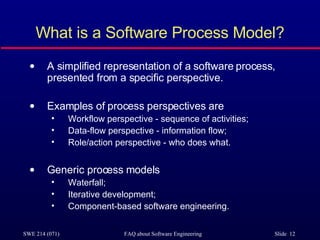
The document provides an overview of software engineering, detailing its importance, core concepts, and the distinctions between related fields. It discusses the software crisis that prompted the introduction of software engineering, the attributes of good software, and key challenges in the field. Additionally, it outlines the software process and various process models, emphasizing the systematic approach required for developing high-quality software.
![Introduction FAQs about Software Engineering [Based on Chapter 1 of Sommerville Book, 7e]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/166-1218006564281267-9/75/slide-1-2048.jpg)