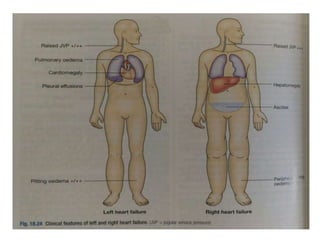
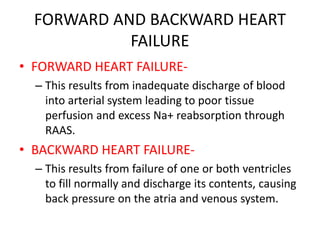
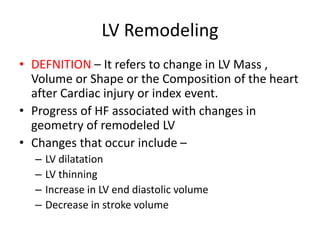
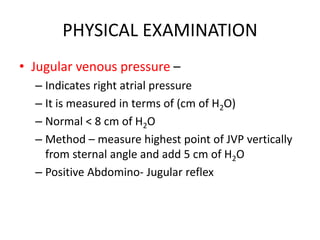
The document provides a comprehensive overview of heart failure, including its definitions, classifications based on ejection fraction, cardiac output, and associated symptoms. It outlines risk factors, clinical features, and physical examination findings relevant to heart failure, emphasizing the implications of left and right-sided failures. Additionally, it addresses the epidemiology, etiology, and potential comorbidities affecting patients with heart failure.