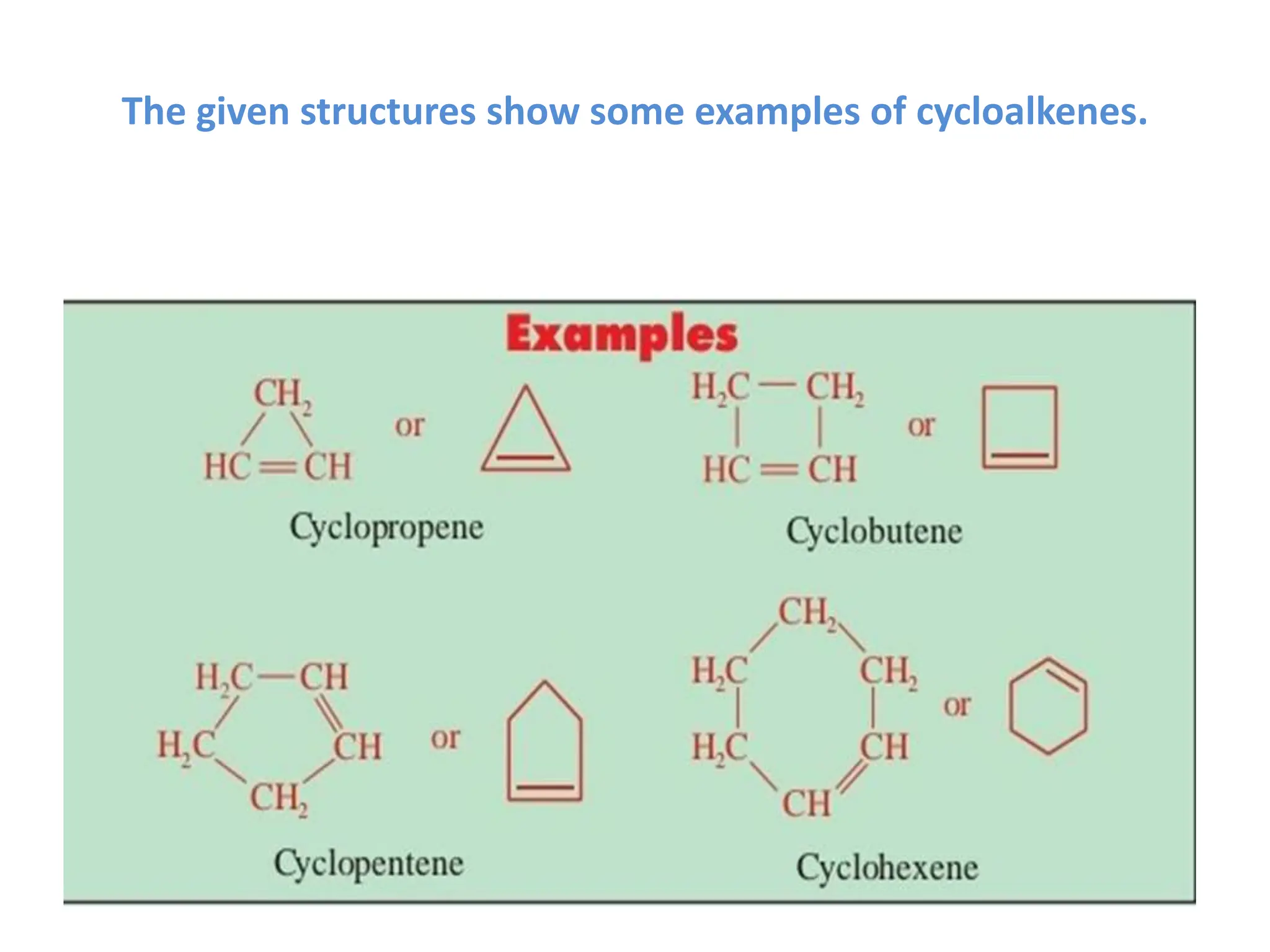
The document provides an overview of organic compounds, specifically hydrocarbons, detailing their classification into alkanes and alkenes based on bonding types and properties. It explains nomenclature, isomerism, preparation methods, and chemical reactions for both alkanes and alkenes, emphasizing their importance in various applications. Additionally, the document discusses cycloalkanes and cycloalkenes, their formation, and uses in industries and drug synthesis.