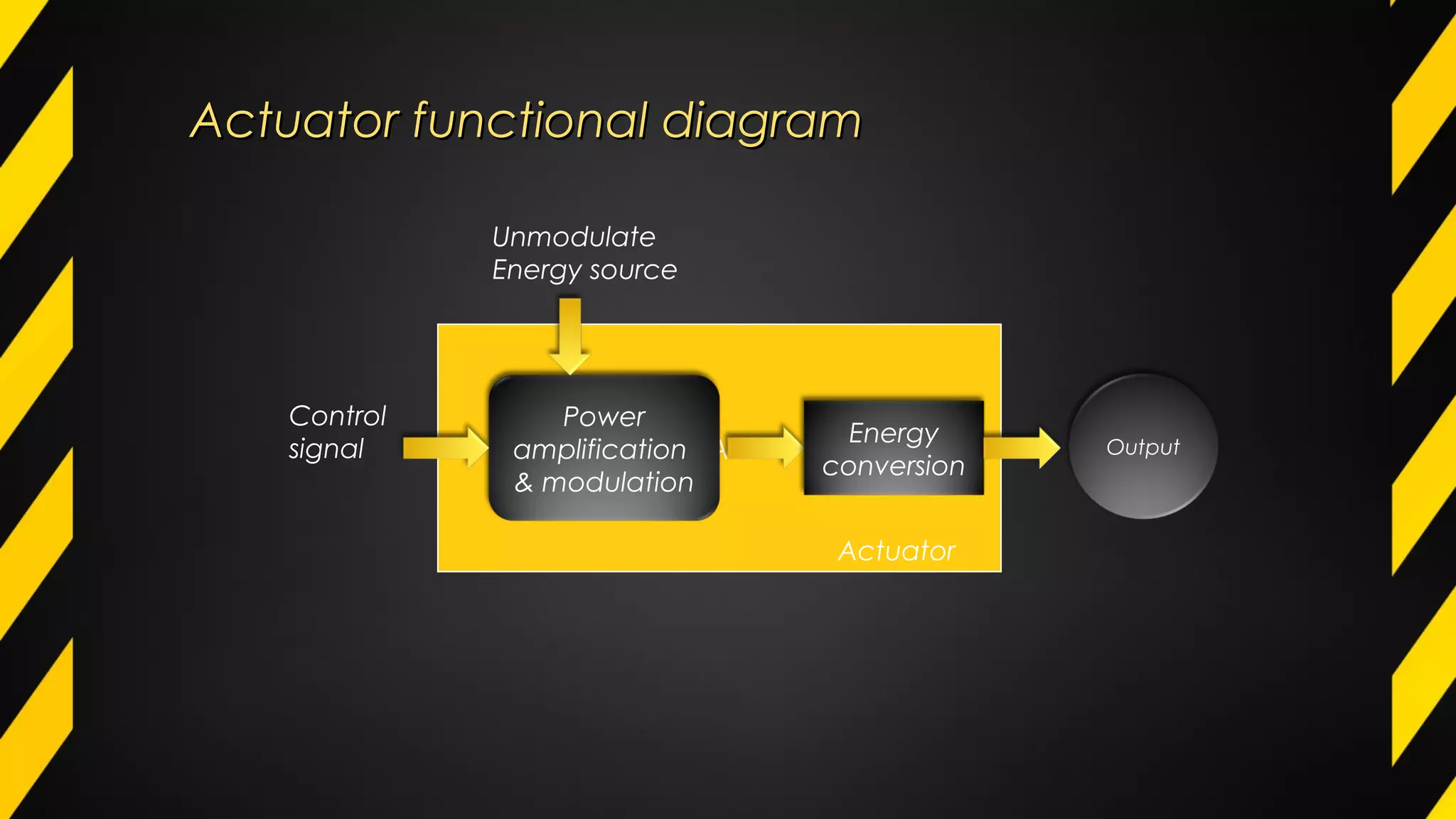
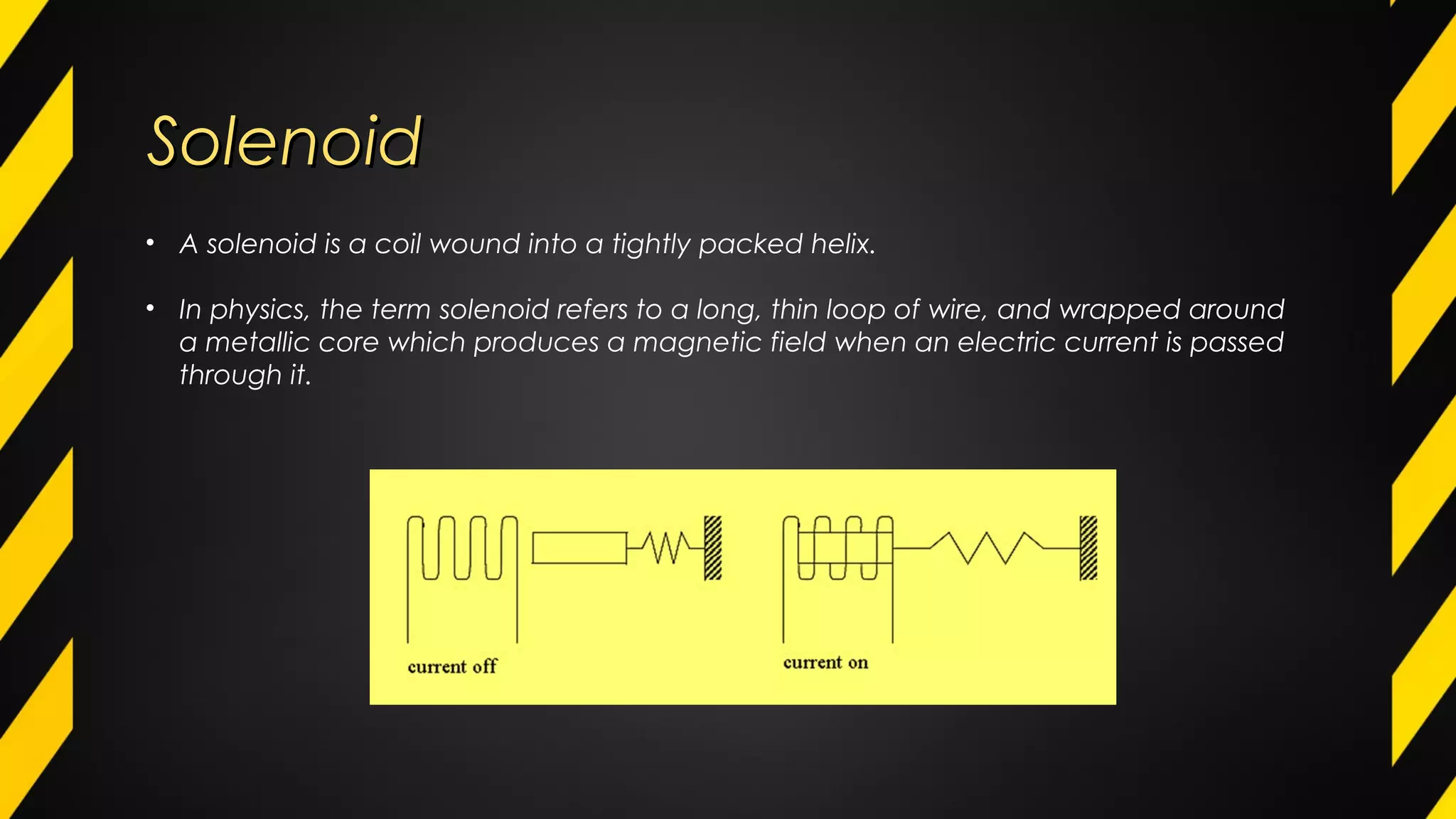
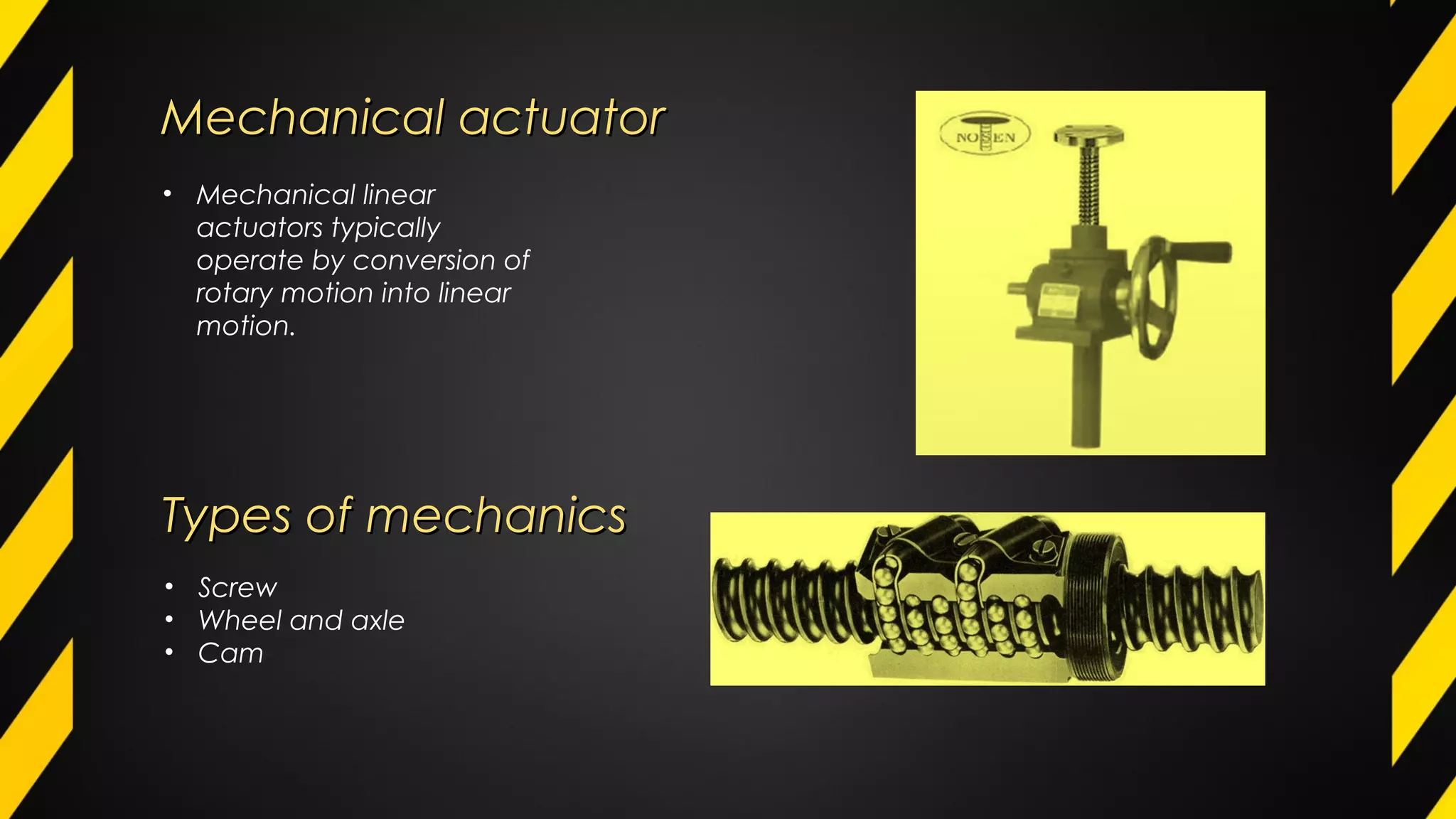
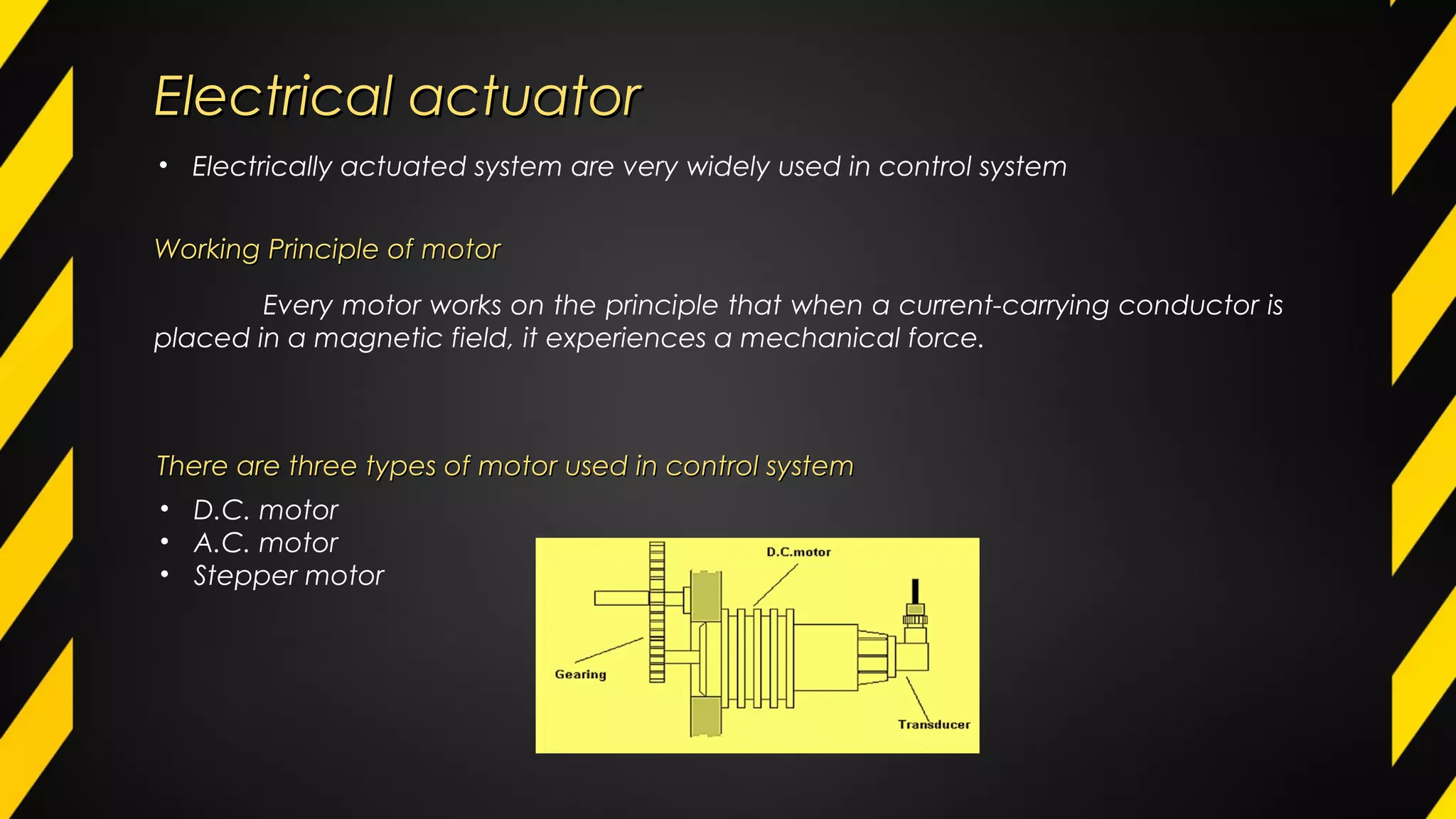
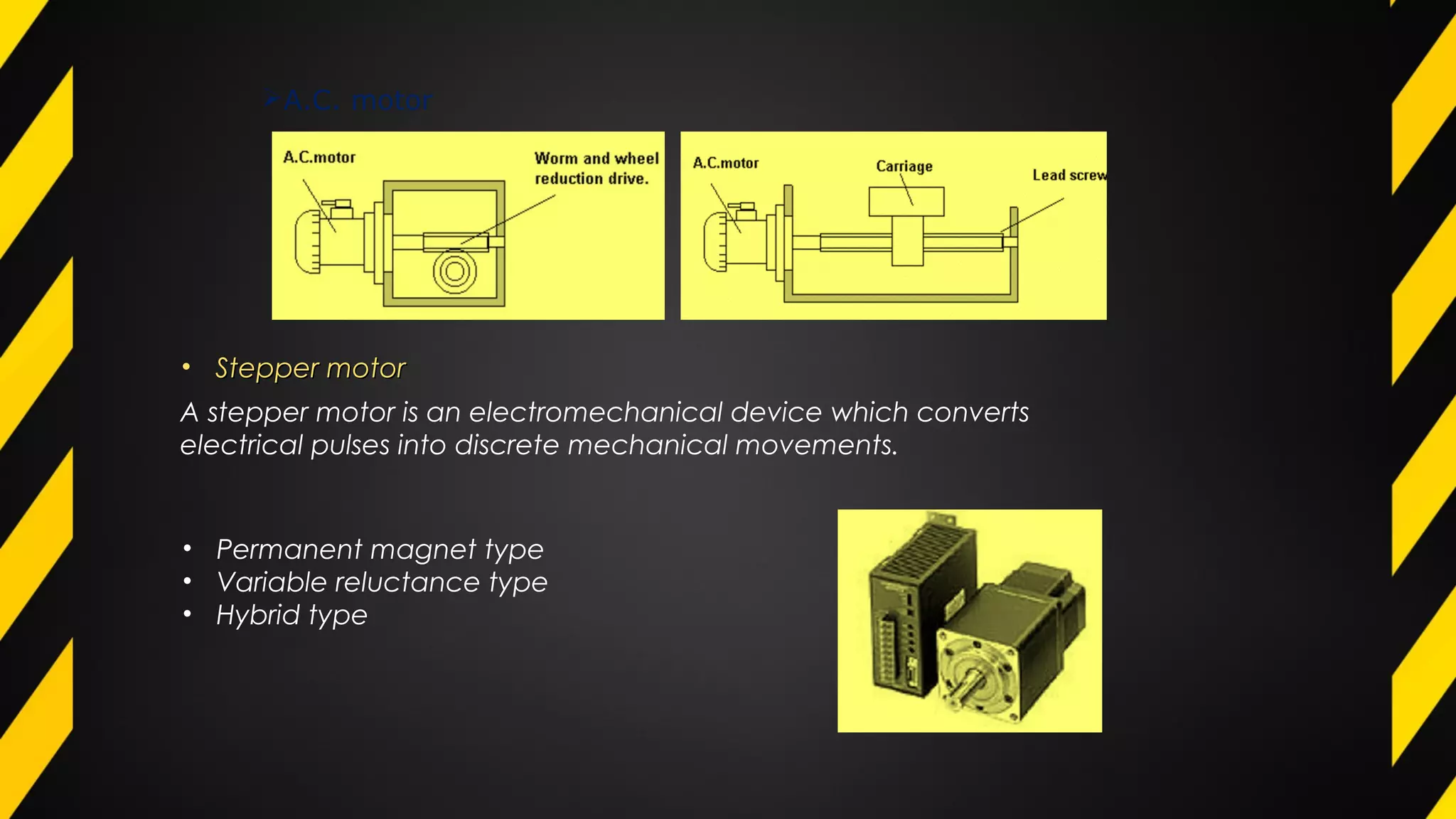
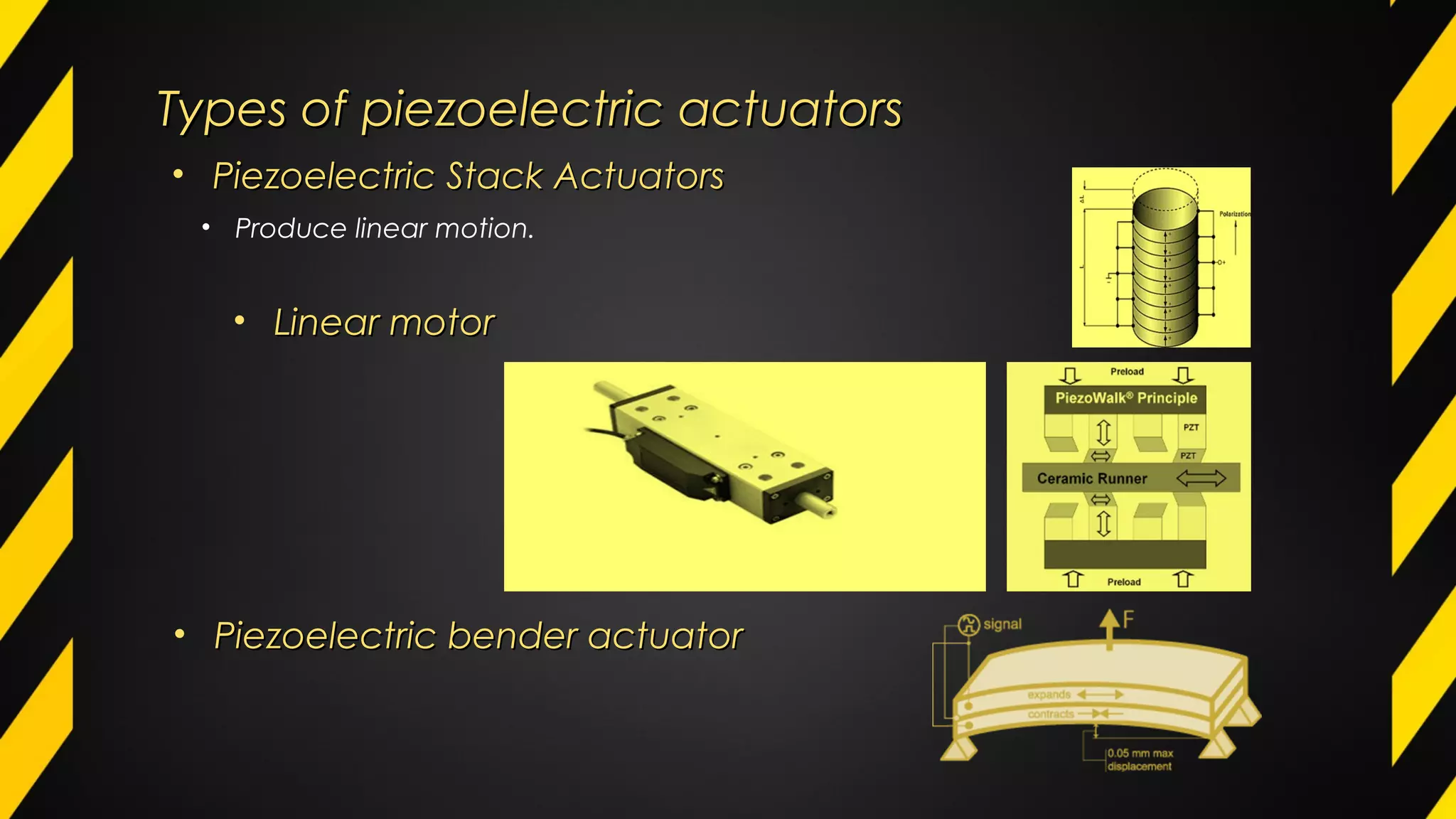
1) An actuator is a device that produces motion or action in response to an input signal. Common types of actuators include hydraulic, pneumatic, mechanical, electrical, and piezoelectric actuators.
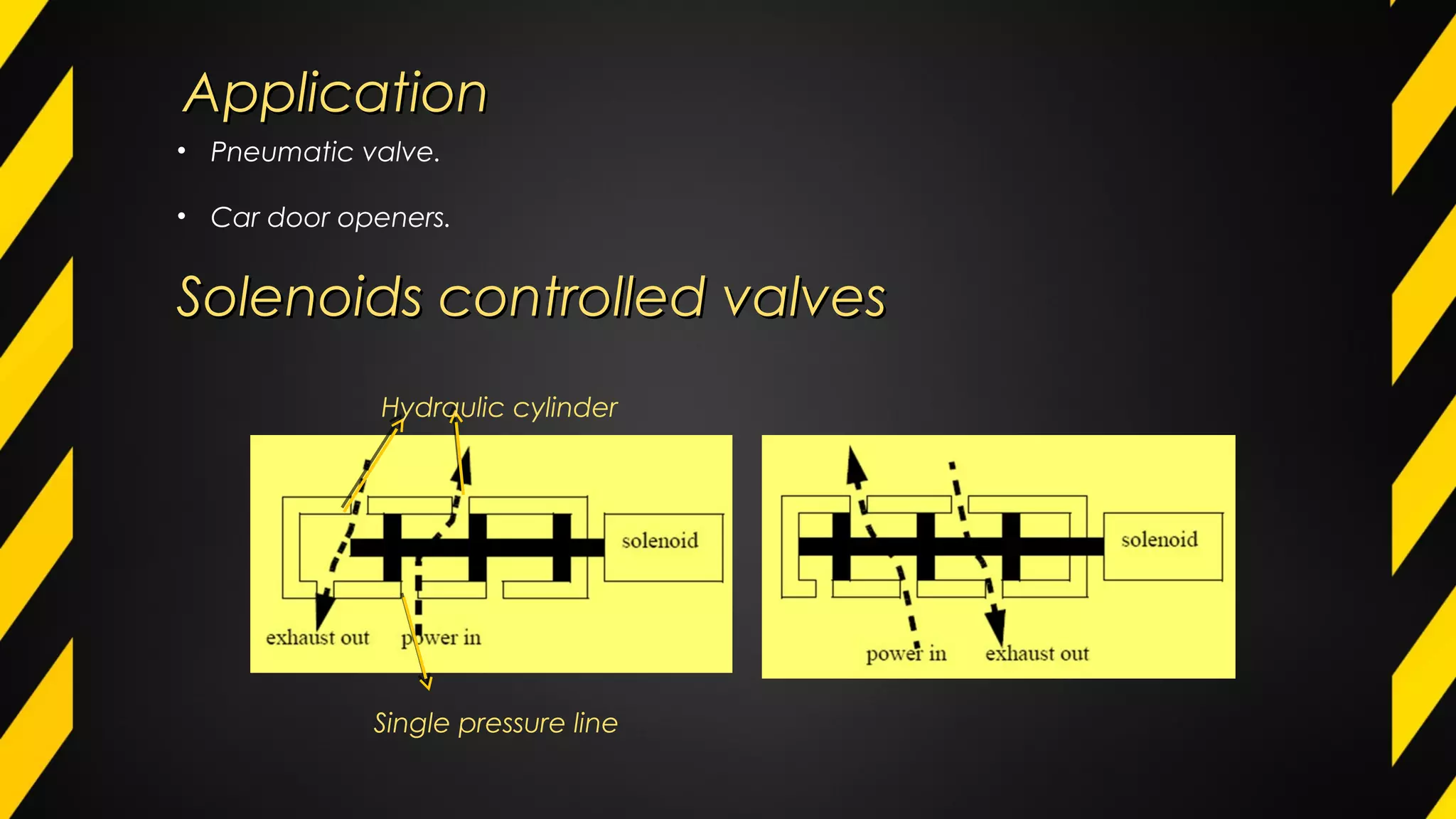
2) Actuators work by converting an input energy source like electricity, air pressure, or hydraulic fluid pressure into motion. Common applications include valves, car door openers, hydraulic jacks, and brakes.
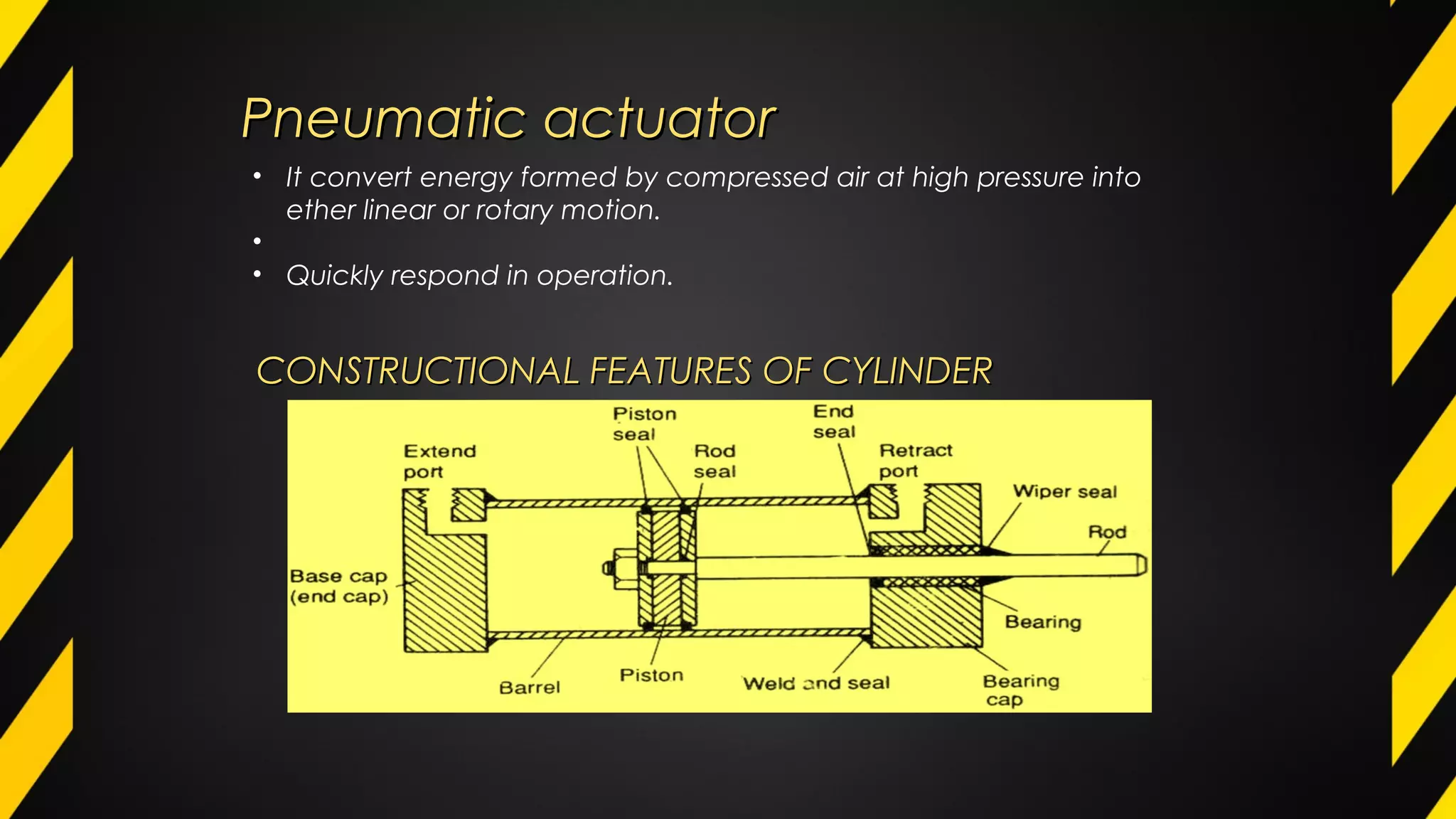
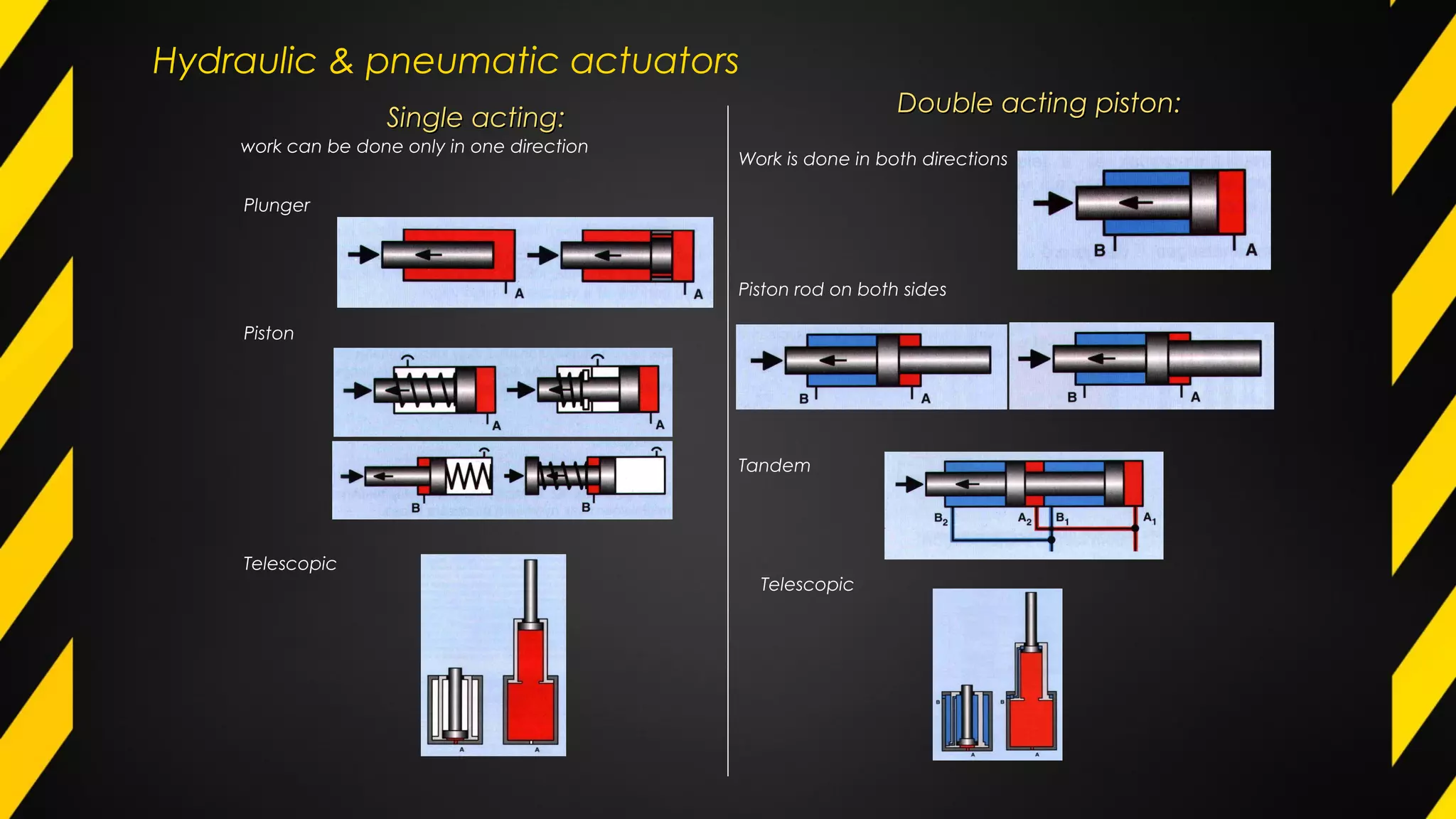
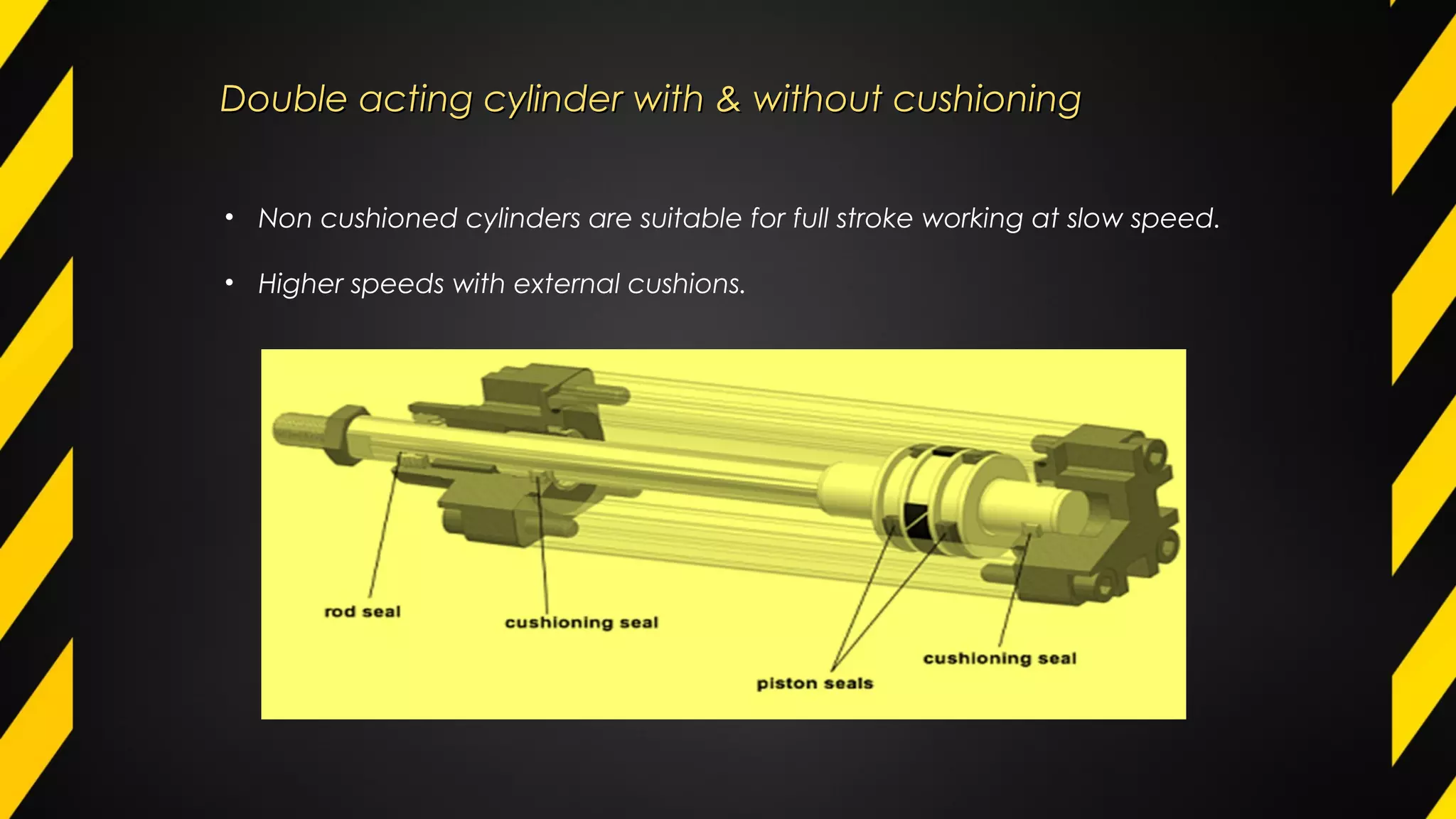
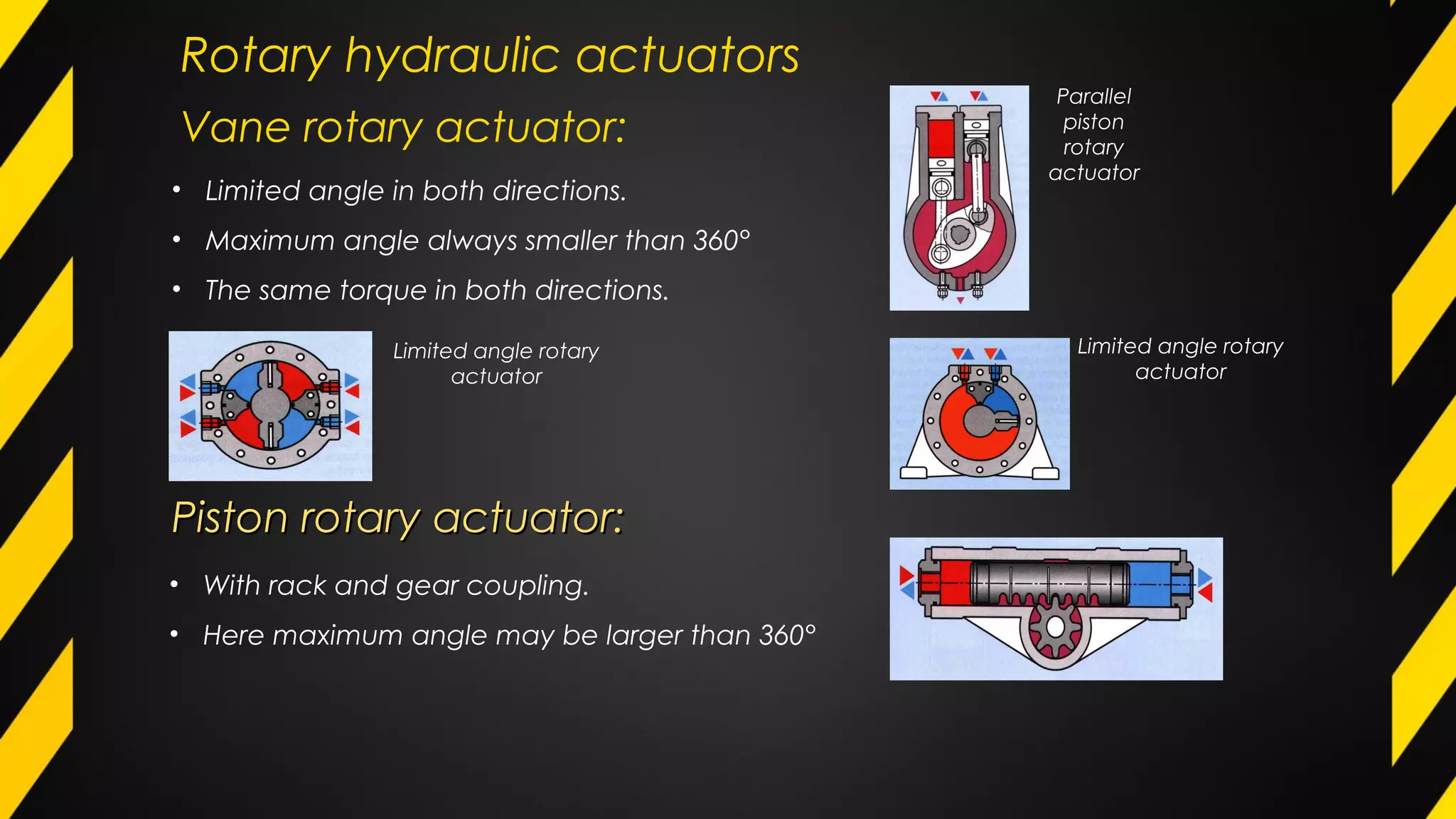
3) Hydraulic and pneumatic actuators are often used to transmit power and control motion due to their ability to generate high forces and respond quickly. Common configurations include single-acting and double-acting cylinders and rotary motors.