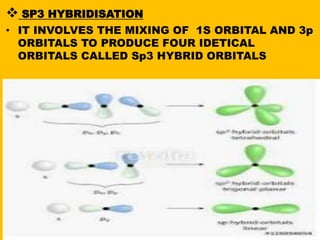
Hybridization is a process where atomic orbitals mix to form new identical hybrid orbitals of equal energy. It allows atoms to form sigma and pi bonds to share electrons with other atoms. The type of hybridization determines the shape and structure of molecules. Sp hybridization forms linear molecules, sp2 forms triangular molecules, and sp3 forms tetrahedral molecules. Examples are given of BeCl2 with sp hybridization and BF3 with sp2 hybridization. Hybridization lowers the energy of orbitals and allows more stable bonding between atoms.





![ STRUCTURE OF BERYLLIUM CHLORIDE (Becl2) sp HYBRIDISATION
• BERILIYUM CHLORIDE , MOLECULE HAS ONE BERILIYUM ATOM AND
TWO CHLORINE ATOMS
• BERILIYUM HAS TWO VELENCY ELECTRONS AND CHLORINE HAS ONE
VELENCY ELECTRON FOR SHARING
Be (4) : [ He] 2s22p0 Cl (17) : [He] 2s22p63s23p6
Be (Excited state) : [He] 2s1 2px
1 2py
0 2pz
0
BeCl2 : [He]
Sp HYBRIDISATION
• DURING THE FORMATION OF BeCl2, 2s AND 2px ORBITALS OF Be
UNDERGO Sp HYBRIDISATION TO FORM TWO IDENTICAL HYBRID
ORBITALS
• THEY ARE ORIENTED LINERLY IN OPPOSITE DIRECTION AT AN ANGLE
OF 180O
• HENCE BeCl2 HAS LINER STRCTURE DUE TO Sp
HYBRIDISATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hybridisation-191209114854/85/Hybridisation-Jonisha-6-320.jpg)