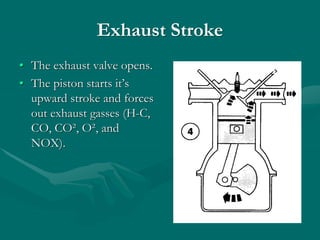
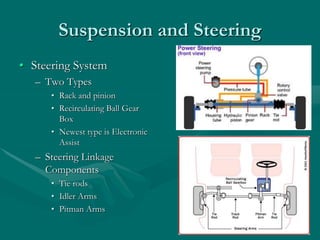
The document provides an overview of the automotive industry, including:
1) It describes the key systems of a vehicle like the engine, drivetrain, chassis, and gives examples of components that make up each system.
2) It explains the different types of repair facilities like dealerships, independent shops, and lube chains and outlines the pros and cons of each.
3) It provides a high-level overview of how new vehicles flow from the manufacturing plant to dealerships where they are inspected and prepared for sale.