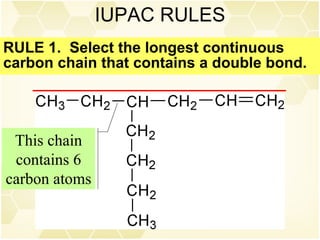
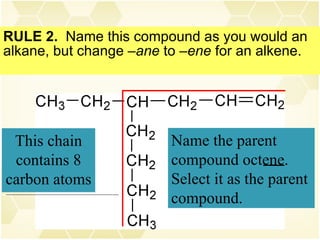
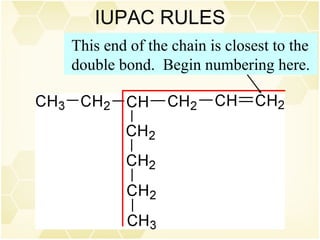
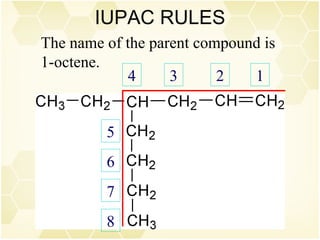
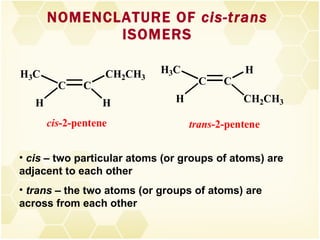
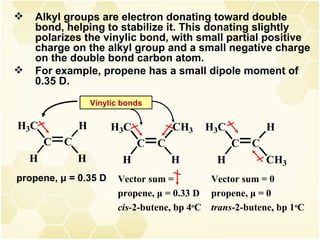
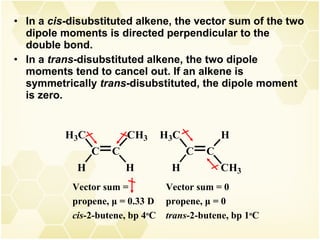
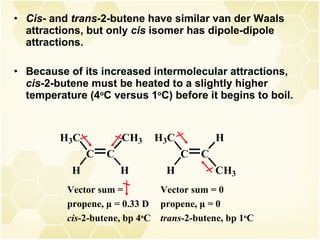
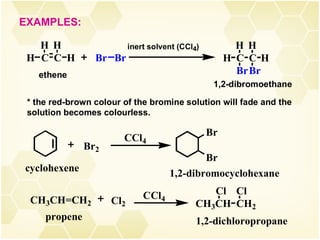
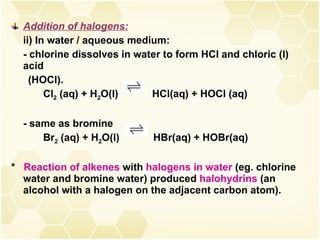
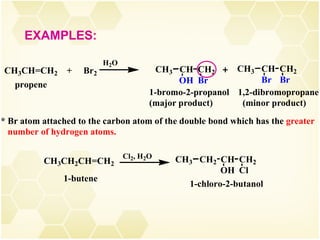
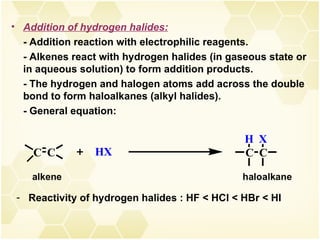
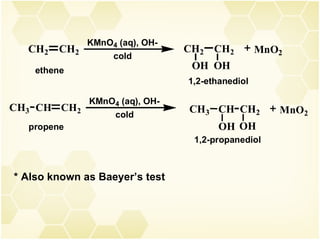
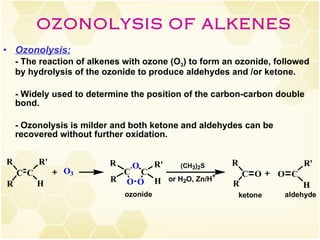
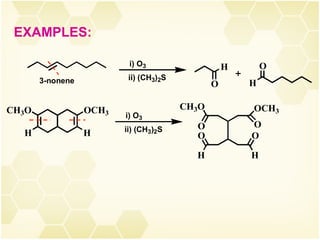
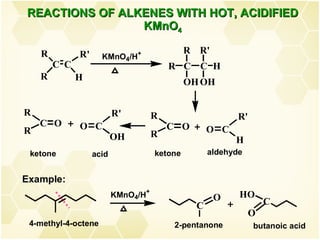
This document summarizes key information about alkenes (olefins):
1) Alkenes contain carbon-carbon double bonds and are classified as unsaturated hydrocarbons. Common examples include ethylene and propene.
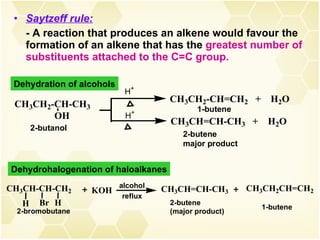
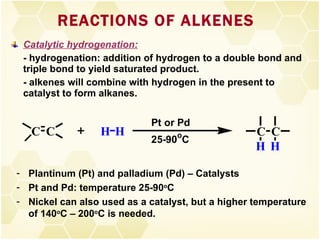
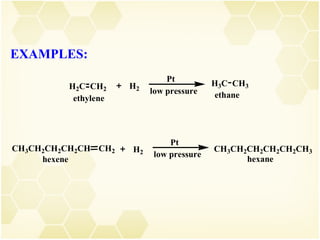
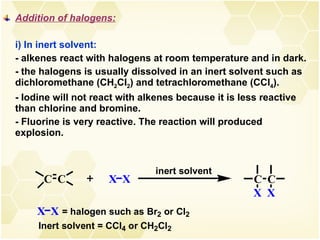
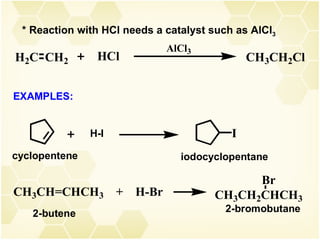
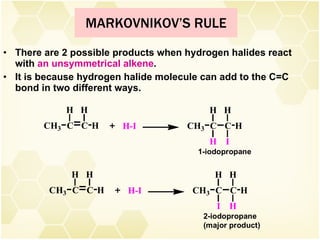
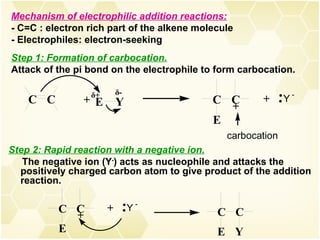
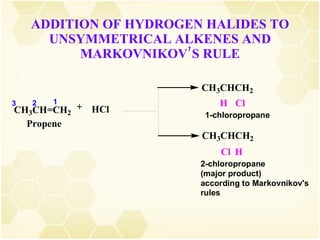
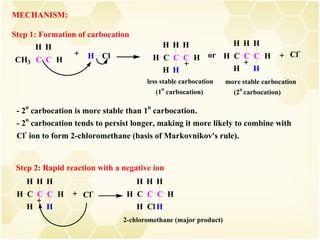
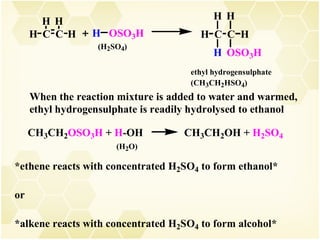
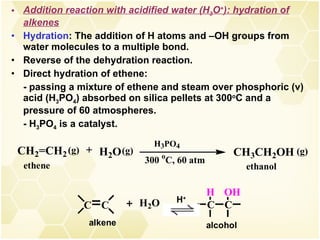
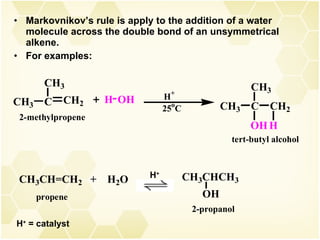
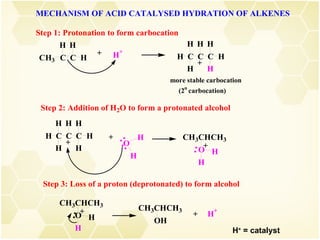
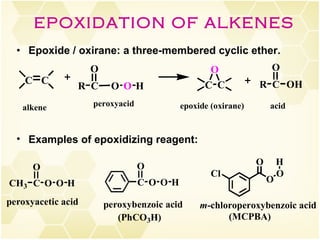
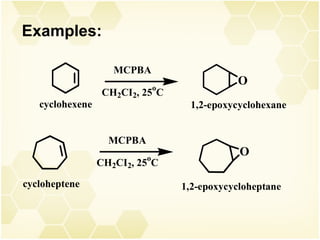
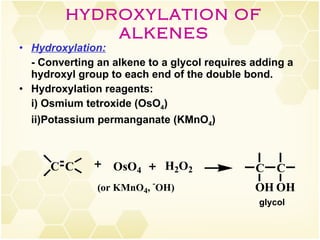
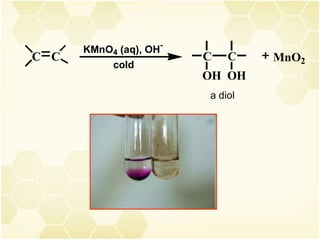
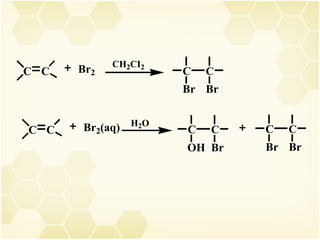
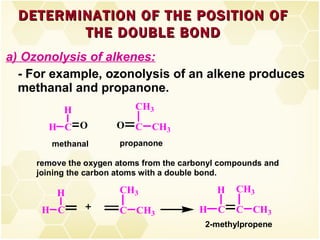
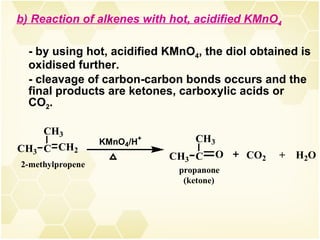
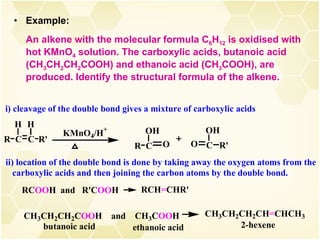
2) Alkenes undergo characteristic reactions such as addition of halogens, hydrogenation to form alkanes, hydration and polymerization. Many of these reactions follow Markovnikov's rule.
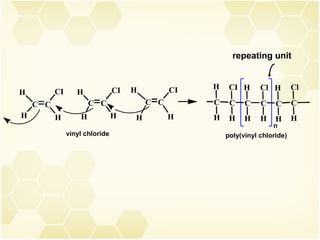
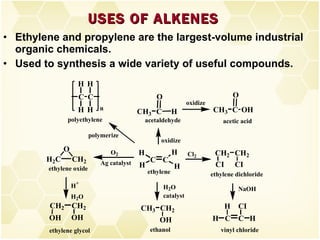
3) Alkenes are industrially important as monomers for polymers like polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC and polystyrene. Ethylene and propylene are the largest volume organic chemicals produced.