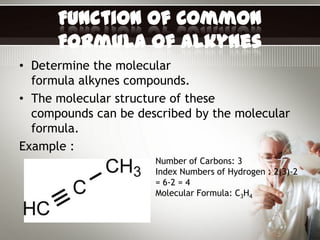
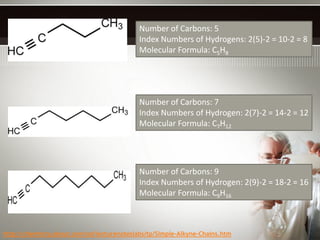
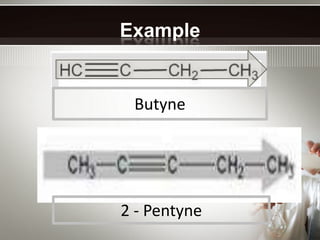
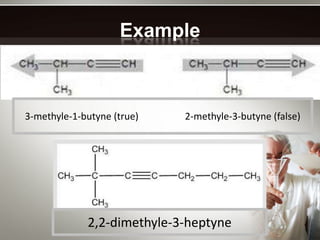
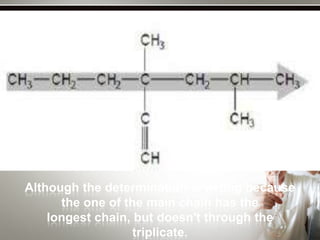
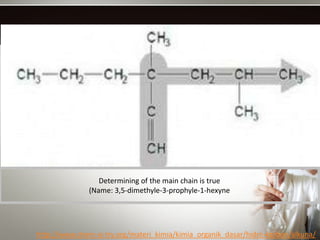
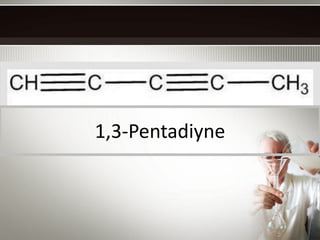
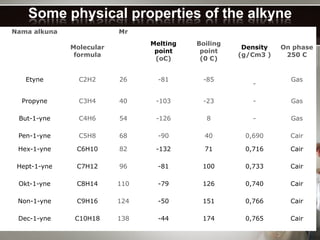
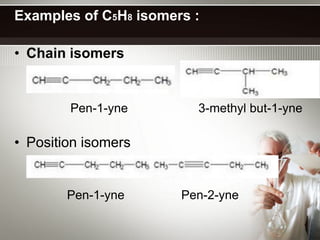
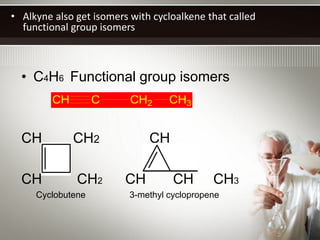
Alkynes are hydrocarbons with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. Common alkynes include acetylene (C2H2), propyne, butyne, pentyne, etc. Their molecular formulas follow the pattern of CnH2n-2. Alkynes are named based on the number of carbons and whether the chain is straight or branched. They are generally reactive due to the triple bond. Alkynes undergo addition, polymerization, substitution, and combustion reactions. They can also form isomers based on chain structure or carbon position.