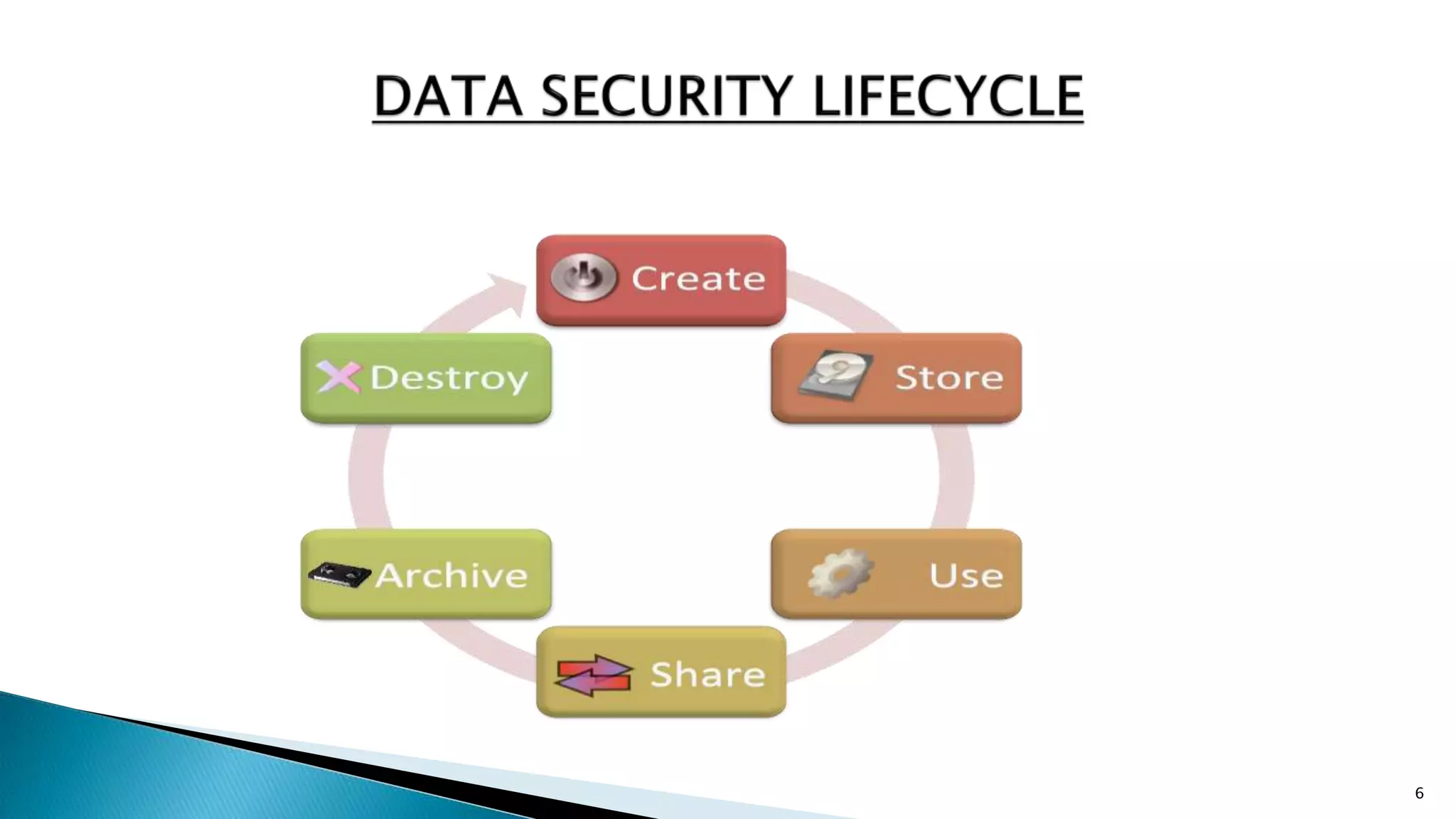
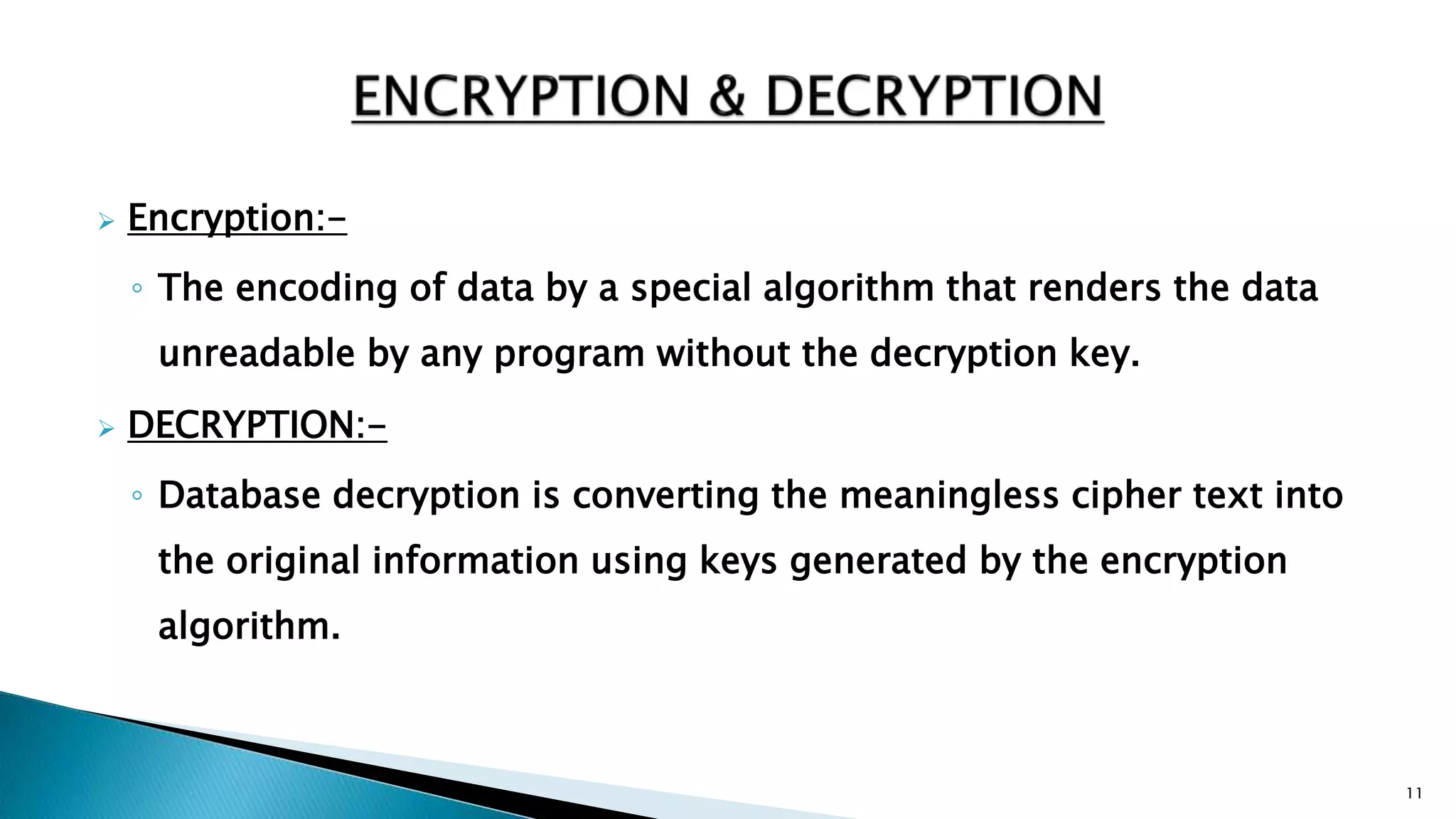
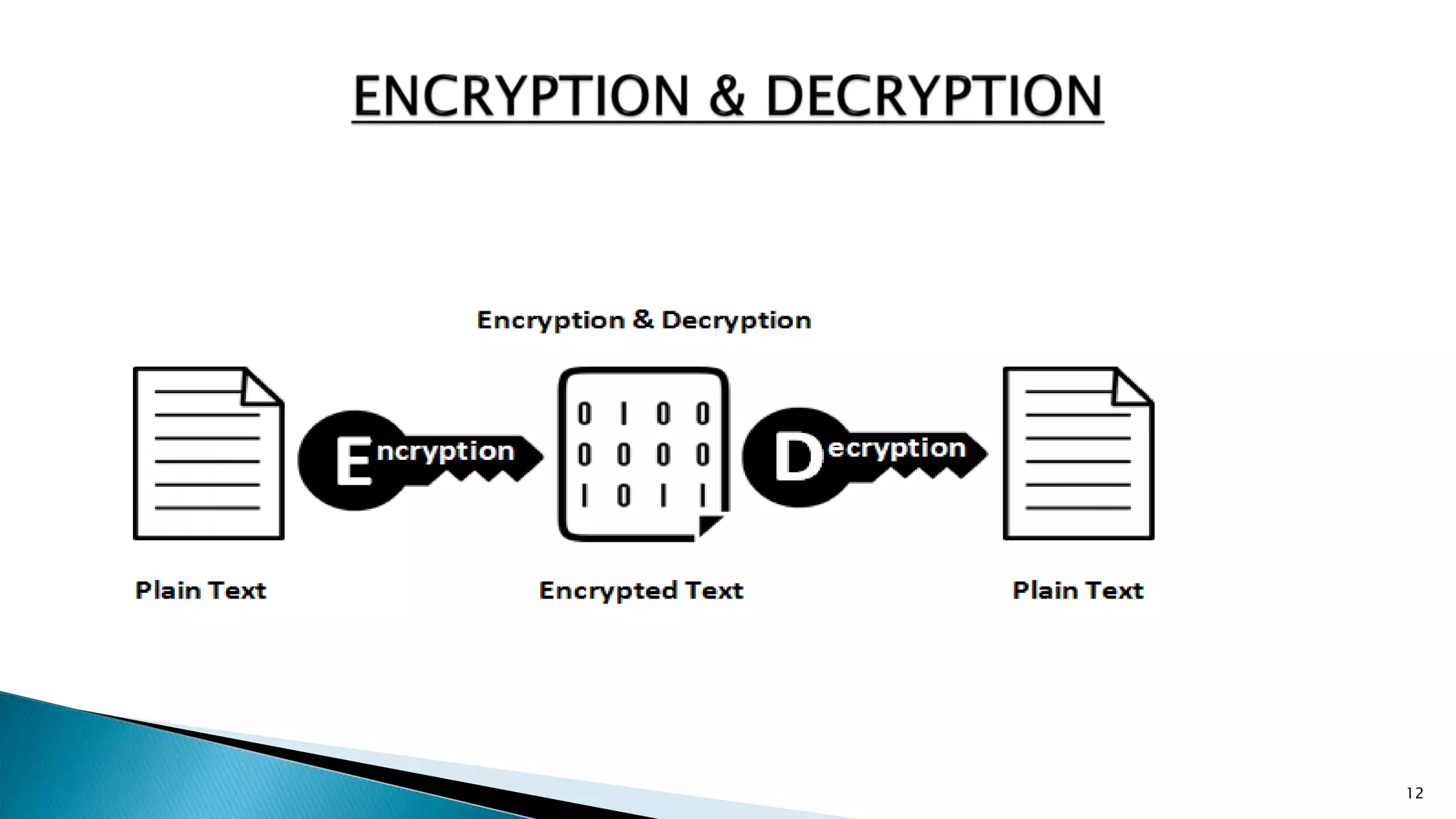
The document discusses database security, which protects data from both intentional and accidental threats through various mechanisms such as authorization, backup, recovery, integrity, and encryption. It highlights the need for a focused security curriculum addressing database-specific issues, as well as the responsibilities of system administrators in managing user access. Key aspects include ensuring data integrity, implementing strong authentication, and developing effective backup and recovery strategies.