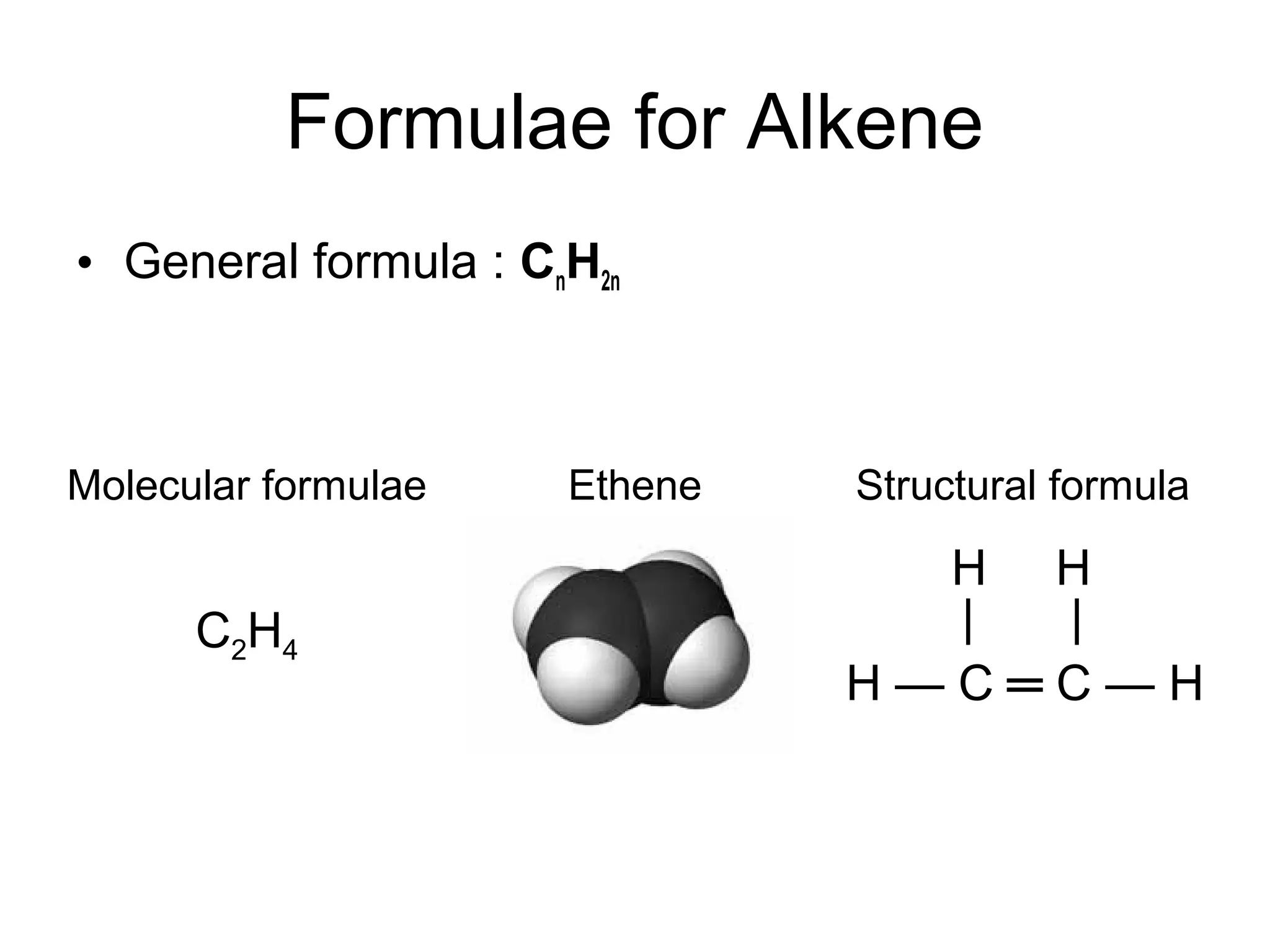
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They have the general formula CnH2n. Common properties of alkenes include being unsaturated, less dense than water, and having lower melting and boiling points than alkanes. Alkenes undergo addition reactions where the double bond is broken and new single bonds are formed. They react with hydrogen, halogens, hydrogen halides, water, and acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution through addition reactions. Polymerization of alkenes forms polymers like polyethene. Alkenes burn with more soot than alkanes due to their higher carbon content.
















![Addition of Hydroxyl Groups
• Ethene,C2H4 reacts with dilute acidified
solution of potassium manganate(VII),
KMnO4 to produce ethane-1,2-diol
• Ethene decolourizes the purple solution of
KMnO4
• Test for a double bond
+ H — OH + [ O ] CH2 — CH2
| |
OH OH
CH2 ═ CH2
acidic KMnO4
Ethane-1,2-diol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160211091851/75/2-3-alkenes-18-2048.jpg)






