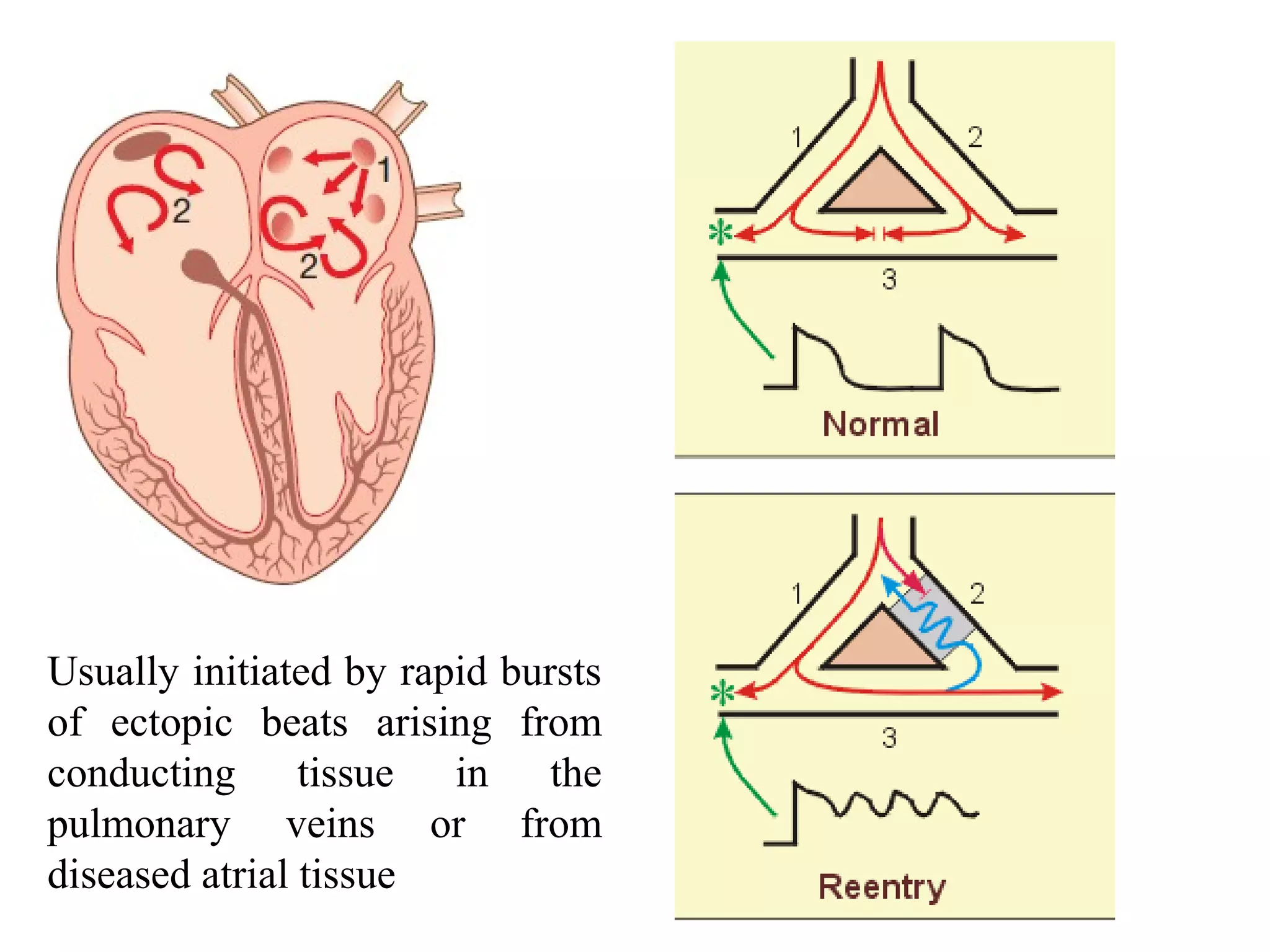
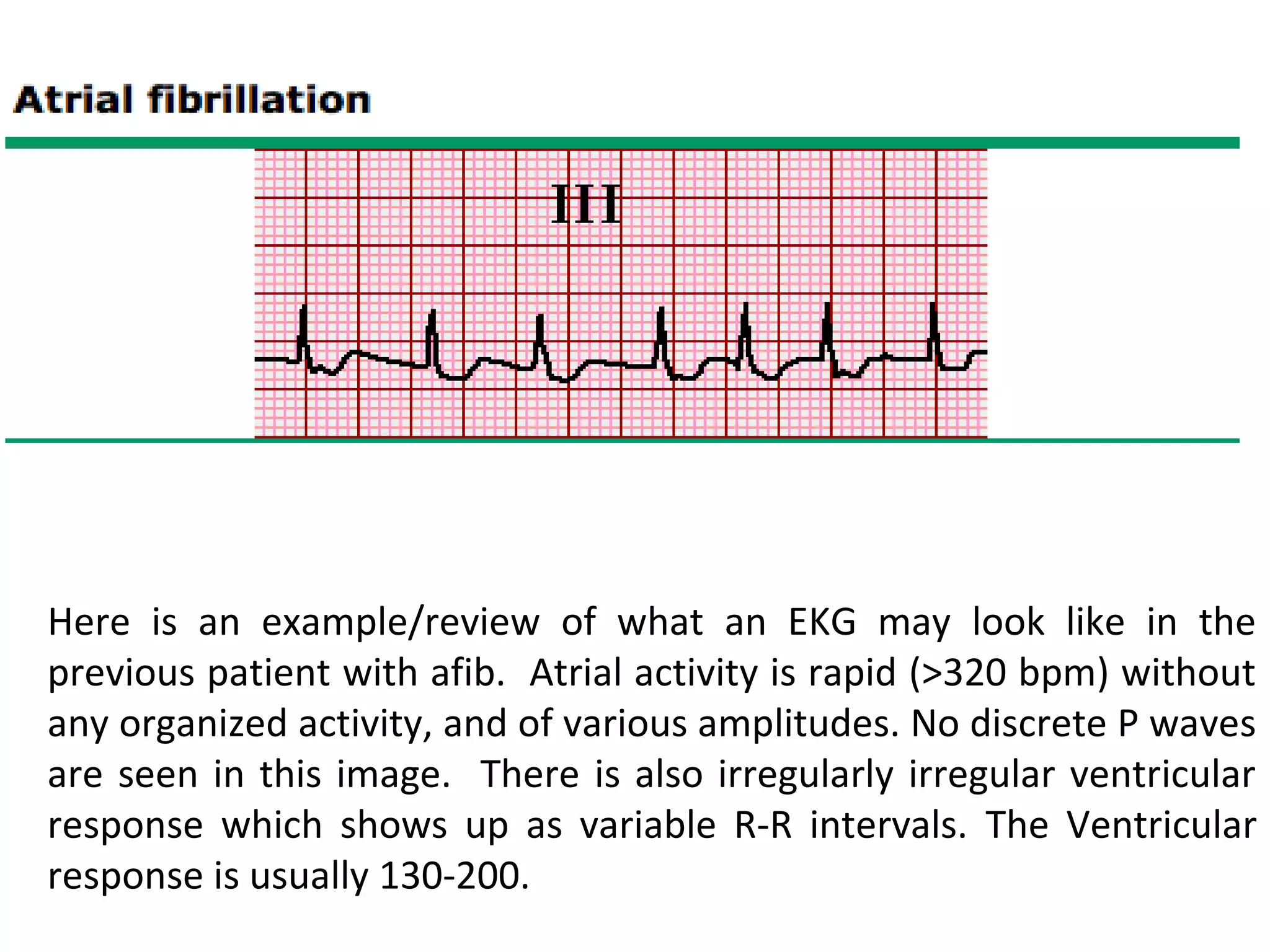
1) Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia characterized by disorganized atrial activity without effective contractions. It increases risk of stroke and prevalence rises with age.
2) Management involves restoring sinus rhythm through drugs, cardioversion, or ablation or controlling heart rate and preventing clots with anticoagulants. Rate control uses beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, or digoxin while restoring rhythm uses antiarrhythmics, cardioversion, or ablation.
3) Treatment depends on whether AF is paroxysmal, persistent or permanent and involves restoring rhythm if possible or controlling rate and preventing complications if not.