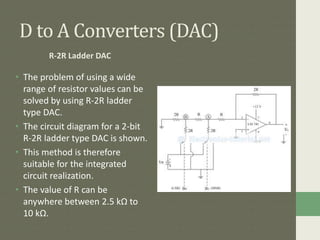
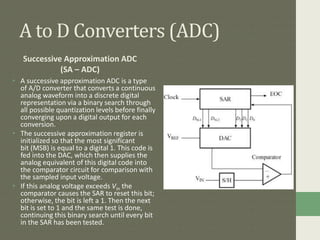
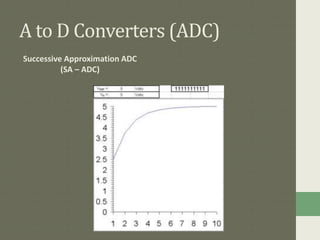
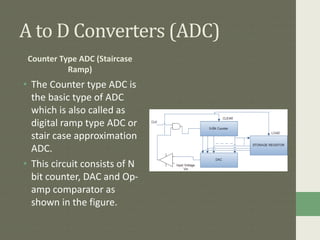
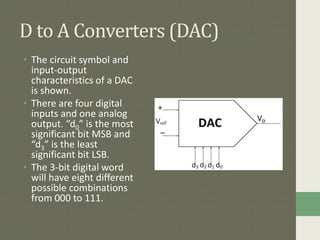
Digital to analog converters (DACs) and analog to digital converters (ADCs) allow the conversion between analog and digital signals. DACs take a digital input and output a proportional analog voltage. Common DAC types include binary weighted resistor DACs and R-2R ladder DACs. ADCs take an analog input and output a digital code representing that voltage. Common ADC types are successive approximation ADCs, dual slope integrator ADCs, and counter/staircase ramp ADCs. Data converters are essential for digital signal processing and the interfacing of analog and digital systems.




![D to A Converters (DAC)
Input – Output Equation
• If the input to a DAC block is an “n” bit
digital word and analog output voltage
V0 then the expression for the analog
output voltage V0 is given by,
• V0 = VFS [d1 2-1 + d2 2-2 + … + dn 2-n ]
• We can substitute VFS by VR .i.e. the
reference voltage to write
• V0 = KVR [d1 2-1 + d2 2-2 + … + dn 2-n ]
• If we substitute ,
D = [d1 2-1 + d2 2-2 + … + dn 2-n ] then
V0 = K VR D
• The input and output equation is
applicable to all types of DACs.
• Where,
VFS = Full Scale
output voltage.
d1 = MSB
dn = LSB
K = scaling factor
D = fractional binary
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/be-180505105932/85/Data-convertors-6-320.jpg)

![D to A Converters (DAC)
Binary Weighted Resistor DAC
• This DAC circuit uses weighted values
of resistor like 2R, 4R, 6R, 8R and so on
depending on the digital inputs
available therefore such type of
network is known as weighted resistor
DAC.
• This circuit consists of a transistor
switch which turns on the switch when
the digital input is ‘1’ and if digital input
becomes ‘0’ it will open the switch.
When transistor switch gets closed,
current flows through the weighted
resistor due to the reference voltage.
• When all such currents from different
weighted resistors get added at
summing point of the operational
amplifier it will produce a proportional
voltage as its output.
• V0 = VR [d1 2-1 + d2 2-2 + ….. + dn 2-n ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/be-180505105932/85/Data-convertors-8-320.jpg)