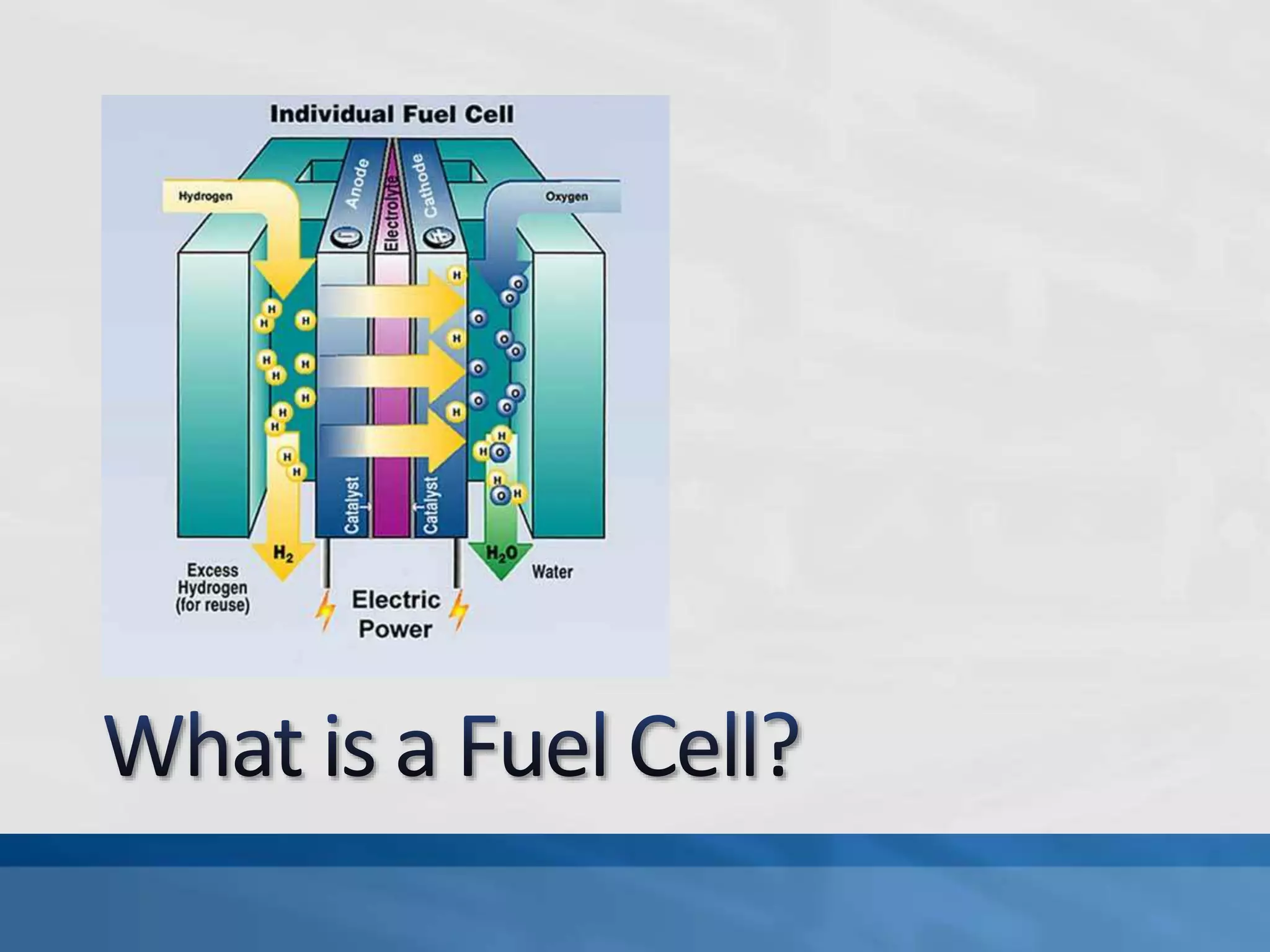
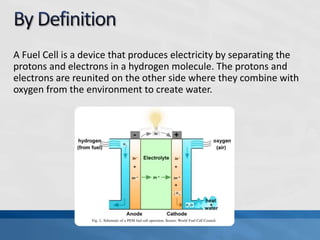
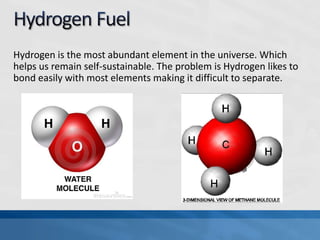
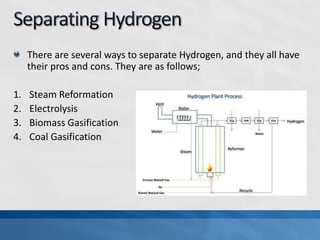
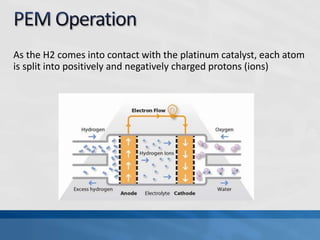
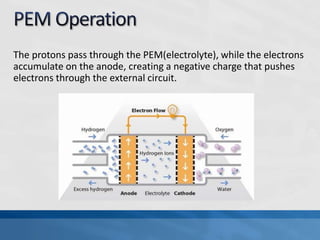
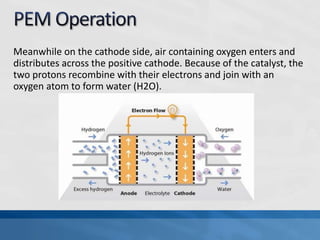
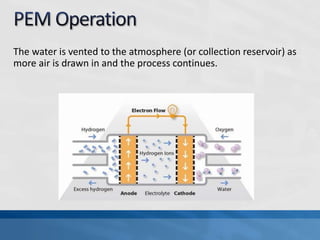
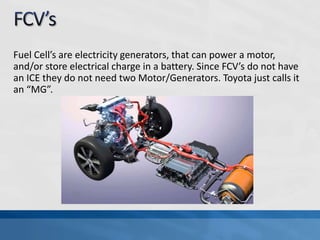
A fuel cell produces electricity through a chemical reaction involving hydrogen and oxygen, separating hydrogen protons and electrons and recombining them to create water. Unlike combustion engines, fuel cells use this separation rather than burning hydrogen to create a more efficient energy transfer. While hydrogen is abundant, it bonds easily to other elements, so separating it requires energy. Improving hydrogen separation technologies or using renewable energy sources could make hydrogen production more feasible as a fuel. Fuel cells offer advantages over combustion engines like zero emissions and higher efficiency. However infrastructure and high production costs need to be addressed for widespread adoption.