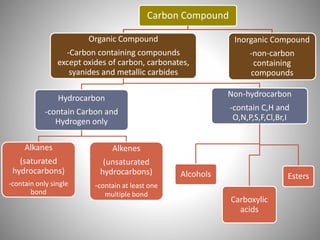
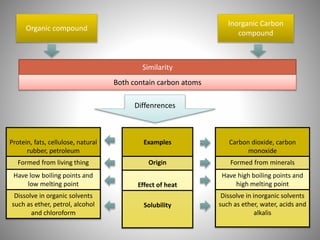
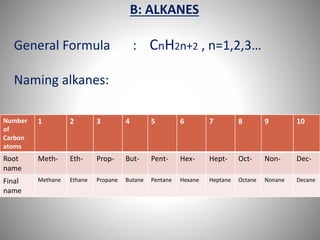
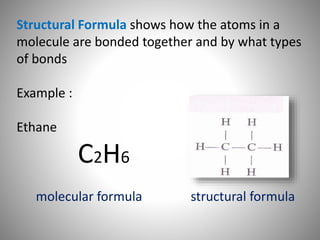
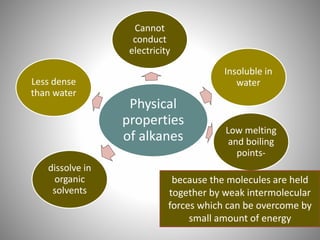
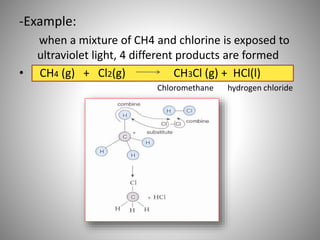
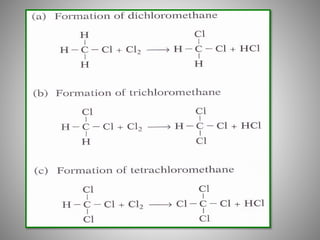
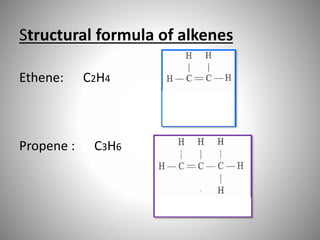
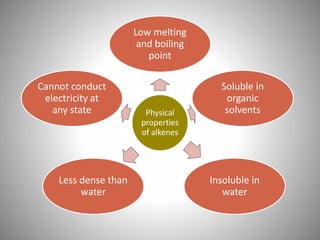
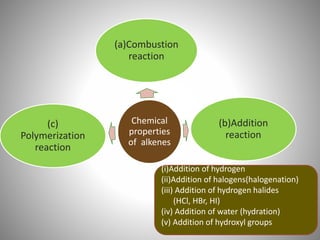
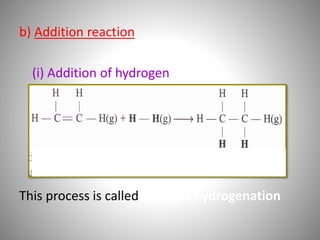
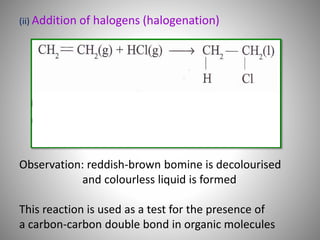
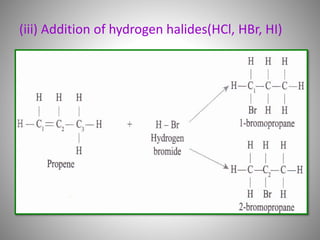
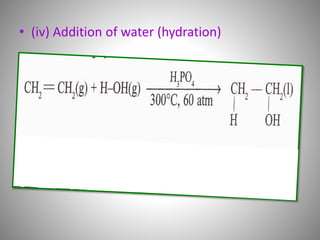
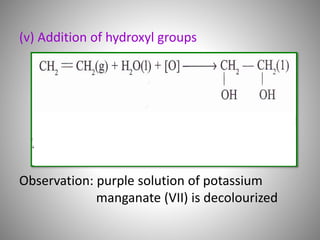
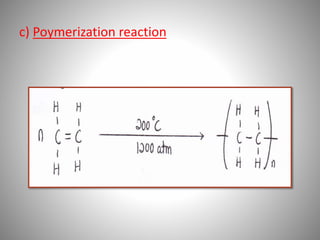
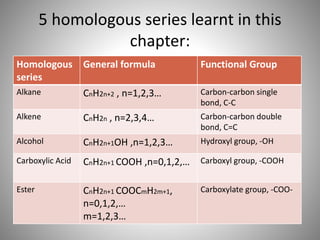
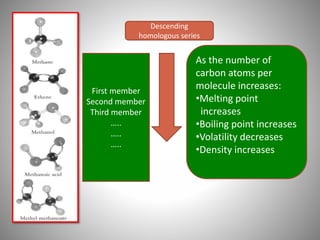
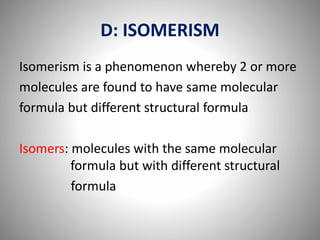
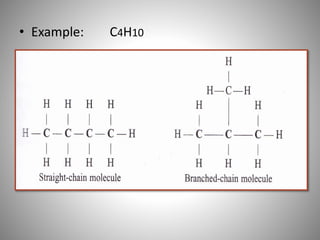
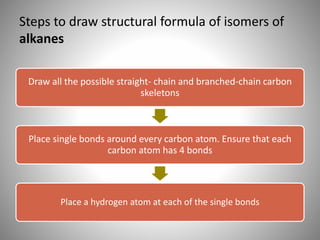
This document discusses carbon compounds and their classification. It describes that carbon compounds contain carbon as a constituent element and are classified as organic or inorganic. Organic compounds contain carbon and are further classified as hydrocarbons or non-hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons only contain carbon and hydrogen and include alkanes and alkenes. Alkanes contain single bonds while alkenes contain double bonds. The document provides examples and properties of alkanes and alkenes. It also discusses isomerism in carbon compounds.