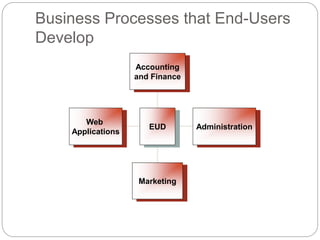
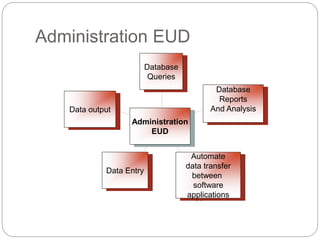
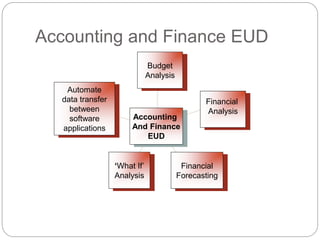
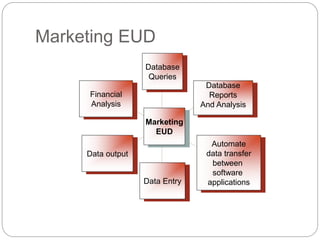
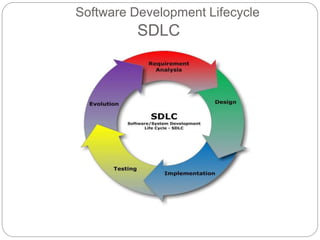
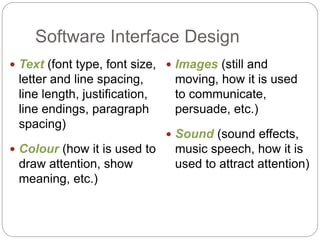
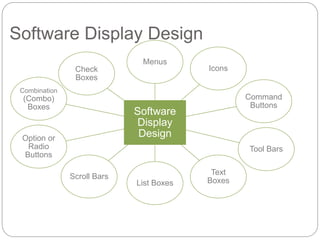
This document discusses end-user software development (EUD). It defines EUD as application software created by non-programming staff within an organization to meet their day-to-day work needs. The benefits of EUD include greater user involvement, utilizing existing resources, and improving decision-making. However, EUD can also lack planning, testing, and security. Common tools for EUD are macros, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), and advanced functions in databases, spreadsheets, and word processors. The document also outlines guidelines for EUD, such as following a software development lifecycle and designing effective human-computer interfaces.













![EUD Guidelines
EUs should be aware of and refer to the following
guidelines when developing application software:
ISO 9126 Software Quality Characteristics
[Available Online]
http://www.sqa.net/iso9126.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anintroductiontoend-usersoftwaredevelopment-180721143548/85/An-introduction-to-end-user-software-development-21-320.jpg)

![References
ISO 9126 Software Quality Characteristics
[Available Online]
http://www.sqa.net/iso9126.html
Office2010SuiteandVersionComparisonGuide.pdf
(2010) [Available Online]
Trulock, V. (2008), Understanding HCI, [Available
Online]
http://ilikecake.ie/hci/index.htm
Usernomics, (2011), [Available Online]
http://www.usernomics.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anintroductiontoend-usersoftwaredevelopment-180721143548/85/An-introduction-to-end-user-software-development-23-320.jpg)
