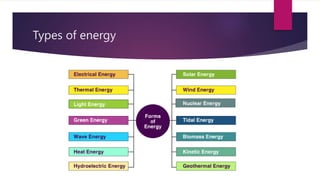
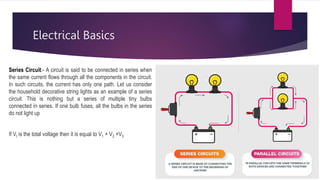
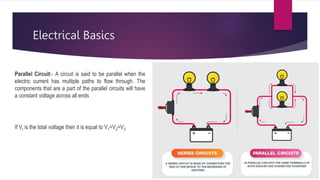
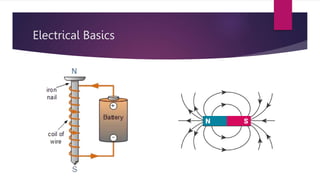
This document provides an introduction to hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). It discusses the historical development of automobiles including early steam-powered and electric cars. Jacob Lohner commissioned Ferdinand Porsche to design one of the first hybrid vehicles in 1890 that used both an electric motor and gasoline engine. Modern hybrid history began in the 1990s when automakers sought to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The Toyota Prius and Honda Insight were the first mass-market HEVs introduced in 2000. HEVs provide advantages like increased fuel efficiency and reduced emissions but also have disadvantages like higher costs and complex maintenance.