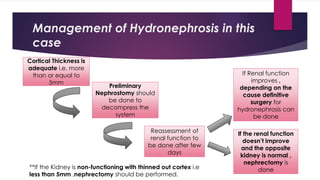
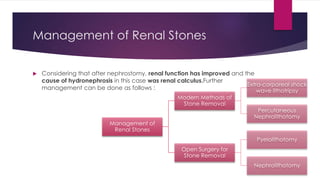
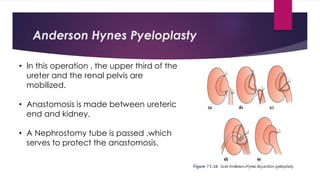
3) Treatment depends on the underlying cause and includes procedures to remove obstructions like stones, repair strictures, or decompress the system with nephrostomy tubes. Surgery may be needed for severe hydronephrosis to prevent kidney damage.