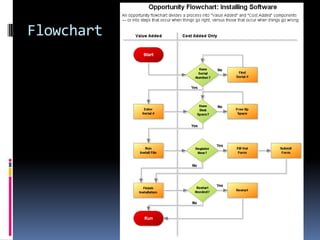
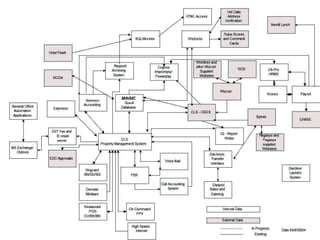
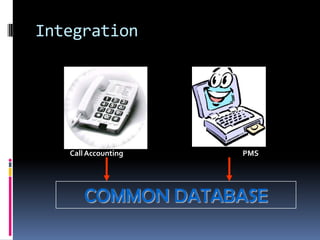
The document discusses software and its importance in computers. It defines software as computer programs, data structures, and documentation. Software is engineered rather than manufactured and does not wear out over time. The document also discusses operating systems, customized software, software quality factors like functionality and usability, and examples of word processing features.