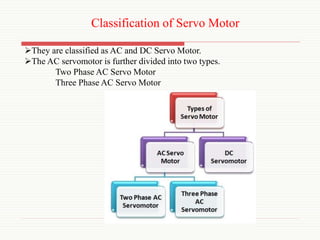
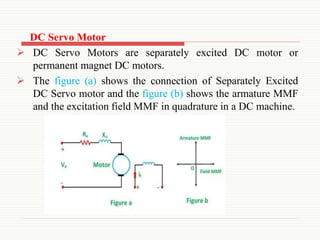
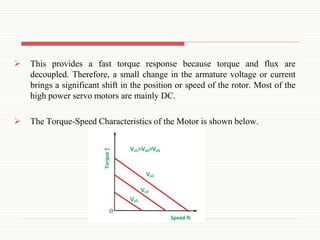
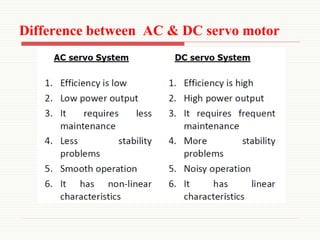
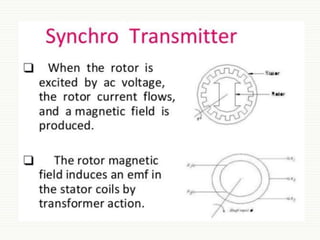
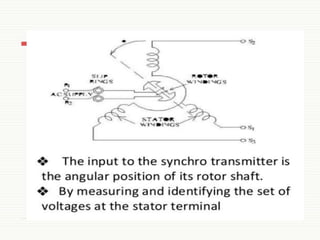
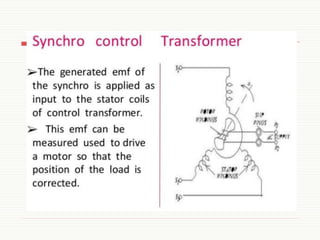
The document discusses servomotors, explaining their definition, construction, operational principles, and classifications into AC and DC types. It highlights their applications in various fields such as robotics, radar systems, and machine tools, emphasizing their precise control capabilities and fast torque response. Additionally, it covers the types of synchro systems related to servomotors and their advantages.