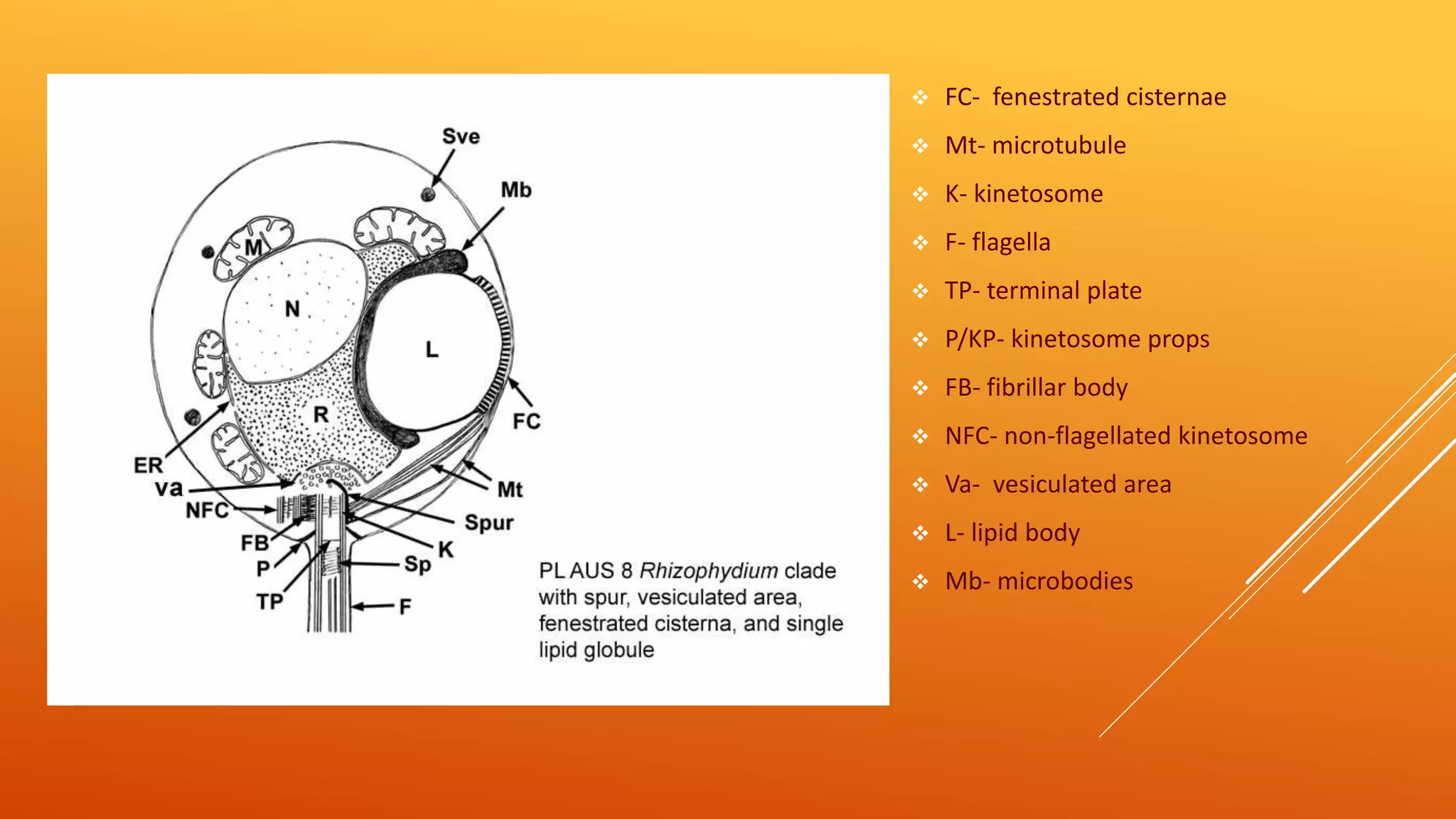
This document discusses chytridiomycota, highlighting its origin, characteristics, and evolutionary relationships with higher fungi. It covers the various reproductive methods, thallus structures, and ecological roles of chytrids, emphasizing the presence of chitin and cellulose, which signify their evolutionary importance. Additionally, it outlines the morphological characteristics of zoospores and their reproduction, including sexual reproduction types and notable chytrid species and their hosts.