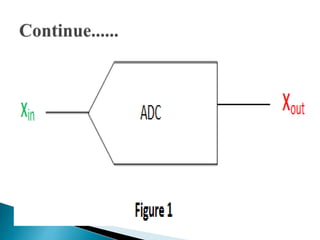
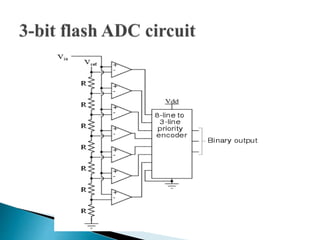
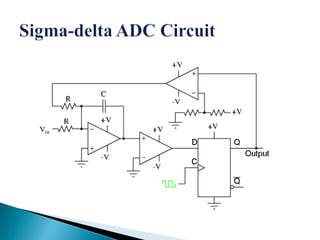
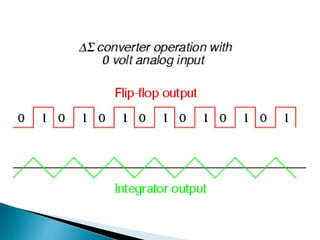
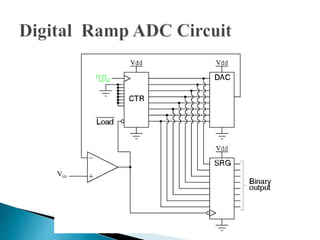
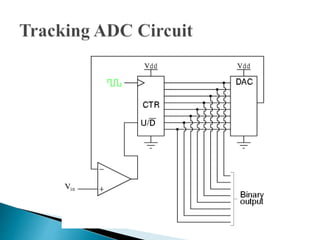
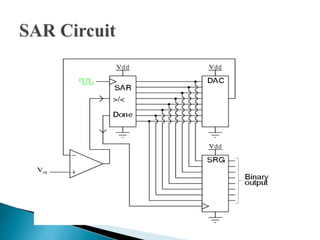
This document discusses different types of analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). It describes flash ADCs, sigma-delta ADCs, digital ramp ADCs, tracking ADCs, and successive approximation ADCs. For each type, it provides a brief explanation of how the circuit works and sometimes includes a diagram. It also lists some common applications of ADCs, such as in transducers, computers, cell phones, microcontrollers, digital signal processing, digital storage, and scientific instruments.