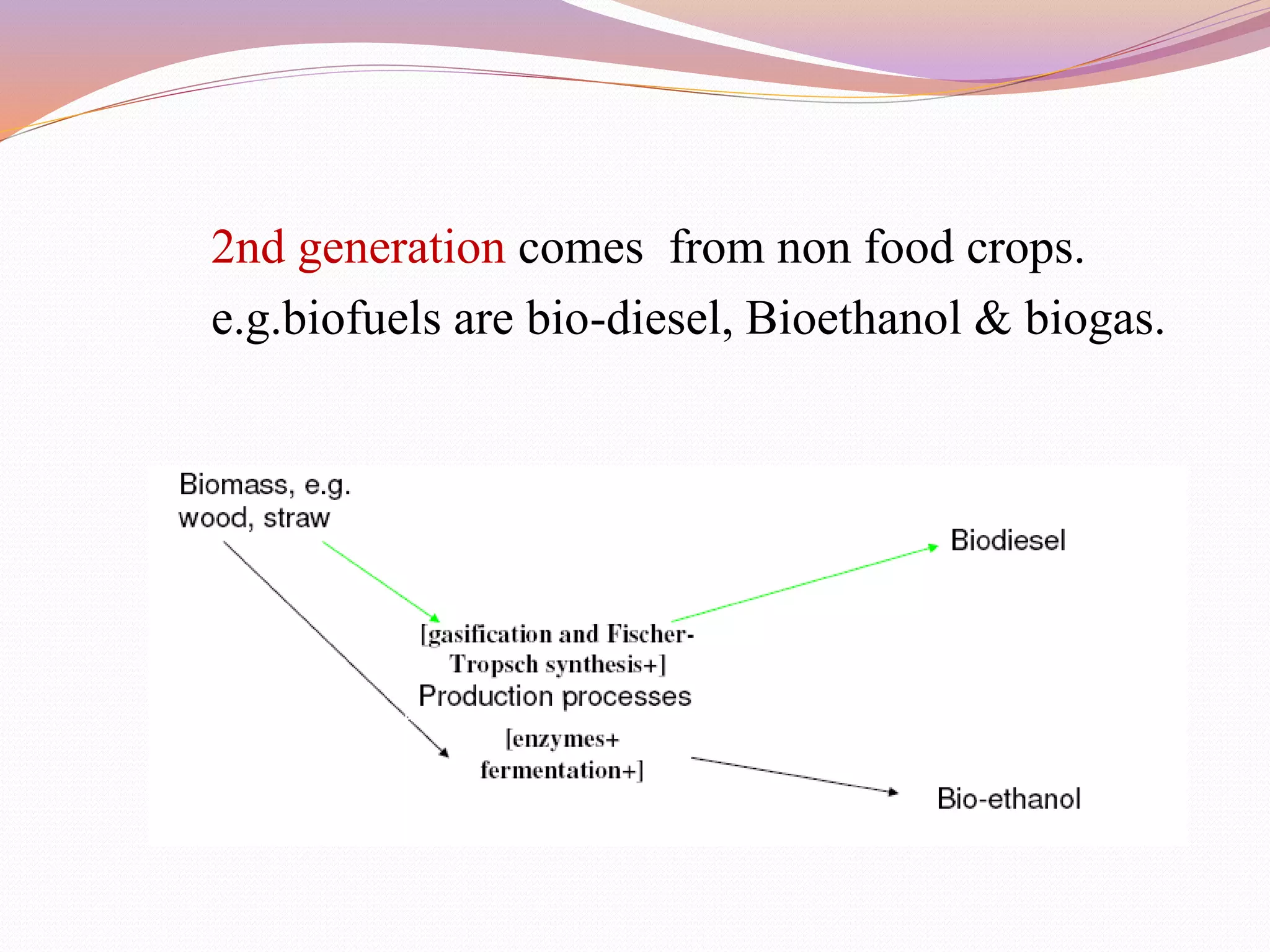
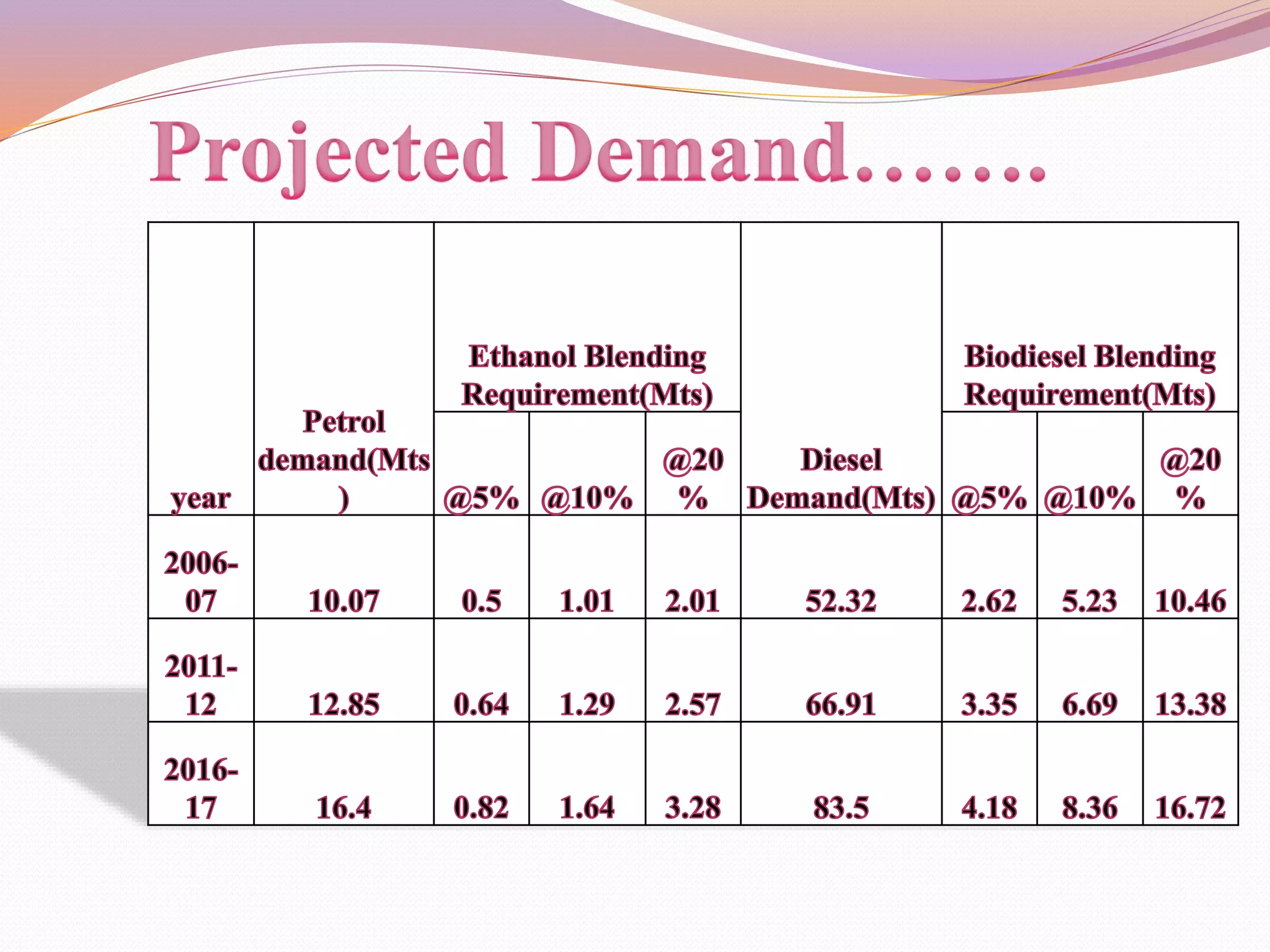
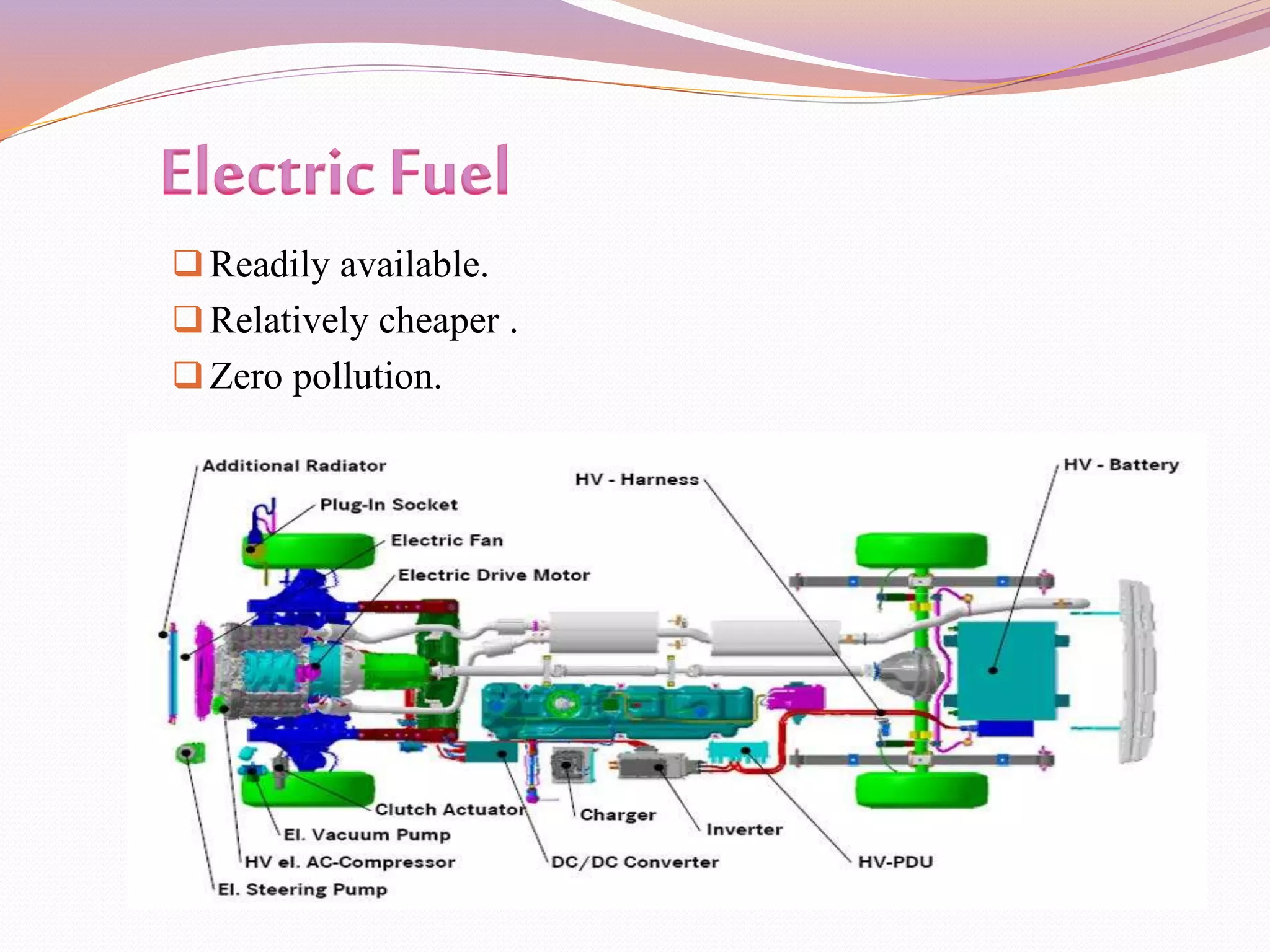
This document discusses various alternative fuels that can be used instead of conventional fossil fuels. It covers 4 generations of biofuels including those from food crops, non-food crops, algae, and those converted from vegetable oils. It also discusses natural gas, electricity in batteries and fuel cells, hydrogen fuel cells, emulsified diesel, and producing fuel from plastic waste as promising alternative fuel sources. The use of alternative fuels can help address issues of rising energy demands, greenhouse gas emissions, and global warming.