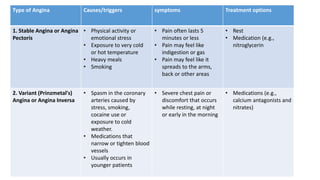
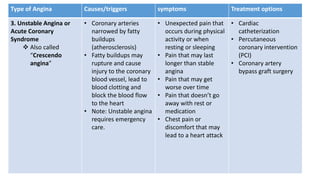
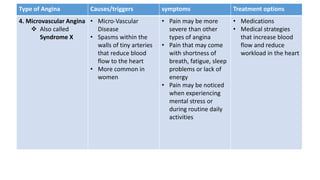
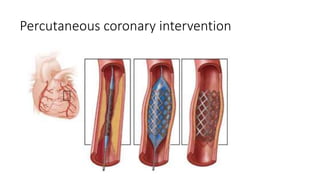
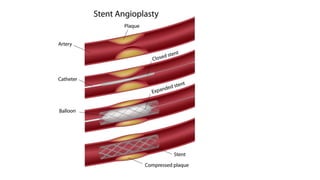
Angina pectoris is a clinical syndrome of chest pain due to transient myocardial ischemia without infarction. It occurs when oxygen demand of the heart exceeds its supply, usually due to coronary artery disease. There are four main types of angina - stable angina, unstable angina, variant angina, and microvascular angina. Diagnosis involves symptoms, ECG, and imaging. Treatment focuses on pain relief, slowing disease progression, and reducing future cardiac events through medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures like angioplasty. Complications can include heart attack, heart failure, and cardiac arrest if not properly managed.