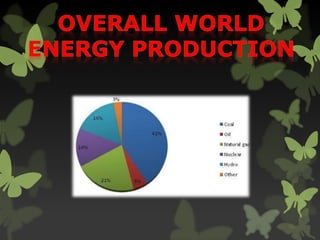
The document discusses the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on foreign oil by transitioning to more sustainable energy sources and bio-friendly fuels. It notes that this transition will be an ongoing process that requires new technology and is expensive. Sustainable energy sources mentioned include hydroelectricity, geothermal, solar, wind and tidal power. Biofuels such as ethanol, biodiesel and hydrogen are highlighted as high-benefit renewable options. Electric vehicles, hybrids and alternative fuels like natural gas are presented as promising technologies but also have challenges and limitations.