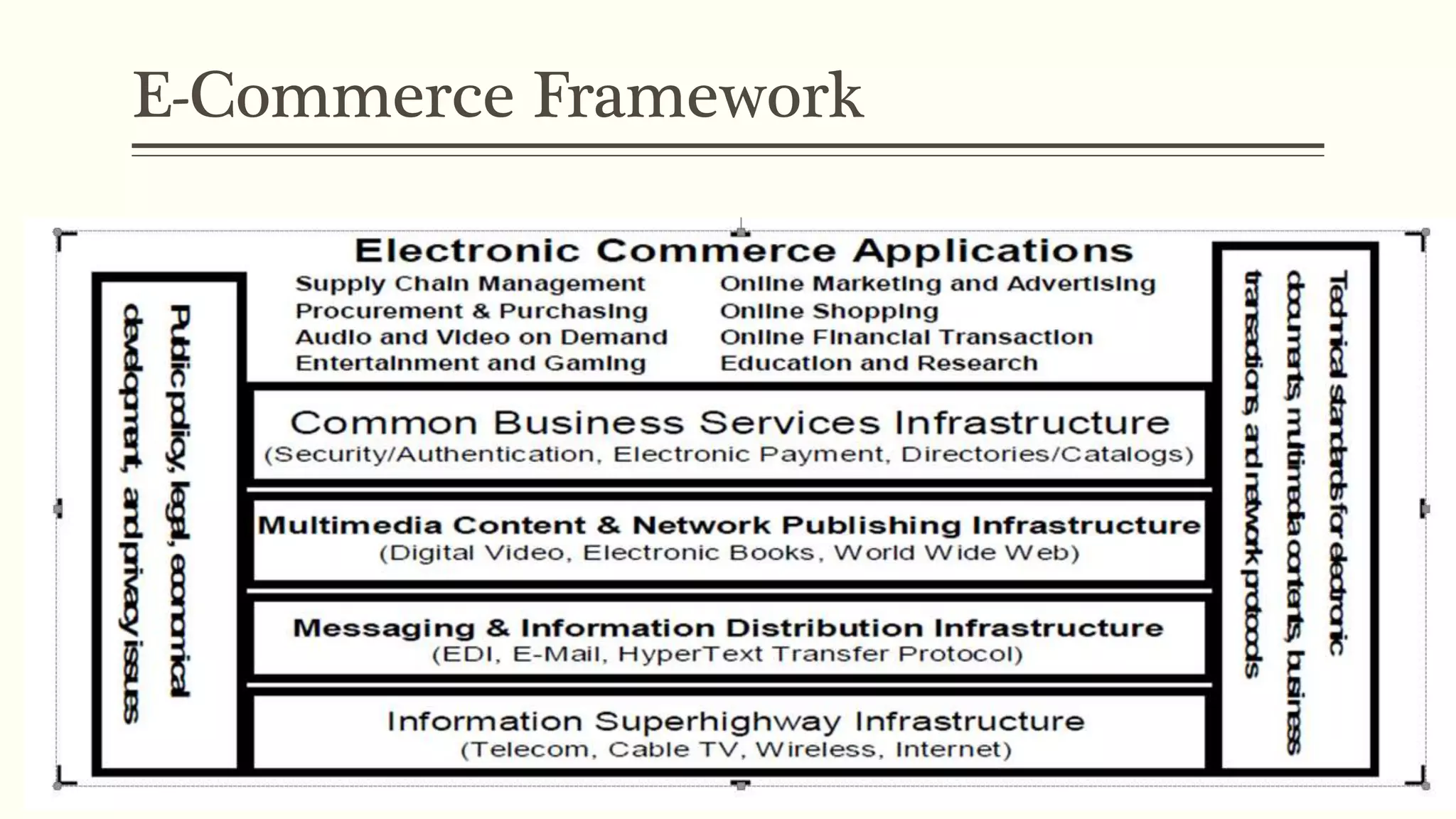
The document provides an overview of electronic commerce (e-commerce), defining it as the buying and selling of products and services over the internet. It discusses various aspects of e-commerce, including its applications, payment methods, and the underlying infrastructure required for its operation. Additionally, it highlights the concept of media convergence in relation to e-commerce, emphasizing the integration of different technologies and industries to enhance user experience.