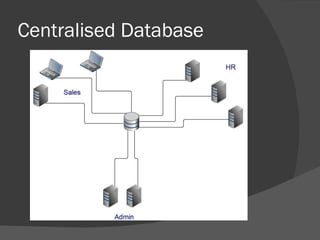
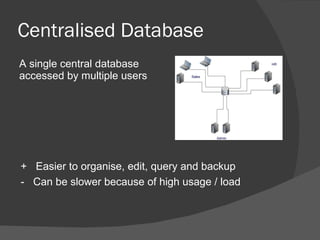
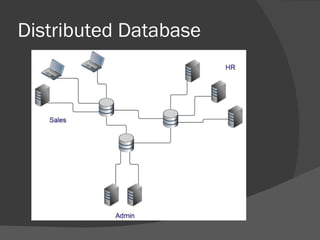
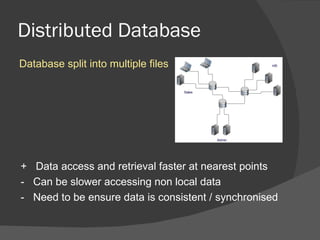
There are several types of databases that can be used depending on needs and priorities. A centralized database stores all data in one location, making organization and backups easier but potentially slowing performance from high usage. Distributed databases split data across multiple locations for faster retrieval from nearby sites, though accessing distant data can be slower and ensuring consistency is important. Horizontal and vertical partitioning further divide distributed databases by specific criteria like common fields or geographic regions. Replication copies all data to multiple locations so it can be accessed locally with changes synced to the central database during off-peak times. Central indexes link to actual data stored elsewhere to reduce updates to the main database and potentially cause delays in retrieving data. Data warehouses and data mining analyze stored information.