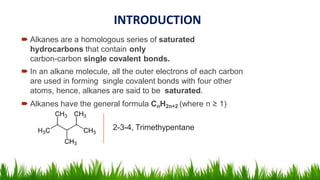
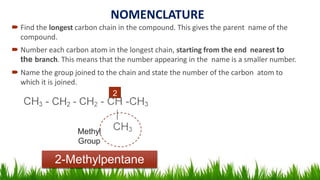
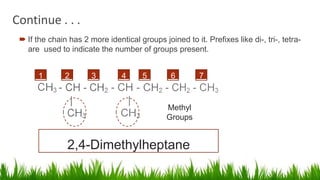
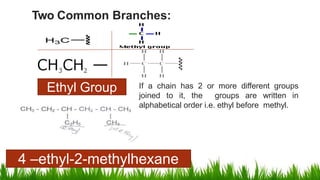
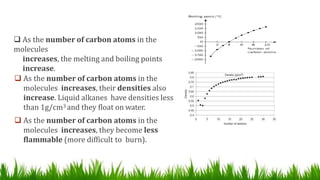
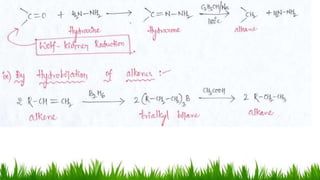
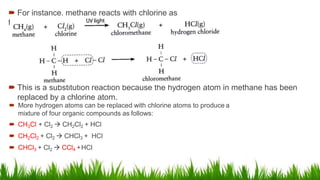
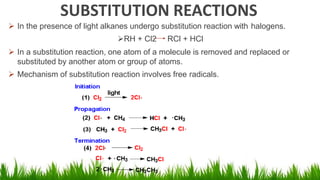
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2. They have single carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds, making them generally unreactive. Alkanes are characterized by increasing melting and boiling points with more carbon atoms. They are combustible, undergoing complete combustion to produce carbon dioxide and water. In the presence of light, alkanes can undergo substitution reactions with halogens like chlorine to produce organohalides. Common applications of alkanes include use as fuels for heating and electricity generation from methane, and as propellants and solvents from propane onwards depending on carbon chain length.