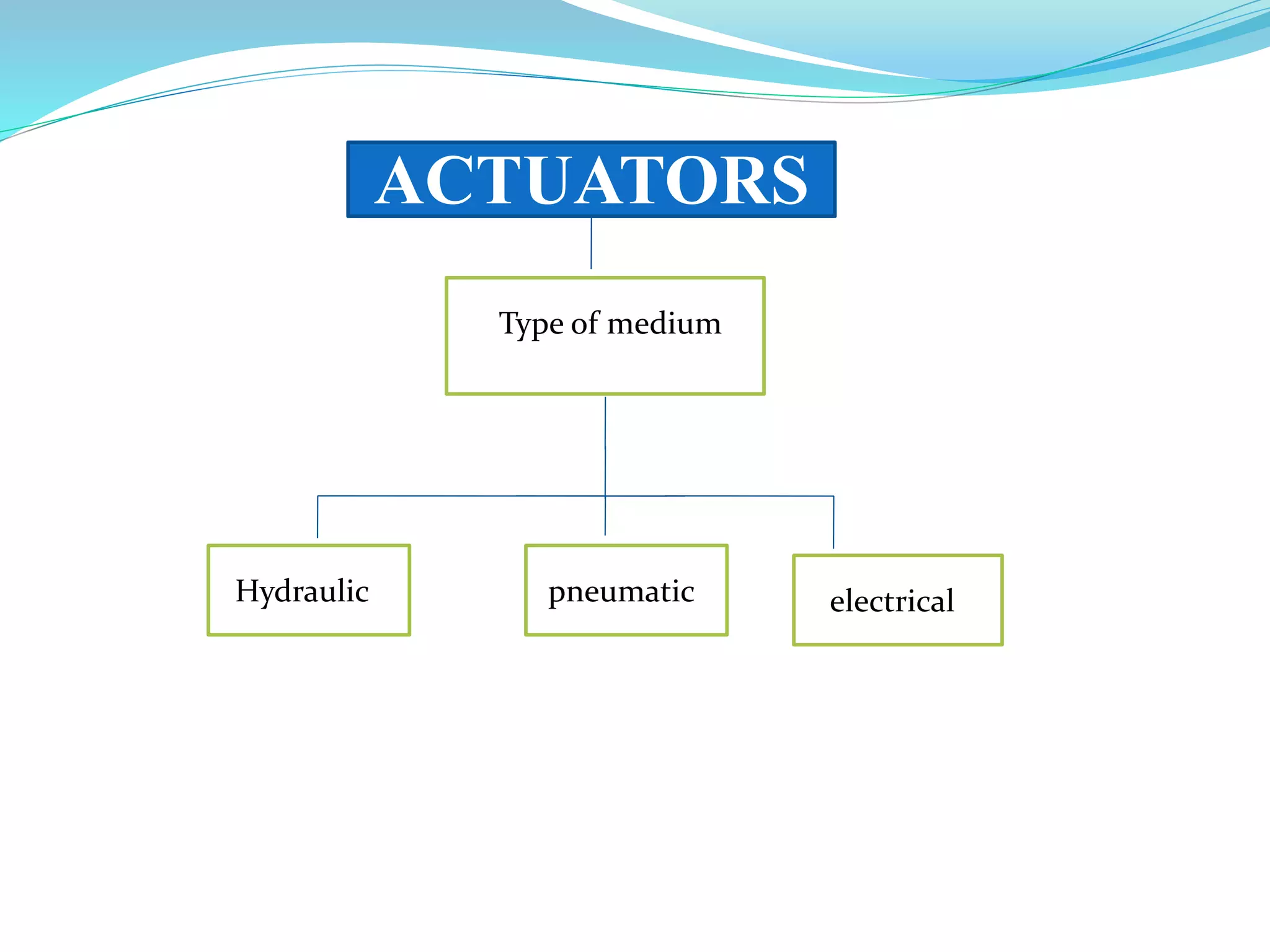
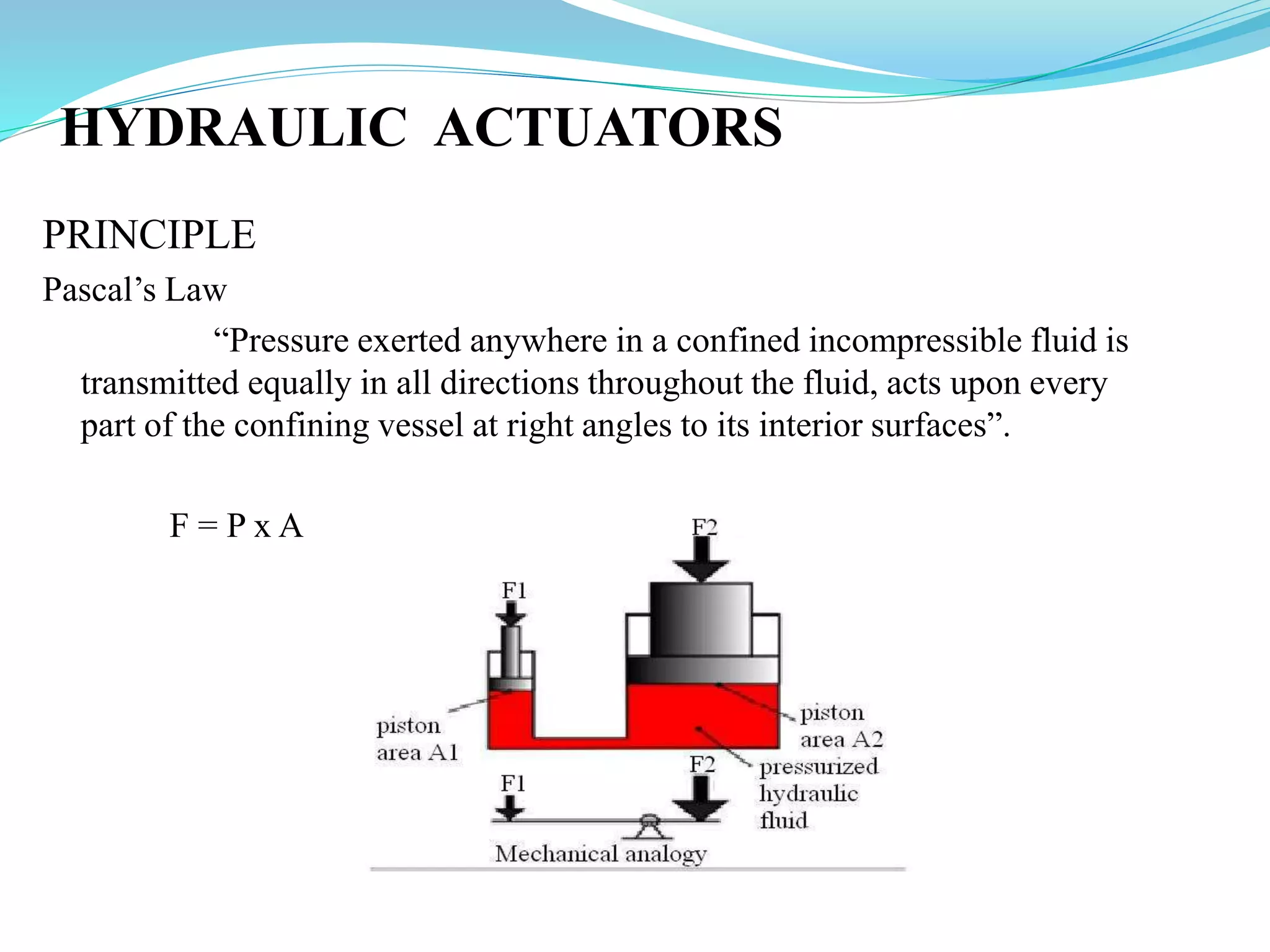
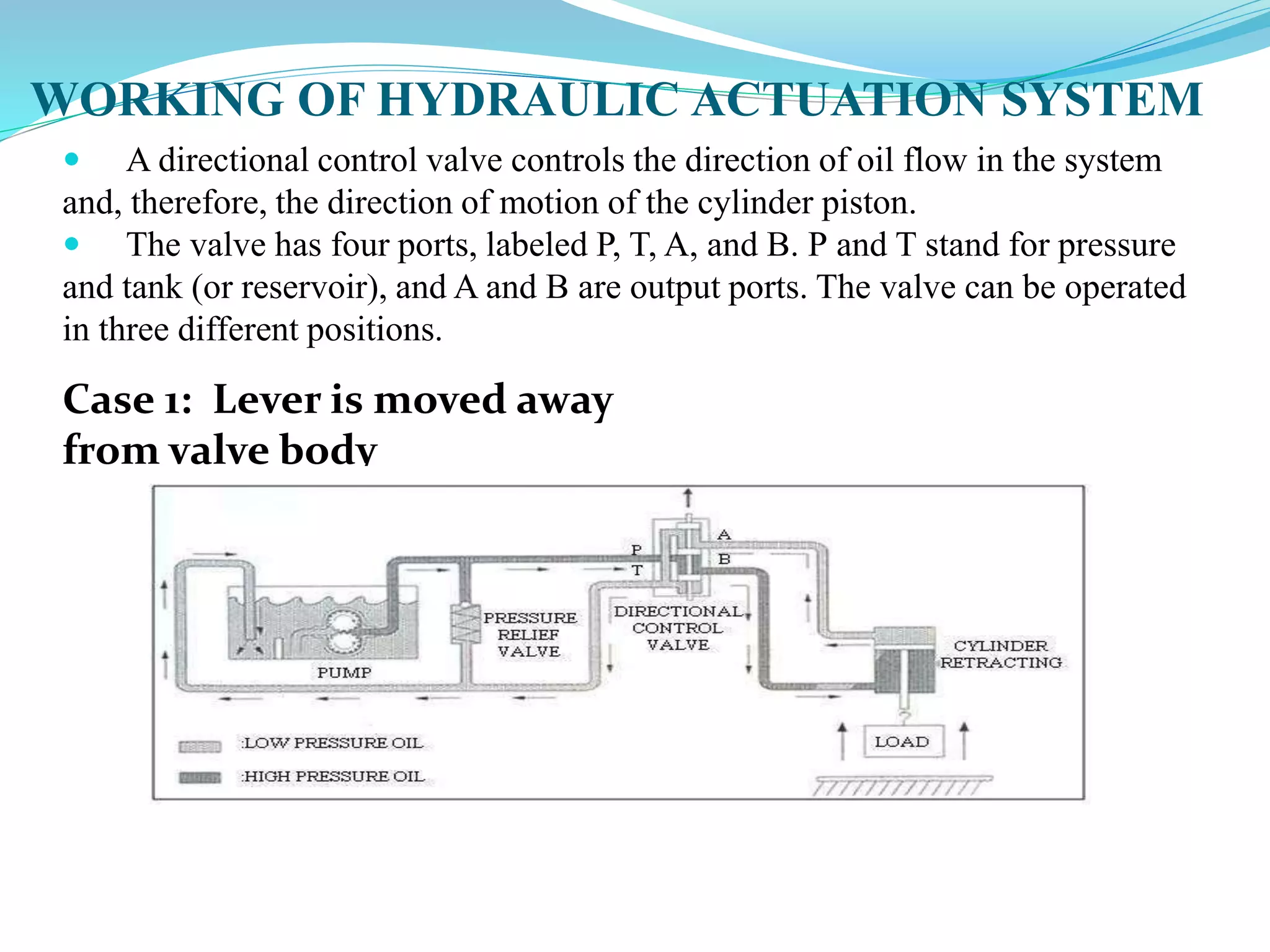
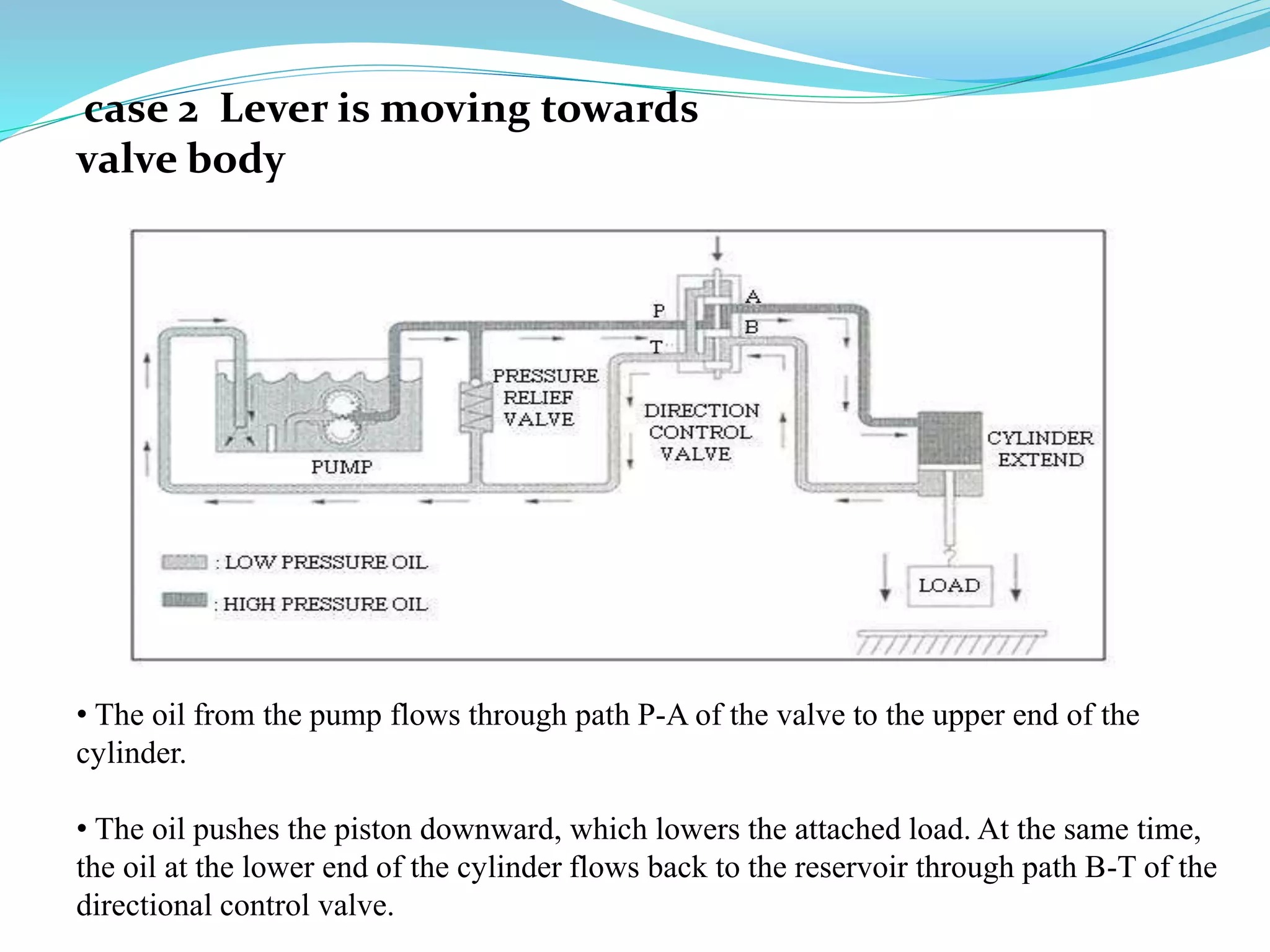
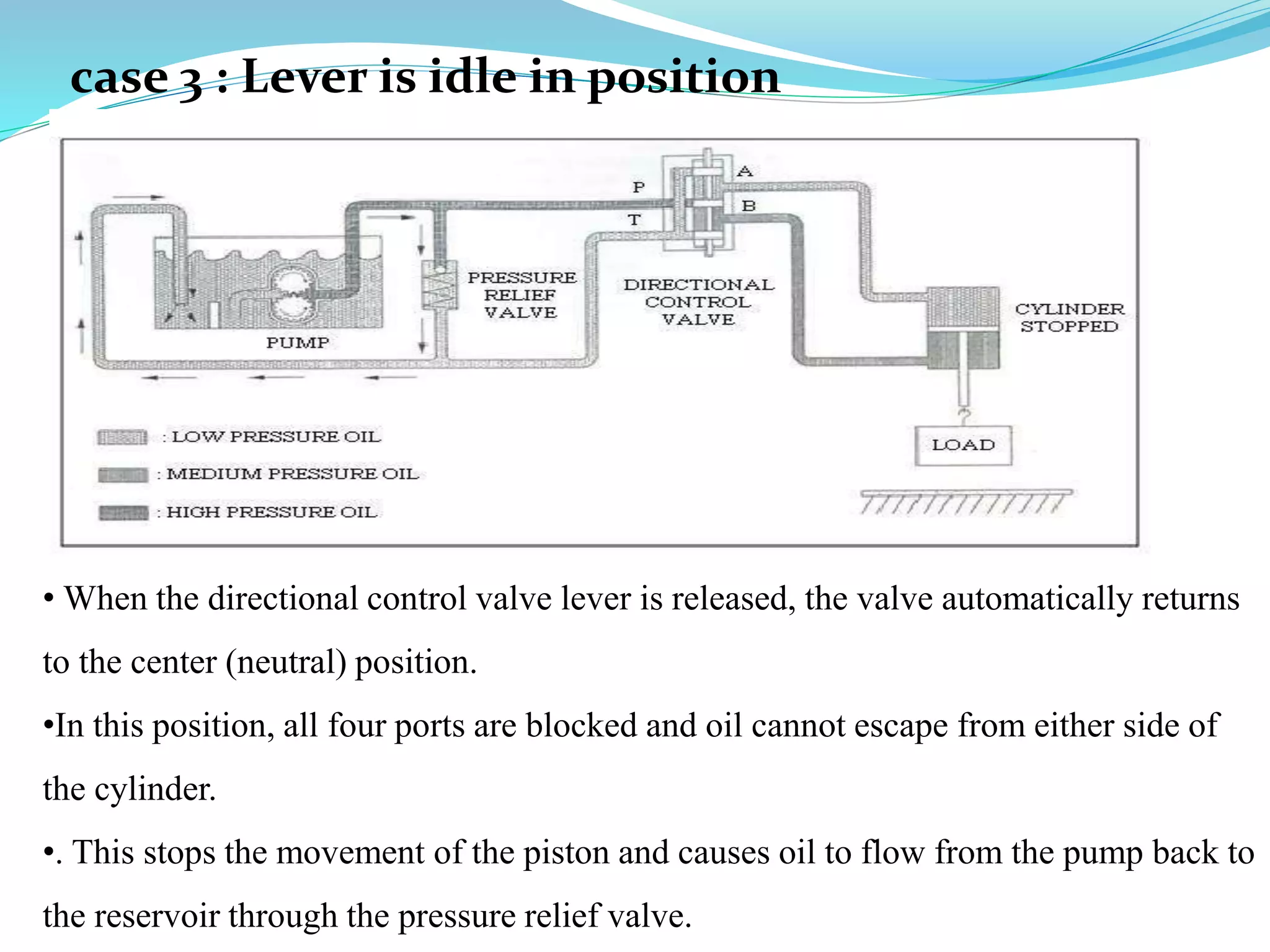
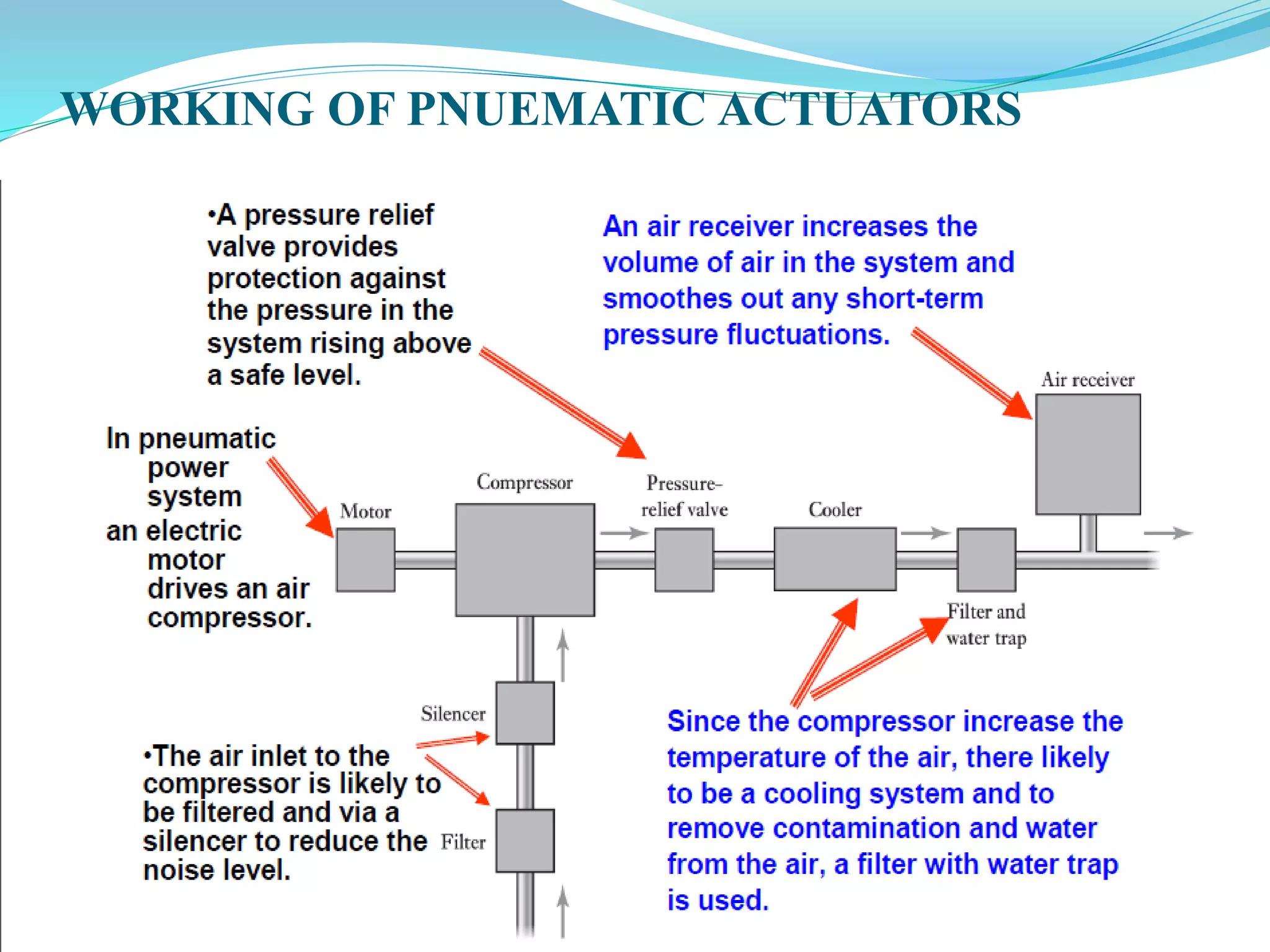
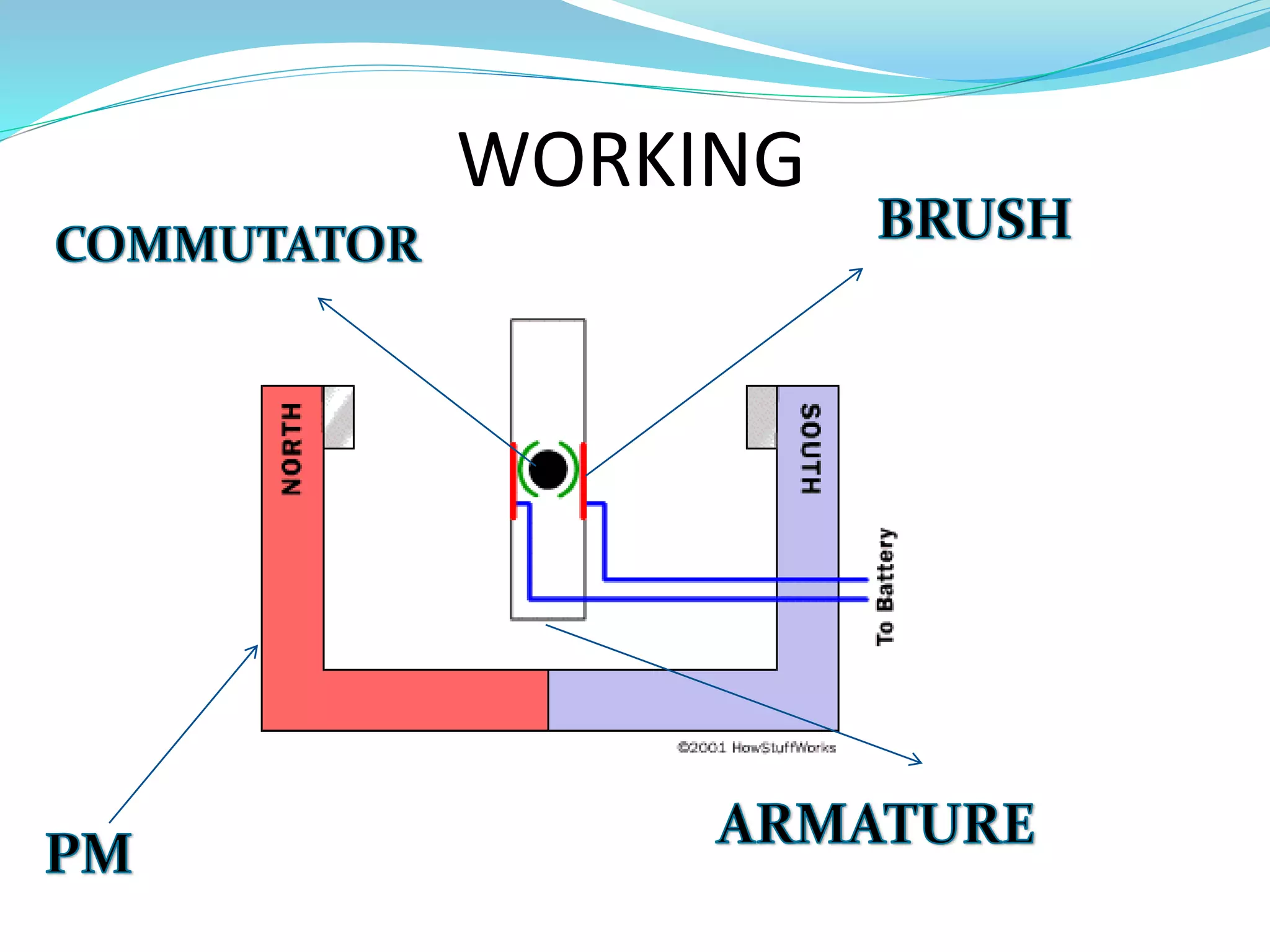
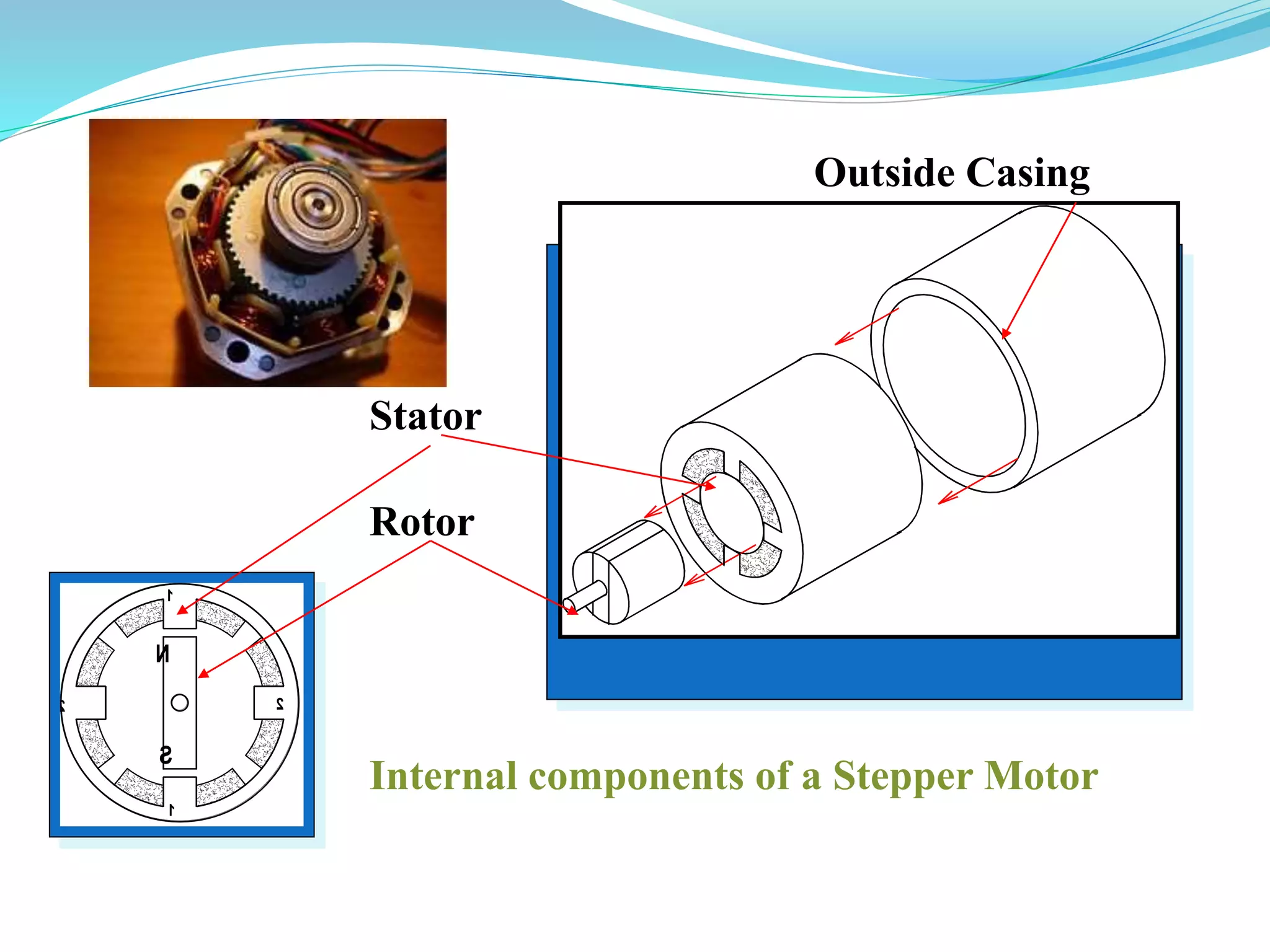
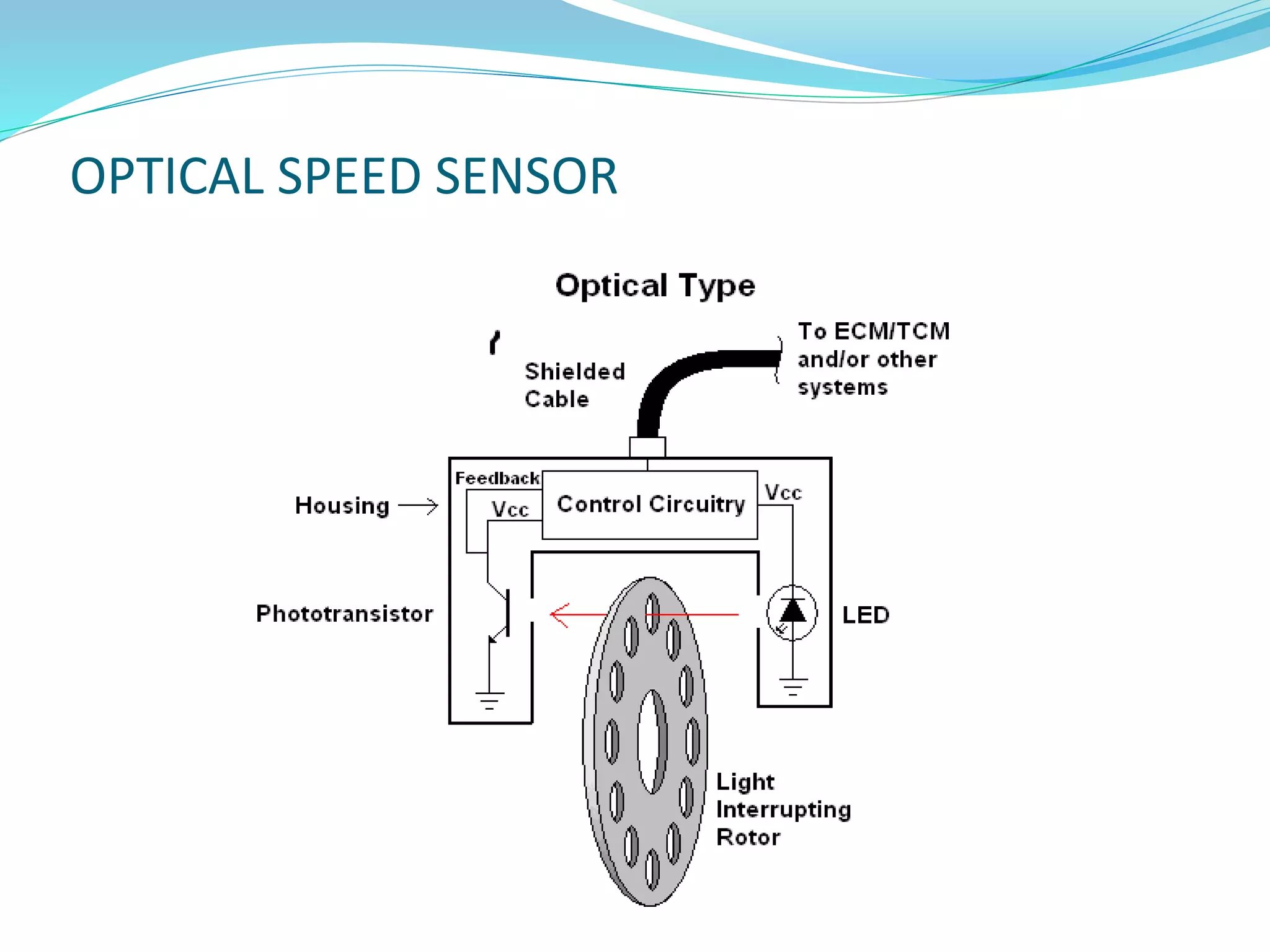
This document discusses different types of actuators including hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric actuators. It provides details on the working principles and components of hydraulic actuators, which use pressurized fluids to transmit force via mechanisms like cylinders and pistons. Pneumatic actuators similarly use compressed air. Electric actuators include DC motors that use electromagnets and commutators, stepper motors that move in discrete steps, and optical speed sensors used in automatic vehicle transmissions. Advantages and disadvantages of each type are listed.