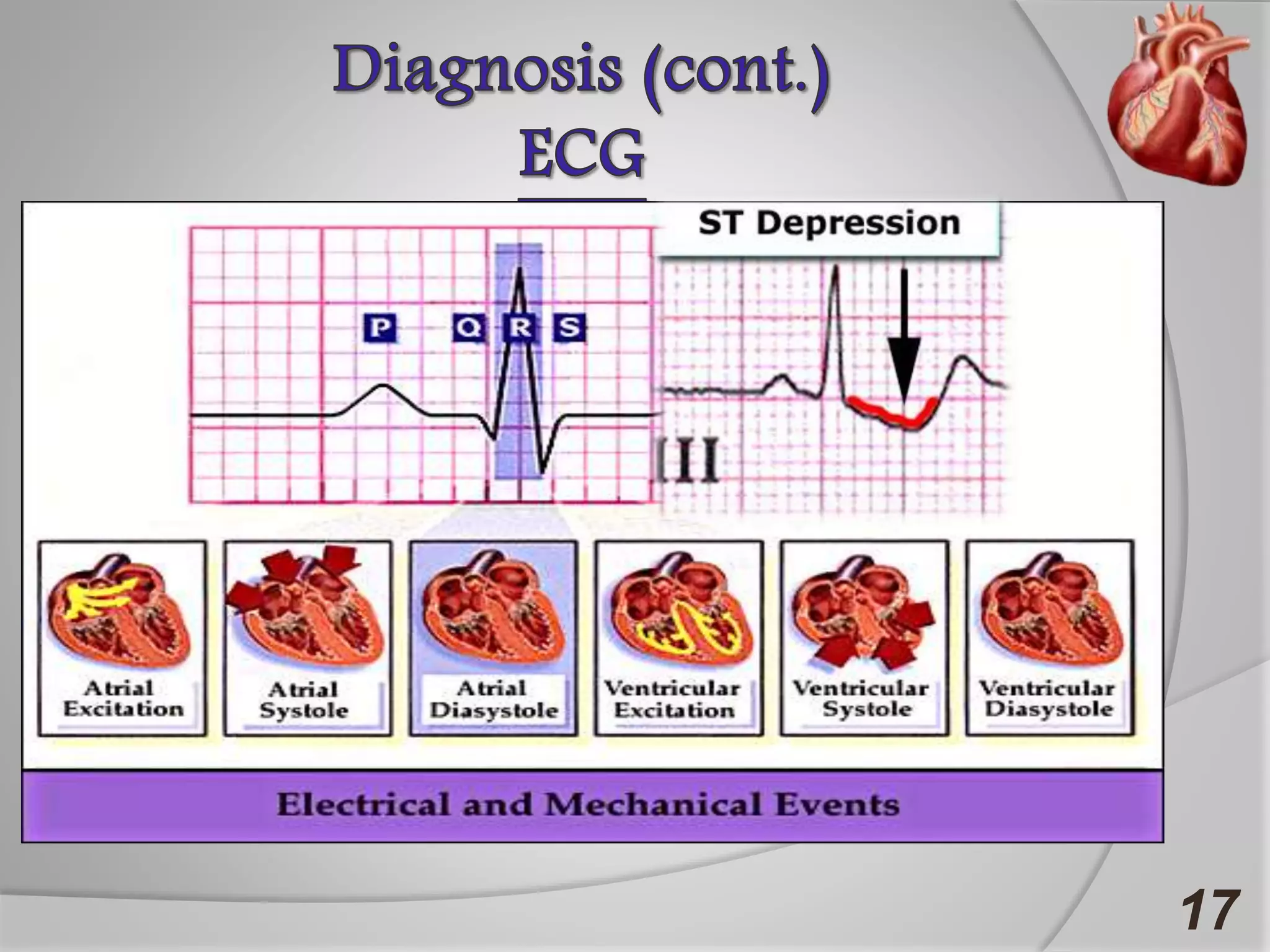
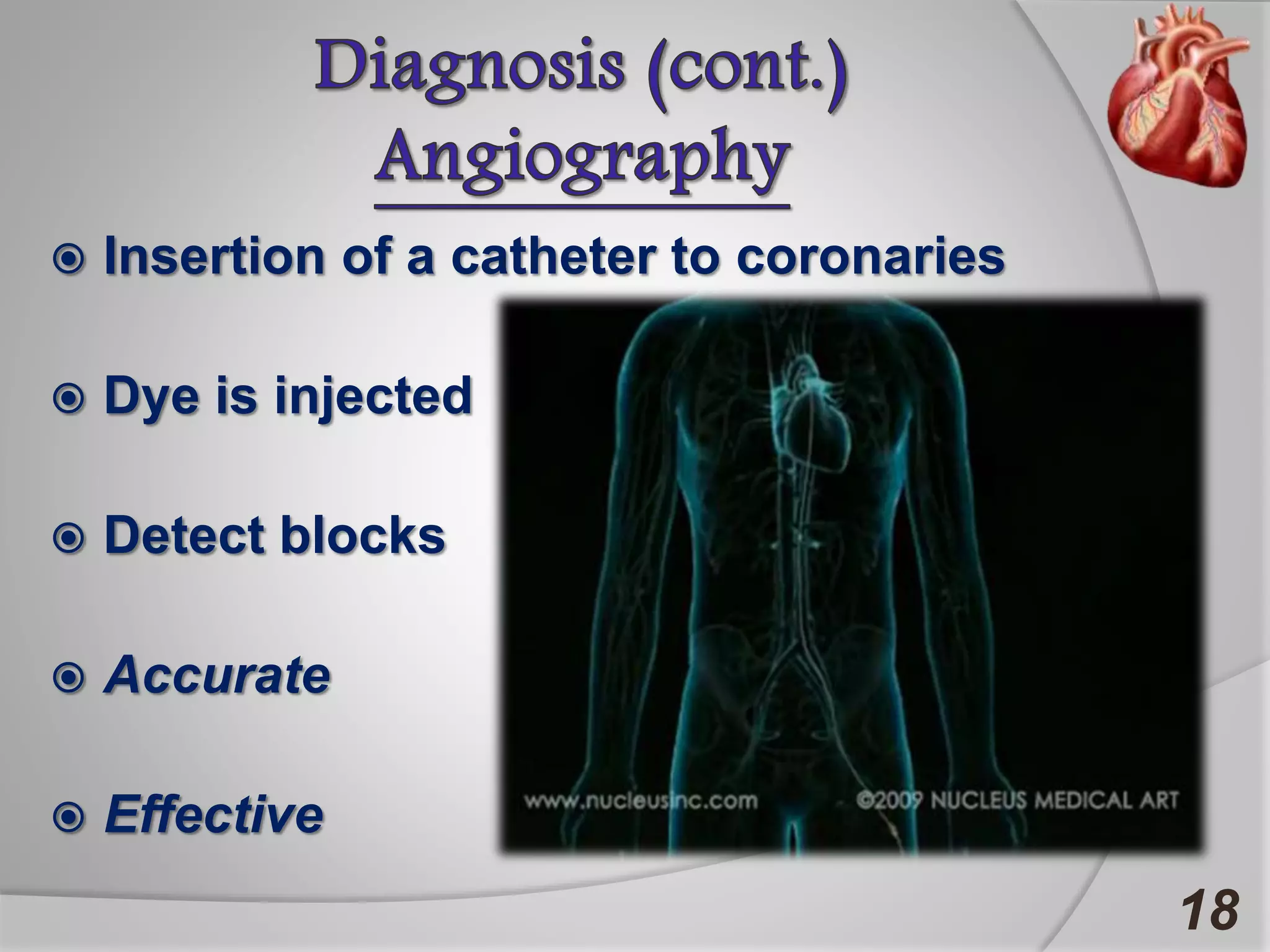
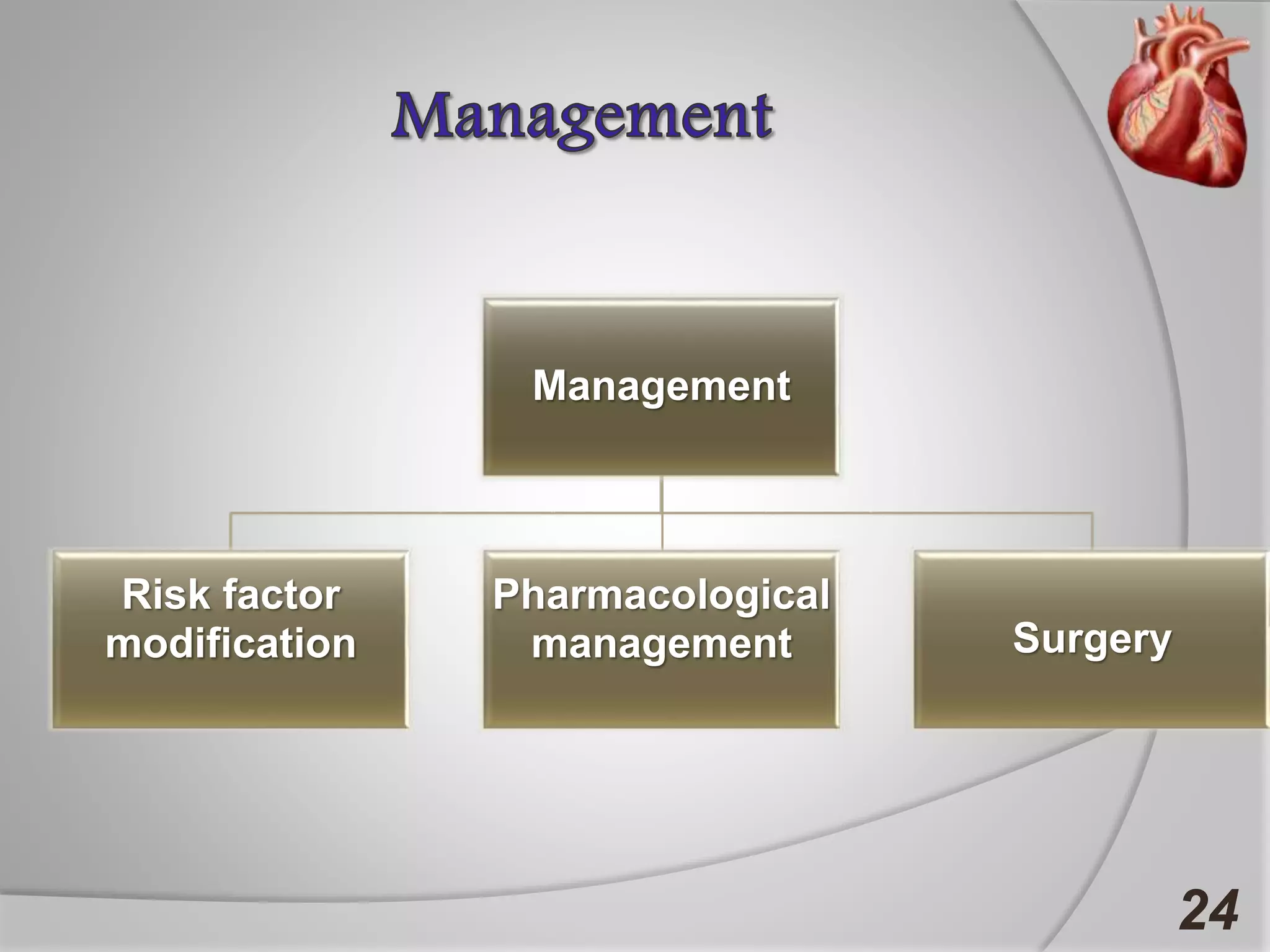
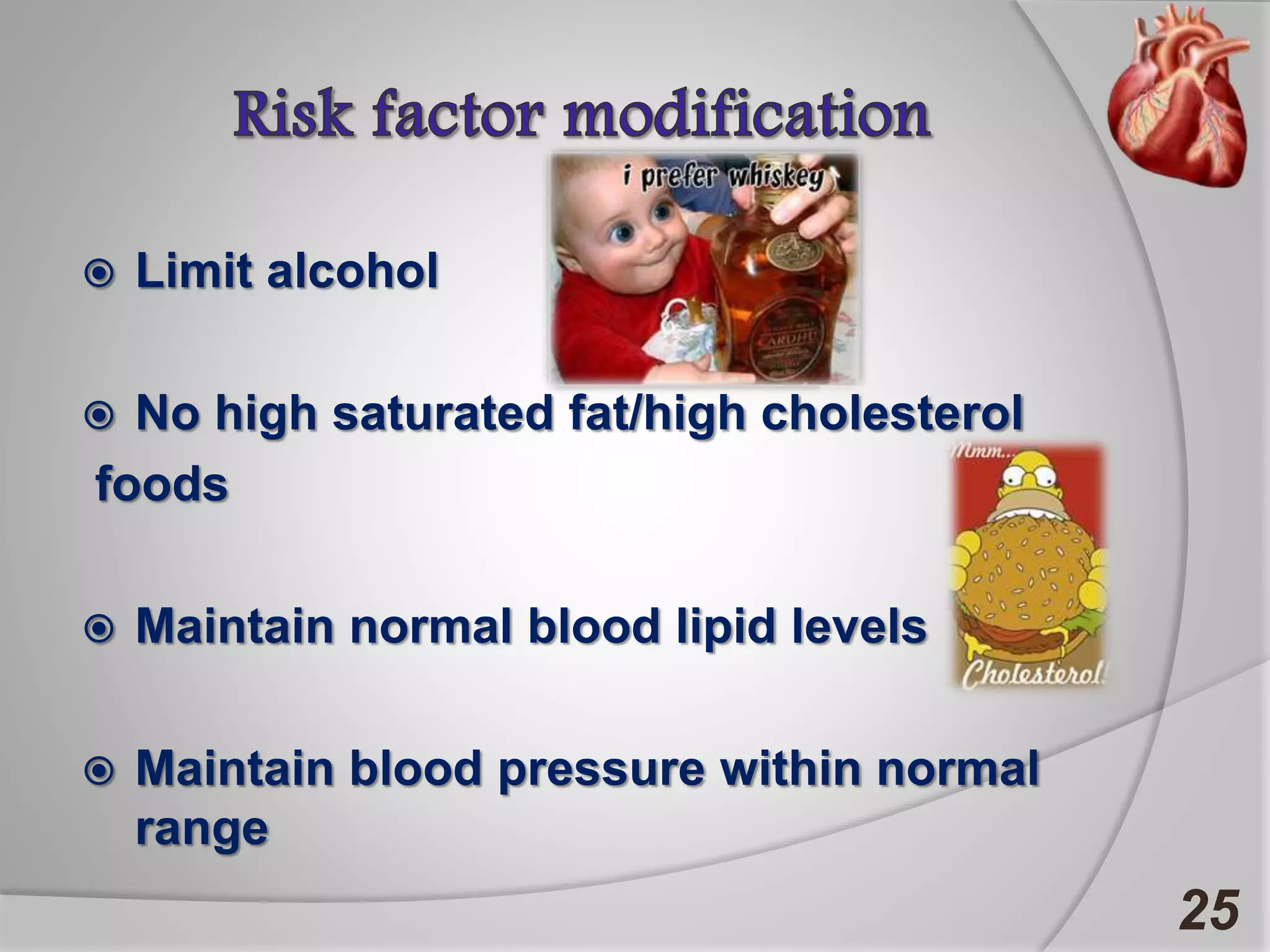
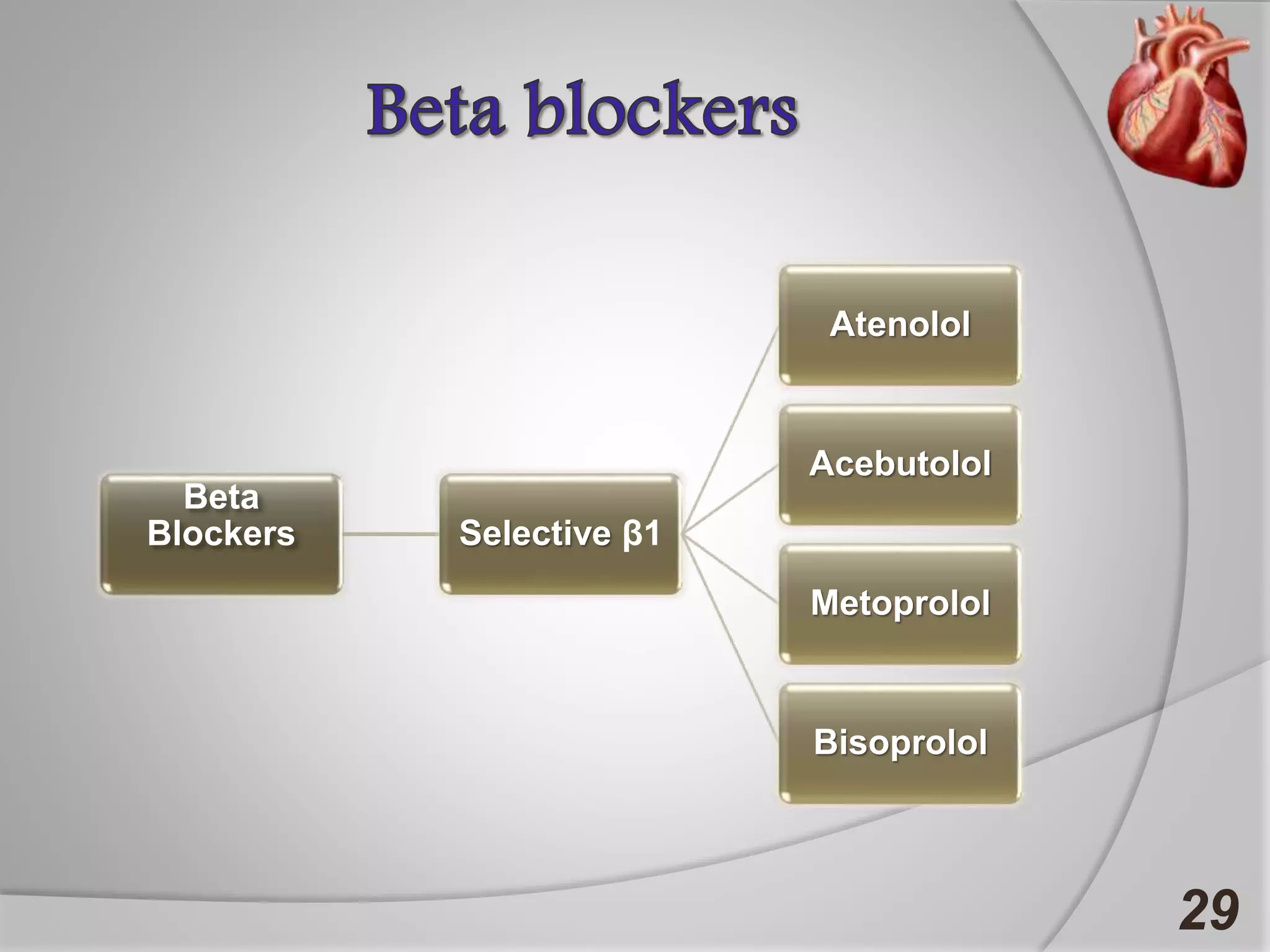
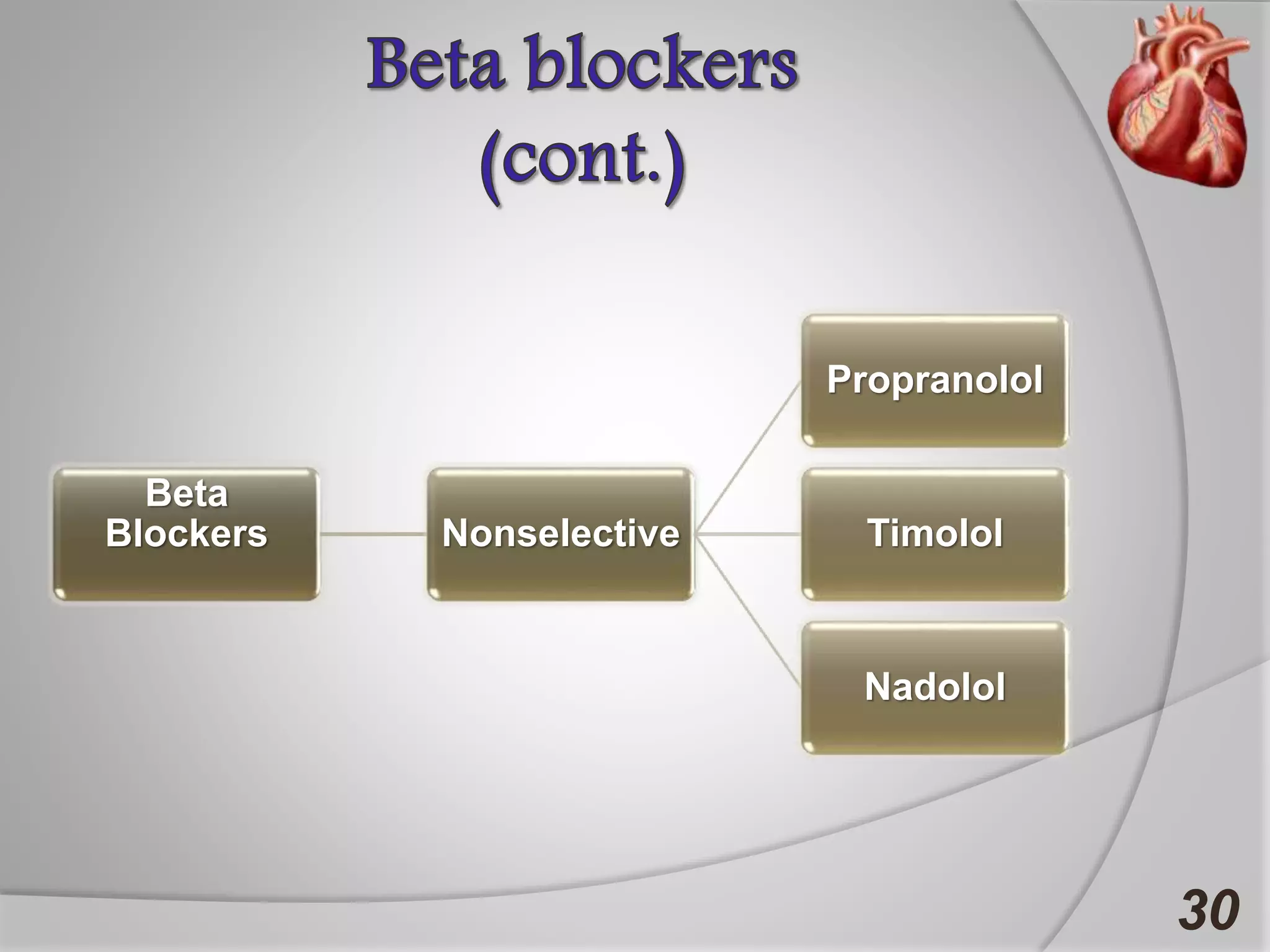
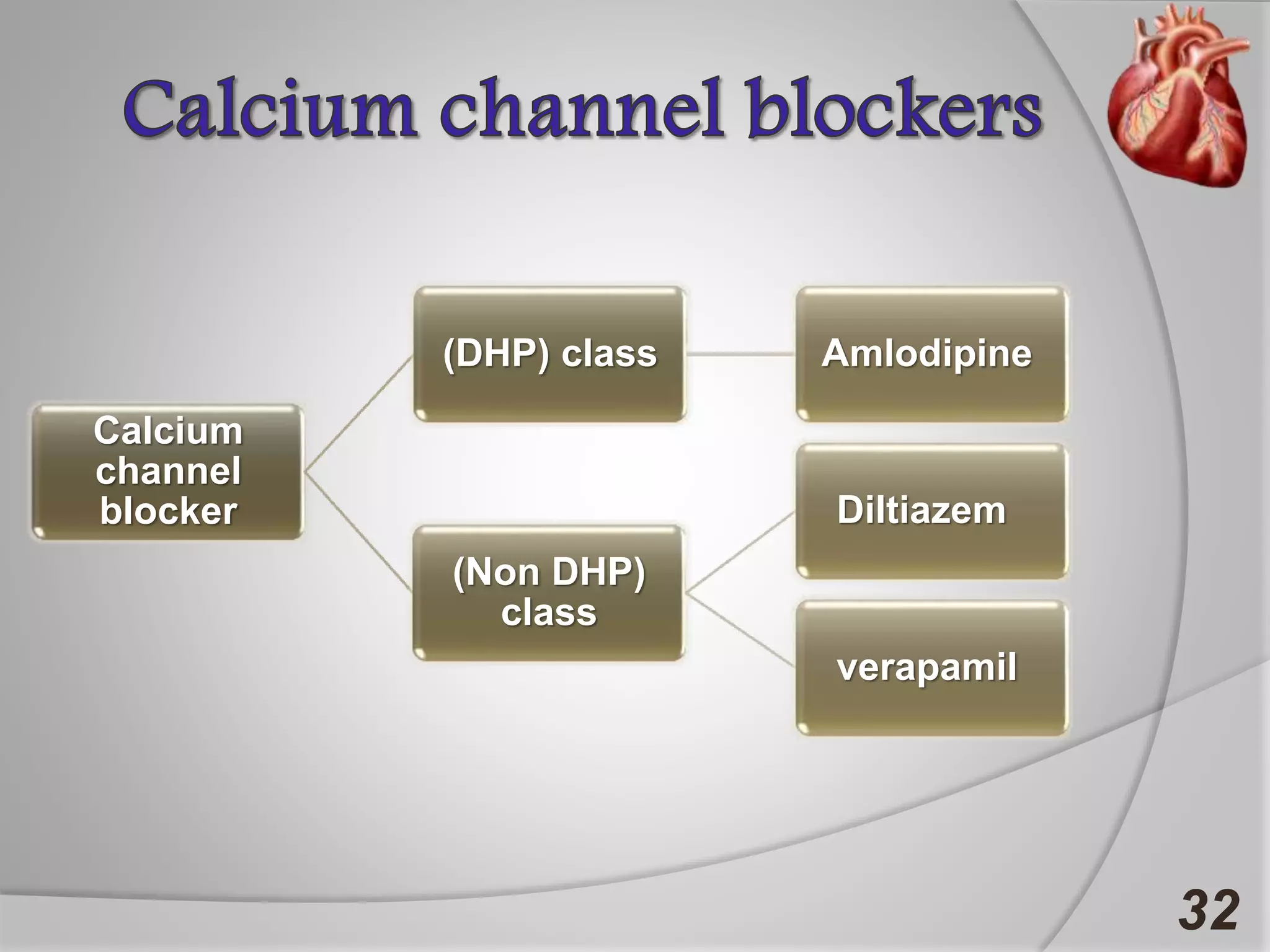
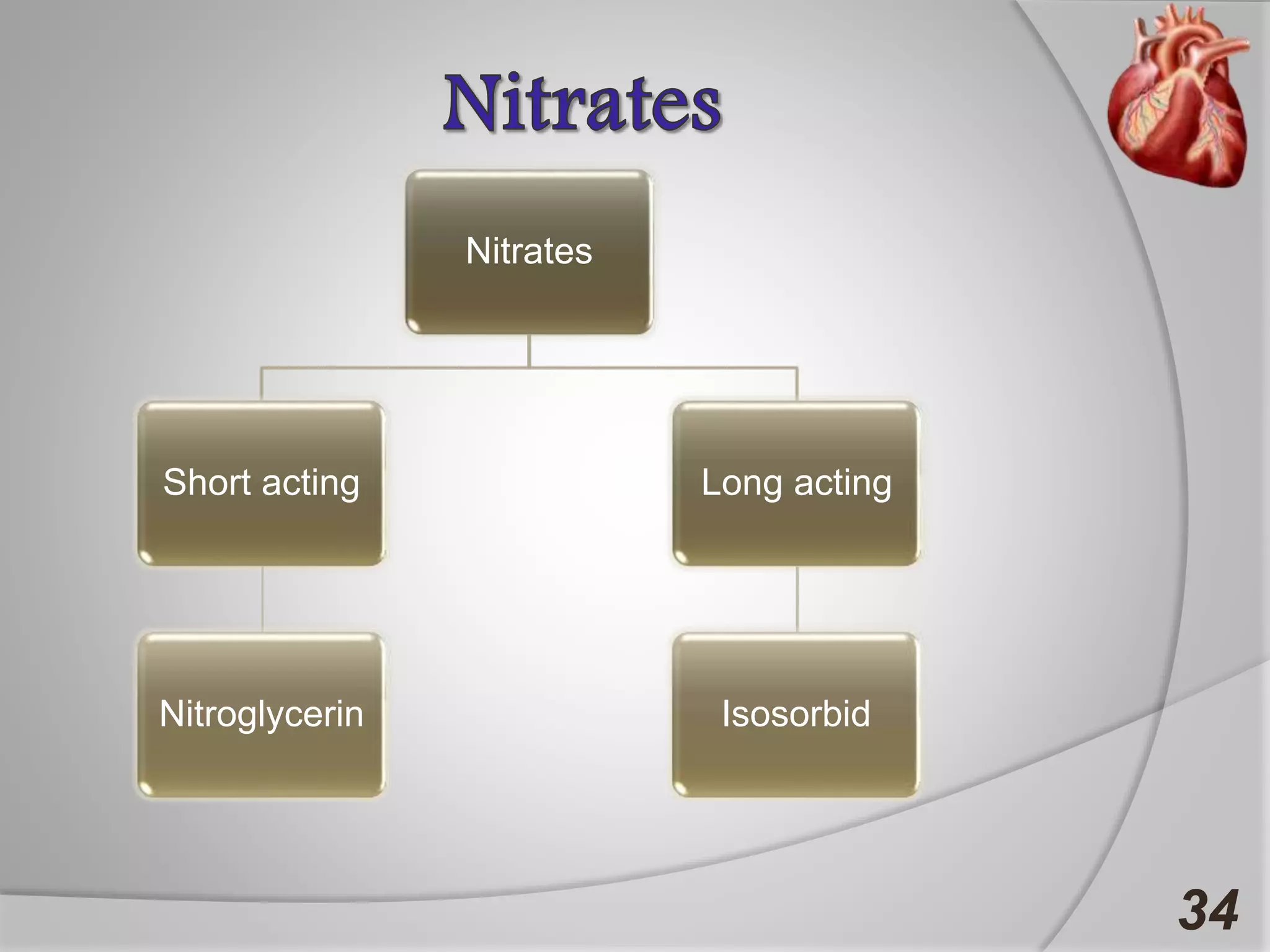
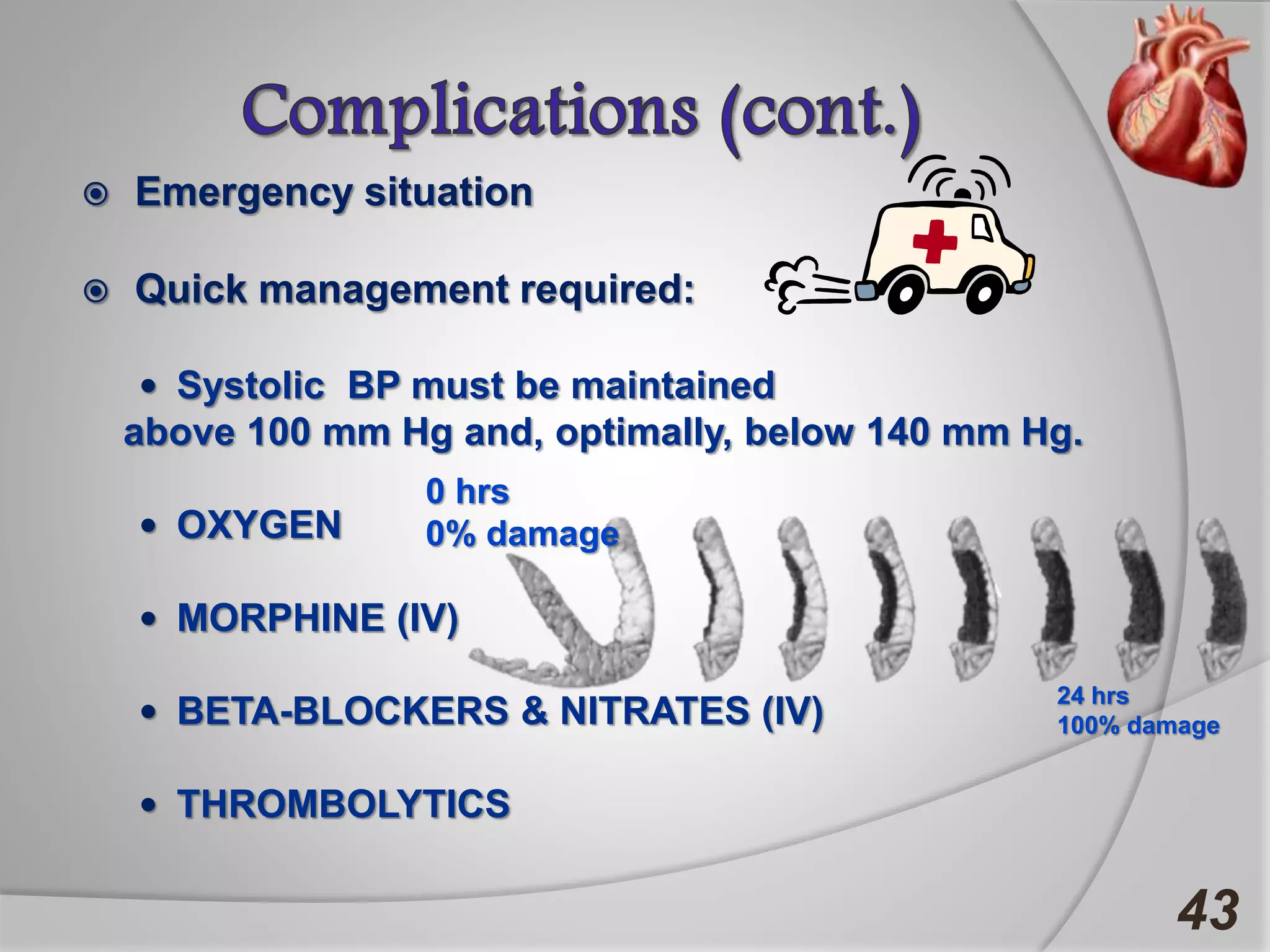
Angina is chest pain caused by transient myocardial ischemia due to an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand. There are three main types of angina: stable angina which is the most common type, unstable angina which can occur at any time and is considered an urgent condition, and Prinzmetal angina which involves coronary artery spasm. Angina is typically diagnosed through ECG or coronary angiography and can be managed through risk factor modification, pharmacological treatments like beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and nitrates, and potentially surgery. The most important treatment is modifying risk factors such as smoking, diet, exercise, and controlling conditions like high blood pressure and cholesterol.