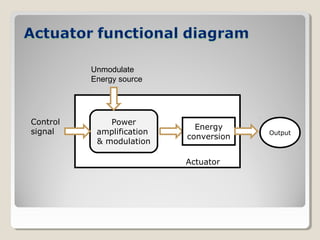
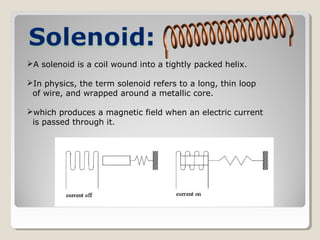
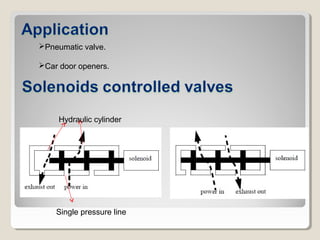
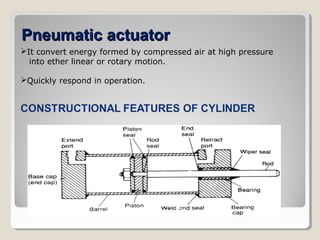
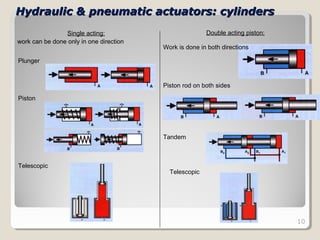
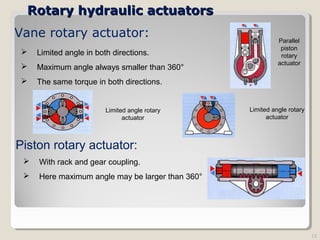
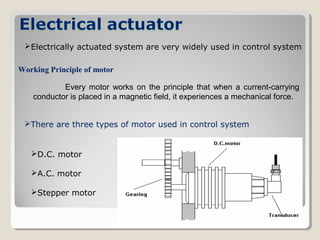
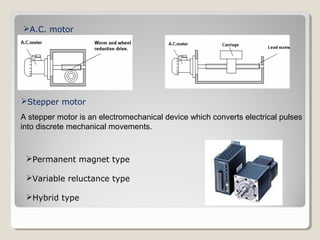
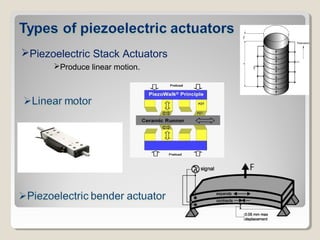
Actuators are devices that produce motion or action in response to an input signal. Common types of actuators include solenoids, hydraulic cylinders, pneumatic cylinders, motors, and piezoelectric actuators. Actuators convert various energy sources like electrical, fluid, or mechanical energy into motion or force. Common applications include industrial machinery, vehicles, and automation equipment.