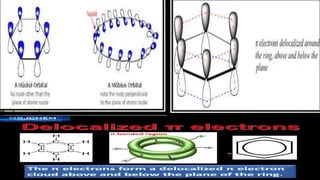
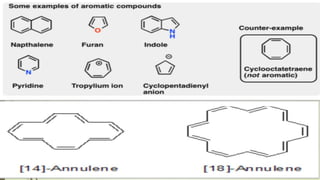
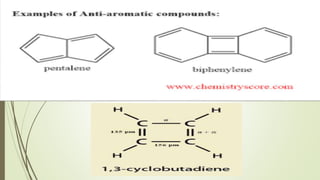
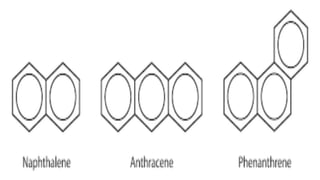
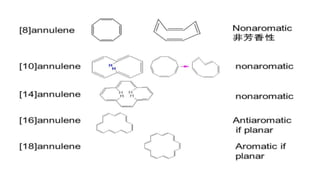
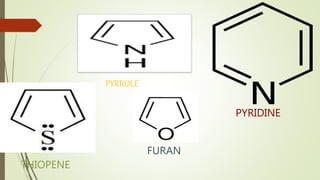
This document provides an overview of aromatic compounds including benzene derivatives, antiaromatic compounds, annulenes, heterocyclic compounds, and metallocenes. It defines aromaticity as involving delocalized pi electrons within a conjugated cyclic system. The key requirements for aromaticity are a cyclic conjugated structure, planarity, and obeying Huckel's rule of 4n+2 pi electrons. Common aromatic heterocycles include furan, pyrrole, thiophene, and pyridine. Ferrocene is provided as an example of a metallocene.

![TOPIC INCLUDES :
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS [BENZENOID
COMPOUNDS ,ETC] .
ANTI AROMATIC COMPOUNDS .
ANNULENES .
HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS .
METALLOCENES .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aromaticity-190408151820/85/Aromaticity-2-320.jpg)







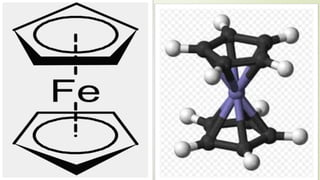
![METALLOCENES :
Organometallic coordination compounds in which one atom of a
transition metal such as iron, ruthenium or osmium is bonded to and
only to the face of two cyclopentadienyl [[hap to]5-(C5H5)] ligands
which lie in parallel planes.
FOR EXAMPLE : FERROCENE .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aromaticity-190408151820/85/Aromaticity-18-320.jpg)