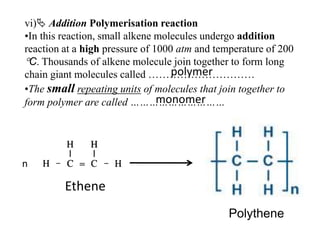
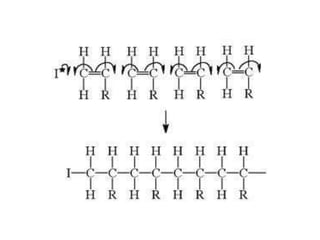
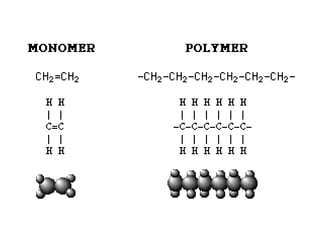
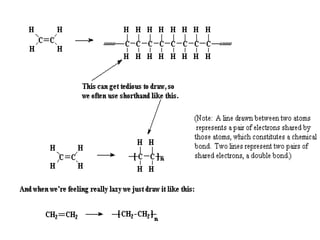
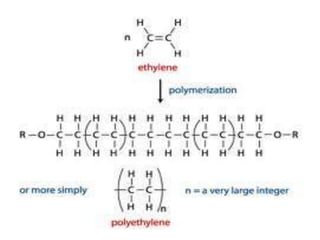
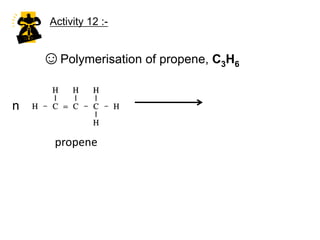
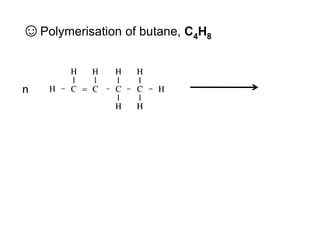
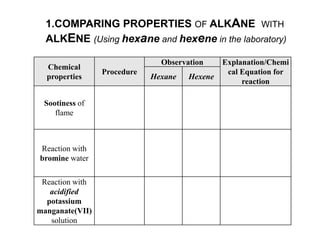
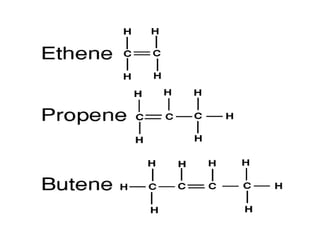
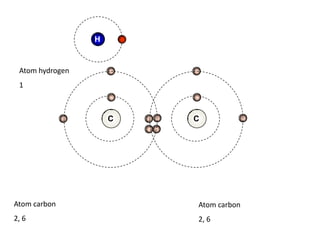
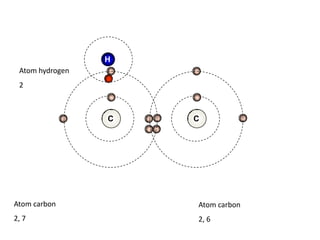
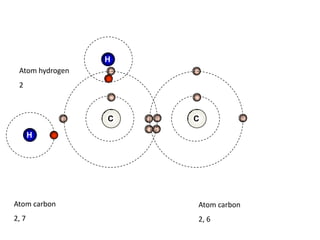
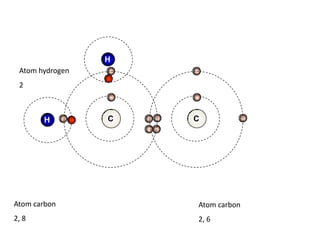
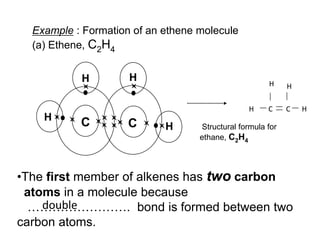
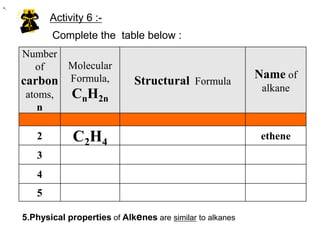
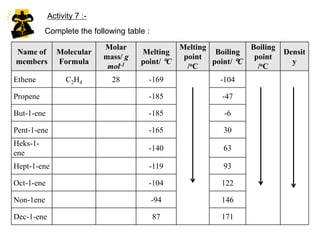
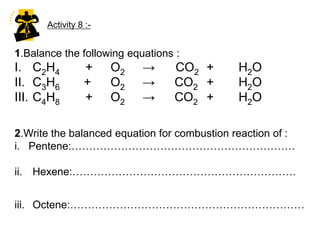
This document describes the properties of alkenes. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain carbon-carbon double bonds. They undergo addition reactions at the double bond, such as hydrogenation to form alkanes. Common reactions include addition of hydrogen, halogens, water, and oxidation. Alkenes polymerize to form polymers by joining many monomer units. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the double bond.








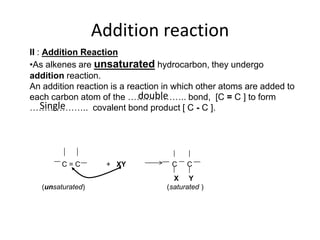
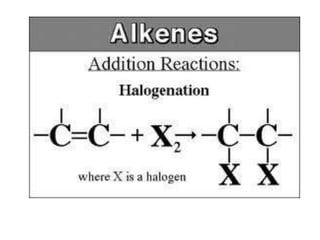
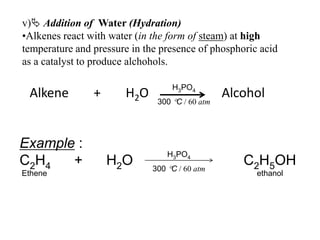
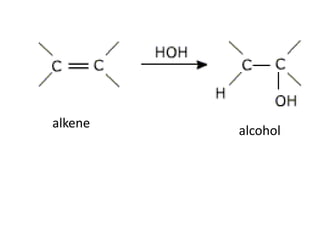
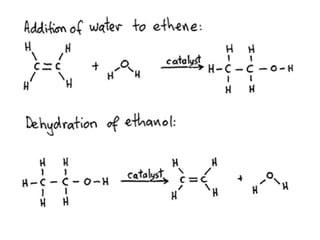
![Addition reactionII : Addition ReactionAs alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbon, they undergo addition reaction.An addition reaction is a reaction in which other atoms are added to each carbon atom of the ……………….. bond, [C = C ] to form ……………….. covalent bond product [ C - C ].double Single C = C + XY C CXY (unsaturated) (saturated )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkane-110515061258-phpapp01/85/Alkane-26-320.jpg)
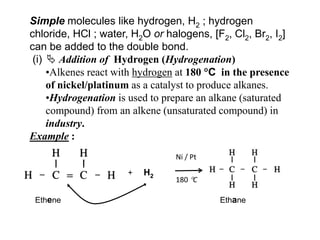
![Simple molecules like hydrogen, H2 ; hydrogen chloride, HCl ; water, H2O or halogens, [F2, Cl2, Br2, I2] can be added to the double bond. (i) Addition of Hydrogen (Hydrogenation)Alkenes react with hydrogen at 180 Cin the presence of nickel/platinum as a catalyst to produce alkanes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkane-110515061258-phpapp01/85/Alkane-28-320.jpg)
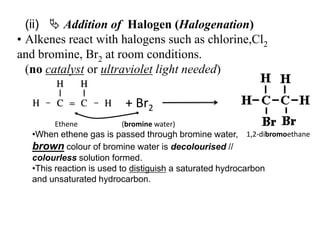
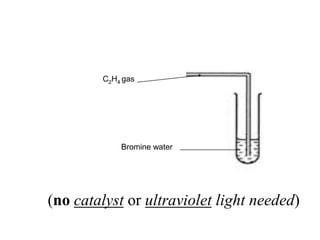


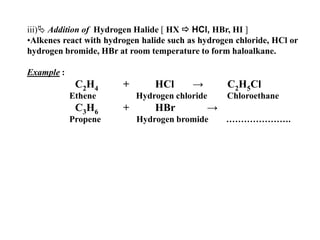

![iii)Addition of Hydrogen Halide [ HX HCl, HBr, HI ]Alkenes react with hydrogen halide such as hydrogen chloride, HCl or hydrogen bromide, HBr at room temperature to form haloalkane.Example : C2H4 + HCl -> C2H5Cl Ethene Hydrogen chloride Chloroethane C3H6 + HBr -> PropeneHydrogen bromide ………………….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkane-110515061258-phpapp01/85/Alkane-37-320.jpg)
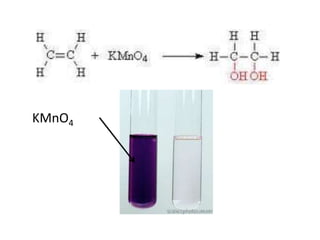
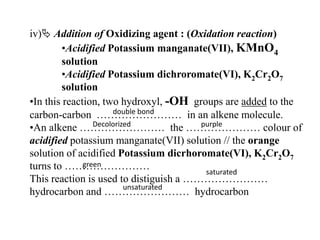
![Example :KMnO4(aq)[Purple]AlkeneColourlessKMnO4C2H6 gasC2H4 + H2O + [O] -> C2H4(OH)2Ethene Ethan-1,2-diolcolourless](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkane-110515061258-phpapp01/85/Alkane-43-320.jpg)
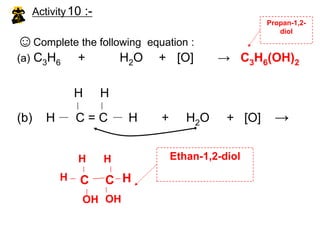
![Activity10 :-Propan-1,2-diolEthan-1,2-diol☺Complete the following equation :(a) C3H6 + H2O + [O] -> C3H6(OH)2H H(b) H C = C H + H2O + [O] ->HHHHCCOHOH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkane-110515061258-phpapp01/85/Alkane-44-320.jpg)