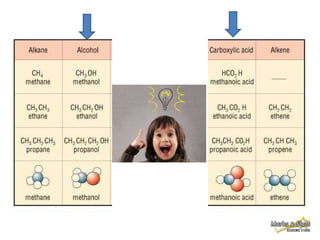
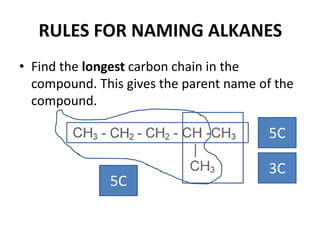
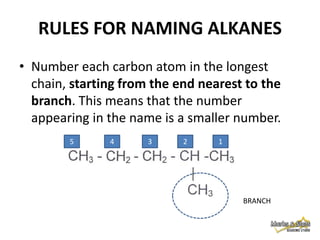
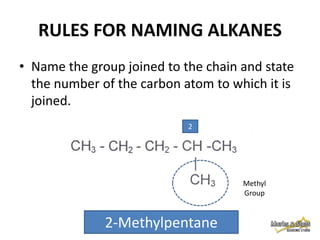
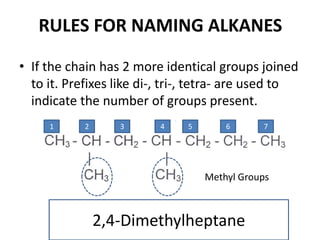
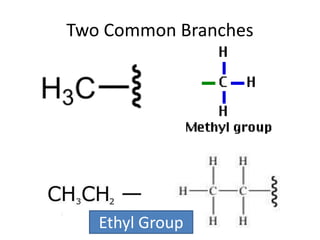
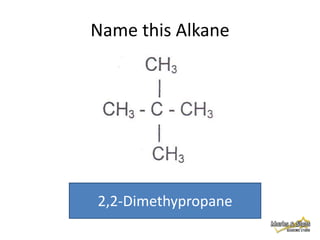
This document discusses alkanes, which are a homologous series of saturated hydrocarbons. The key points are:
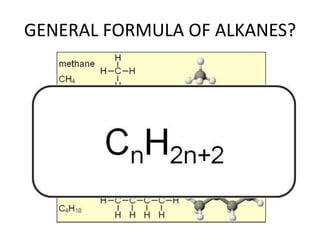
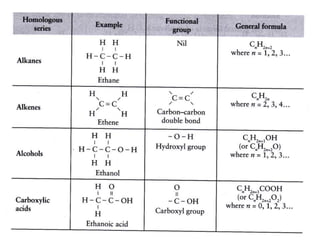
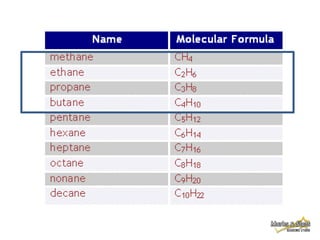
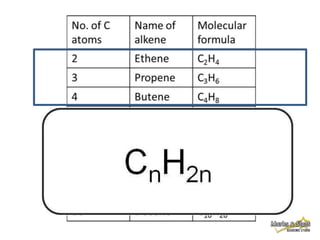
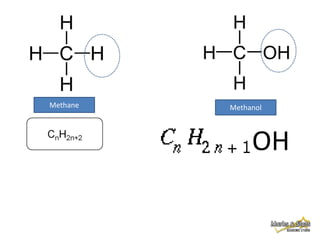
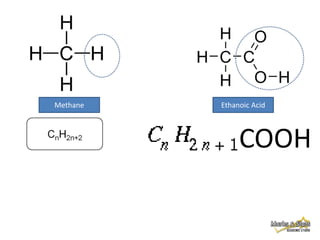
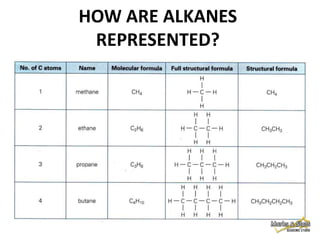
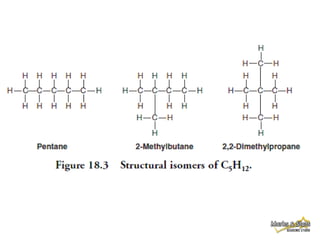
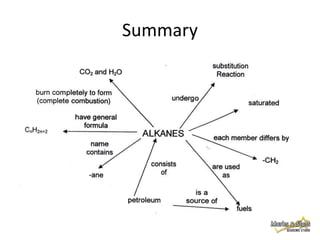
1. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 and are characterized by single carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds, making them saturated.
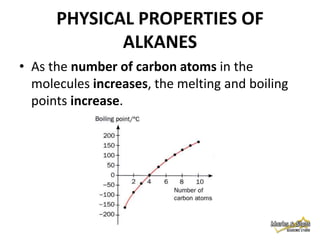
2. Physical properties of alkanes, such as melting/boiling points, viscosity, and density, increase with increasing number of carbon atoms due to stronger intermolecular forces.
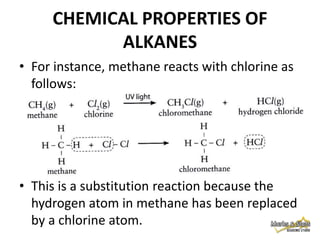
3. Alkanes are generally unreactive due to strong bonds, but can undergo combustion reactions releasing energy, and substitution reactions replacing hydrogen with other atoms.