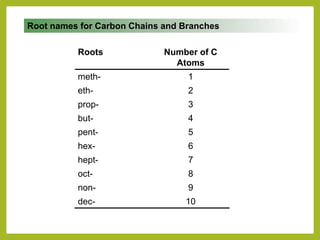
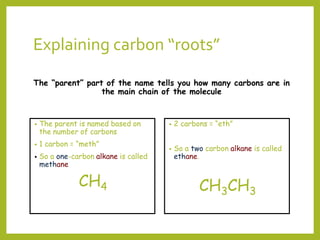
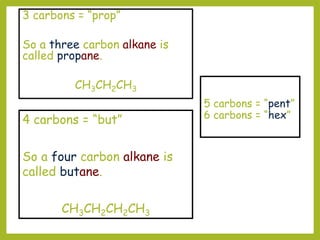
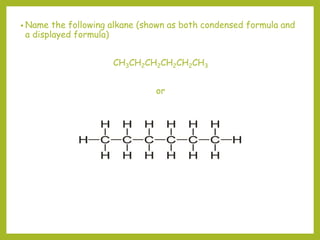
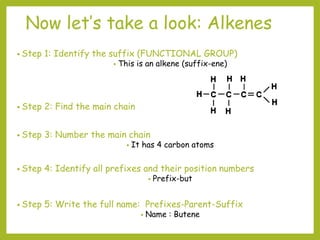
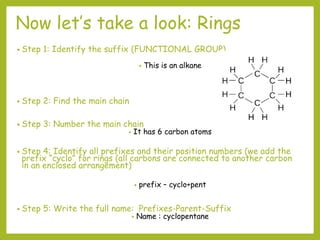
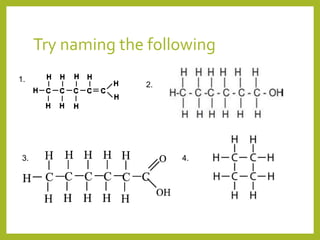
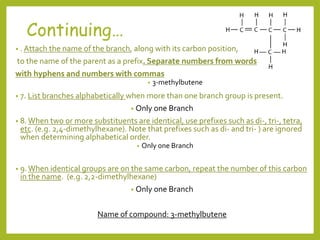
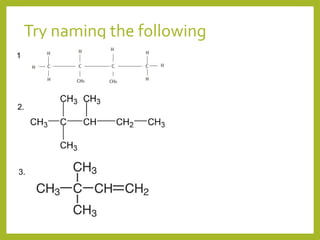
The document provides an overview of IUPAC nomenclature rules for naming organic compounds. It explains that organic compound names have three parts: a prefix, root, and suffix. The prefix indicates functional groups, the root name comes from the number of carbon atoms in the main chain, and the suffix denotes the type of compound. It provides examples of applying the rules to name alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and cyclic and branched compounds.