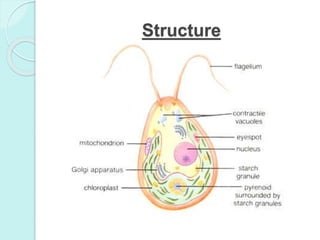
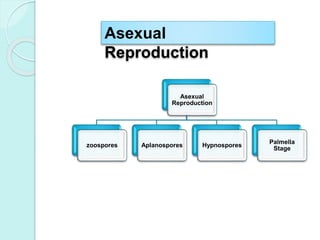
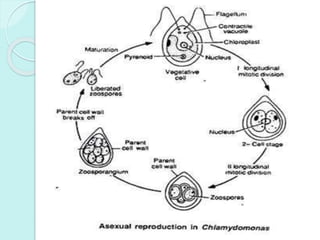
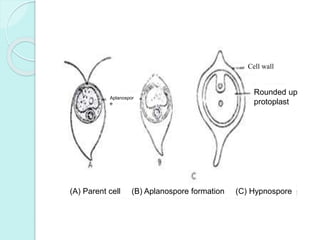
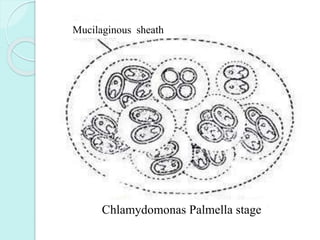
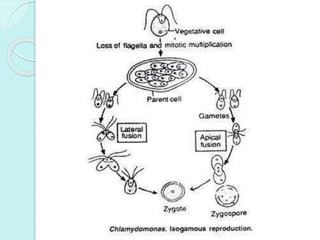
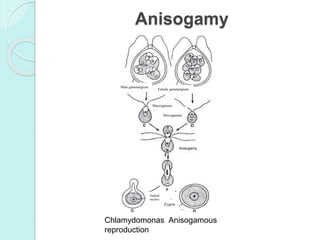
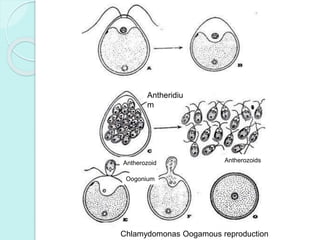
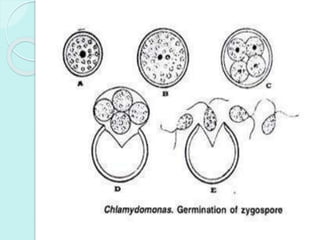
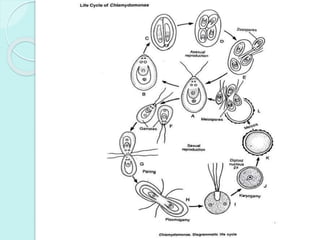
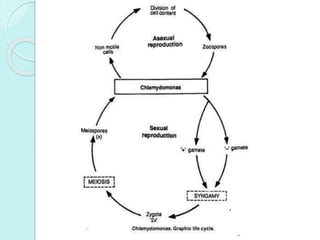
Chlamydomonas is a unicellular, motile green alga with a varied thallus shape, characterized by a multilayered cellulose cell wall and a cup-shaped chloroplast containing pyrenoids for starch synthesis. It reproduces both asexually through zoospores, aplanospores, and hypnospores, and sexually via isogamy, anisogamy, and oogamy, forming a resistant zygospore during unfavorable conditions. The flagella, cytoplasmic structures, and the presence of a stigma for photoreception are significant features of Chlamydomonas.