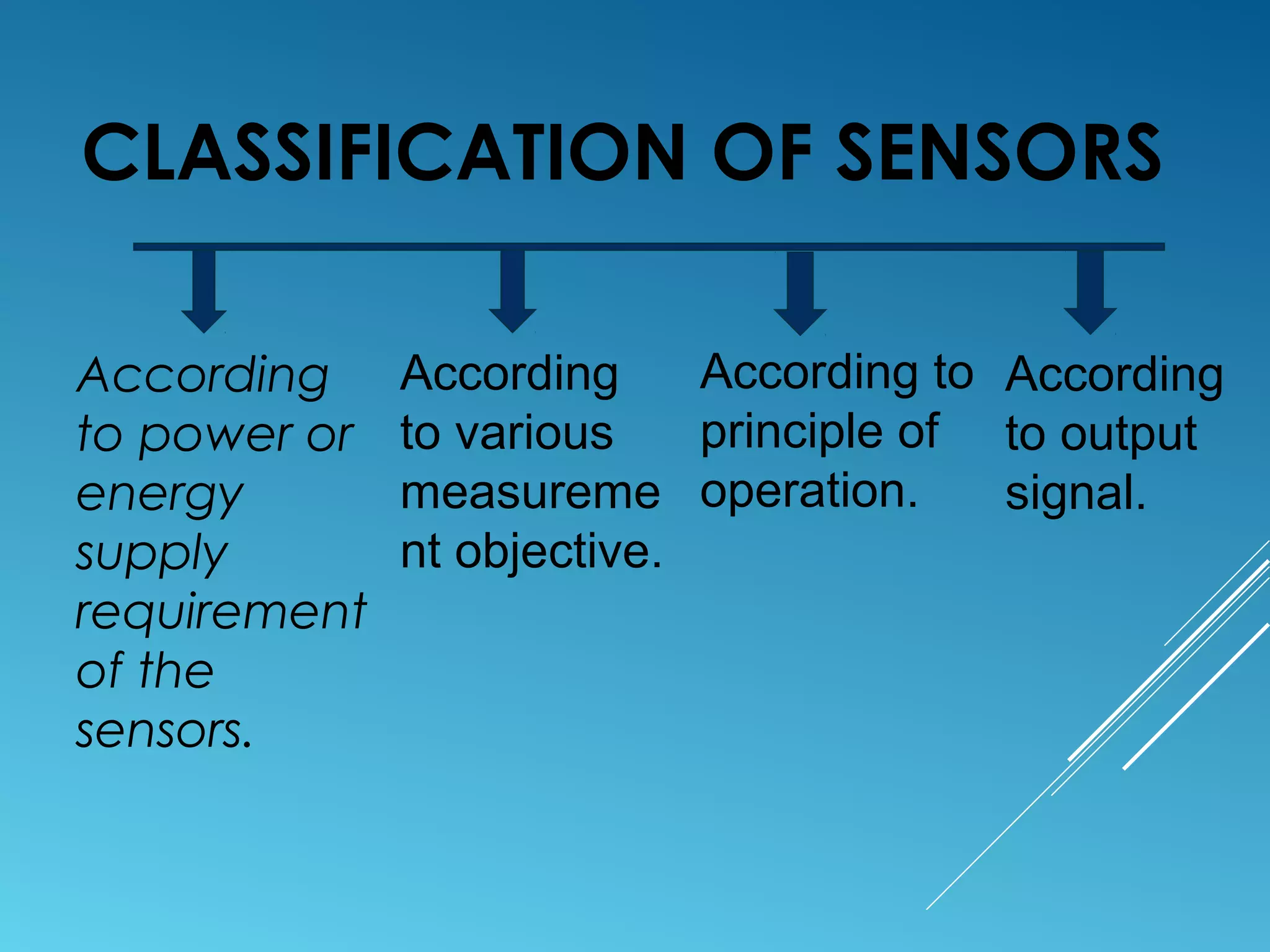
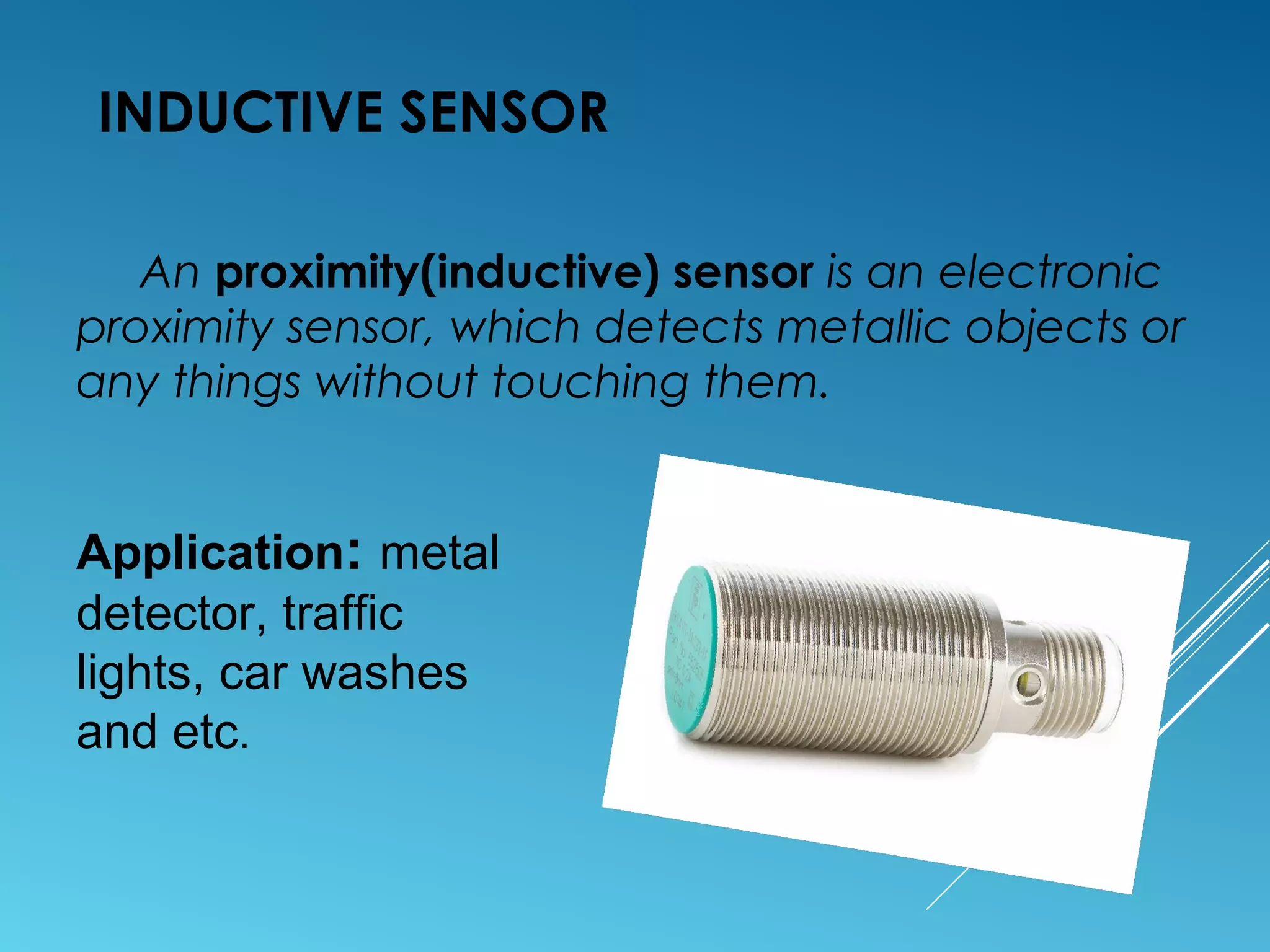
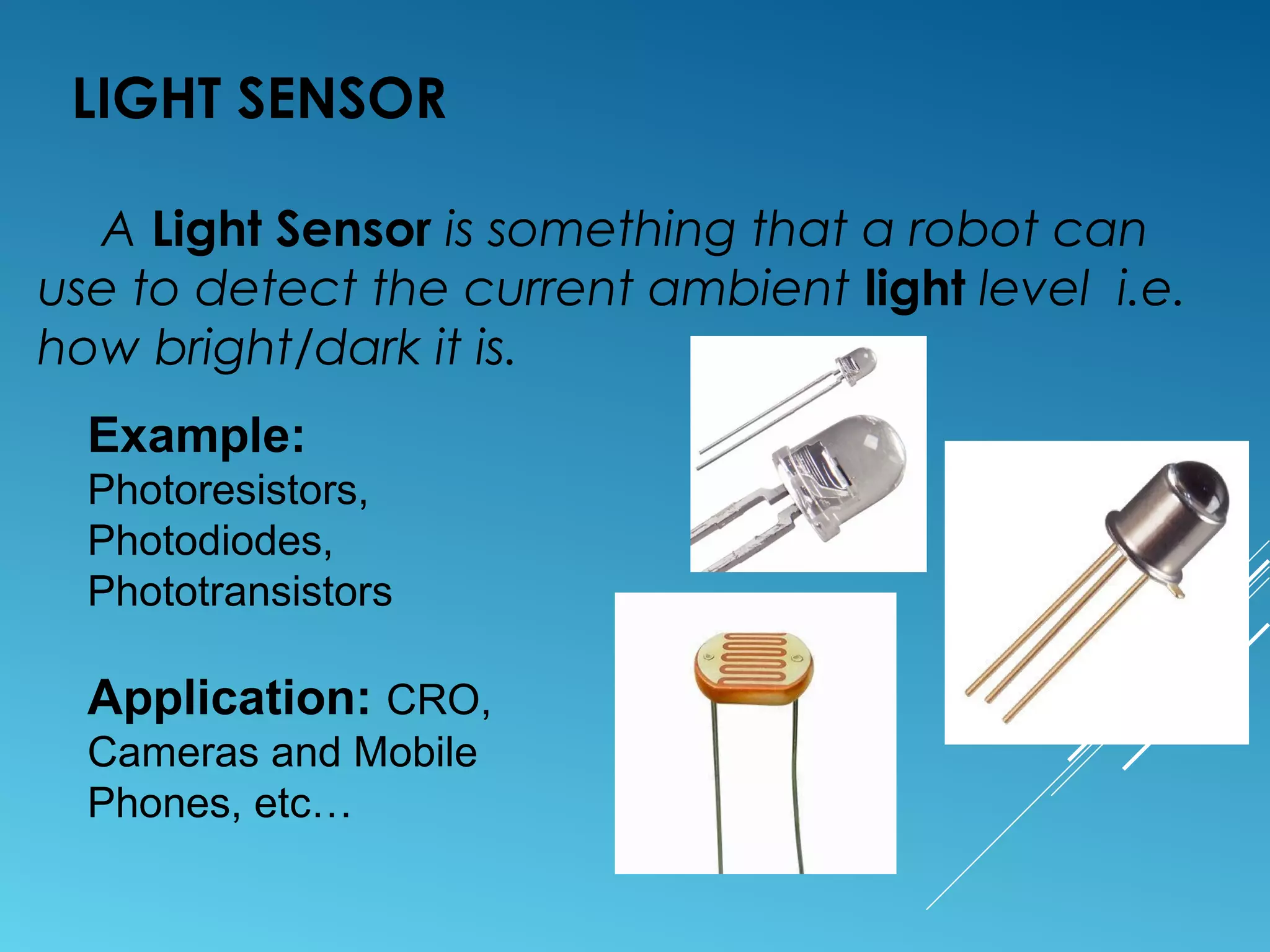
This document discusses different types of sensors, including:
- Active sensors that require power and passive sensors that do not.
- Analog sensors that produce continuous signals and digital sensors that produce digital outputs.
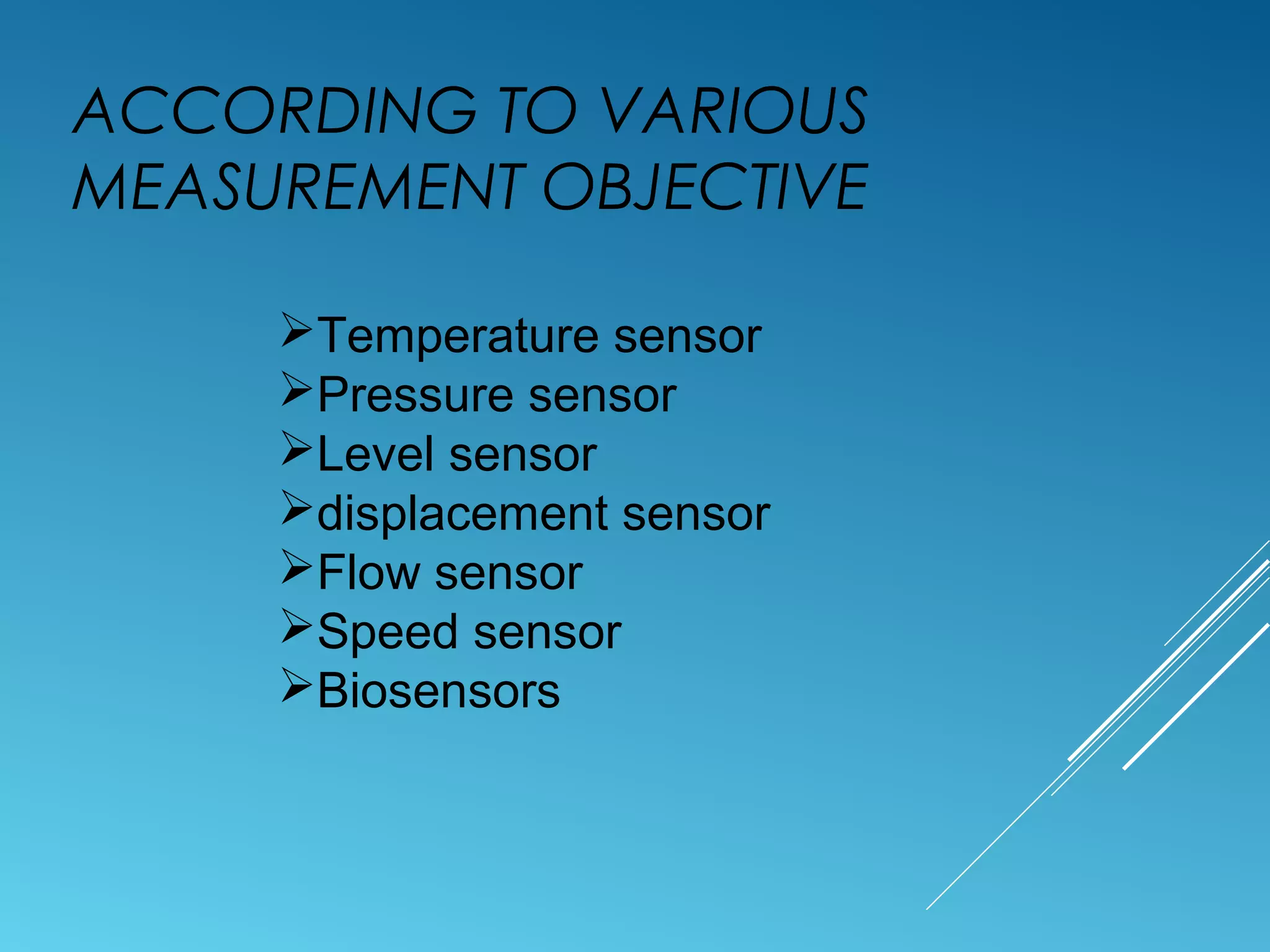
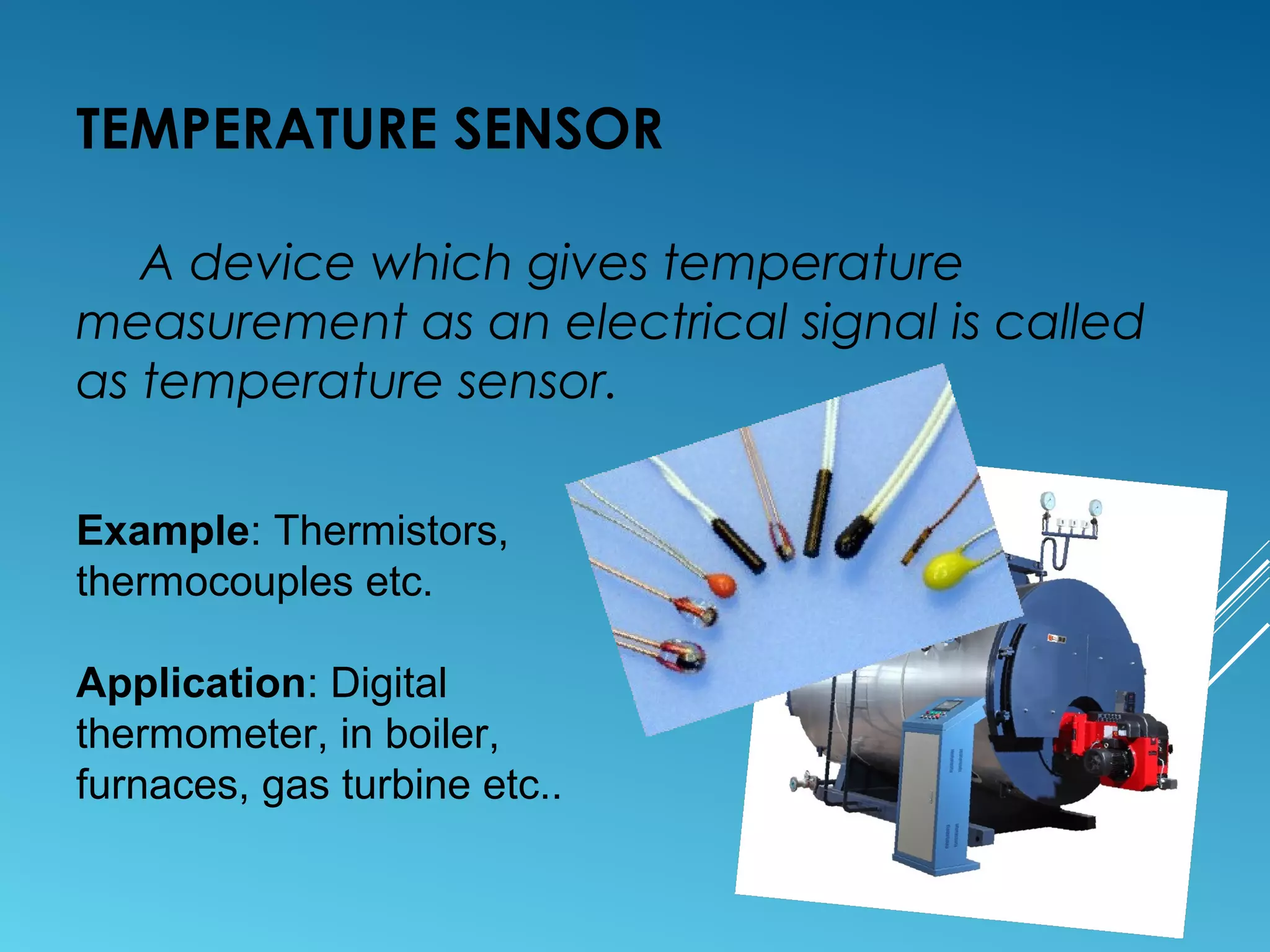
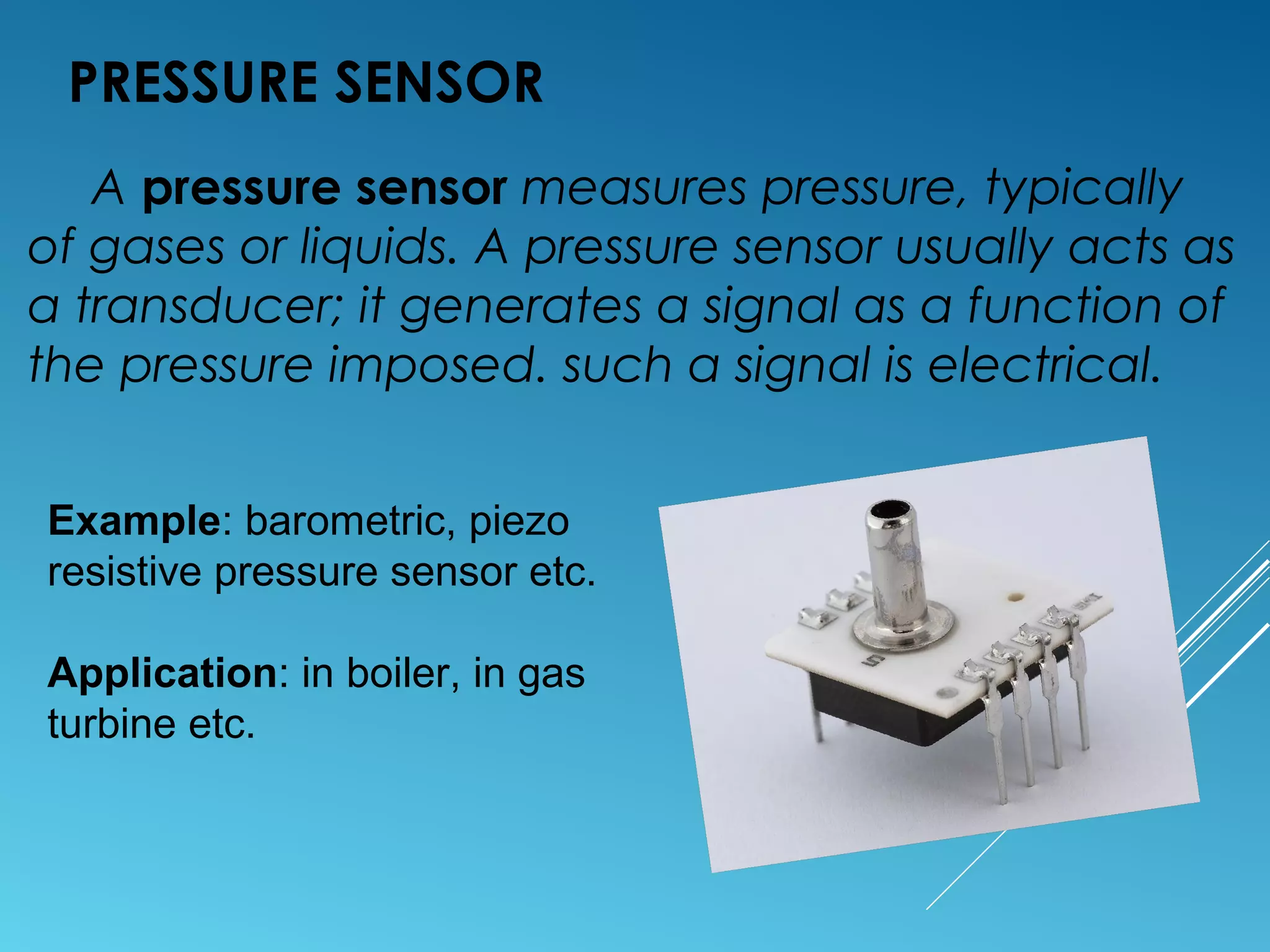
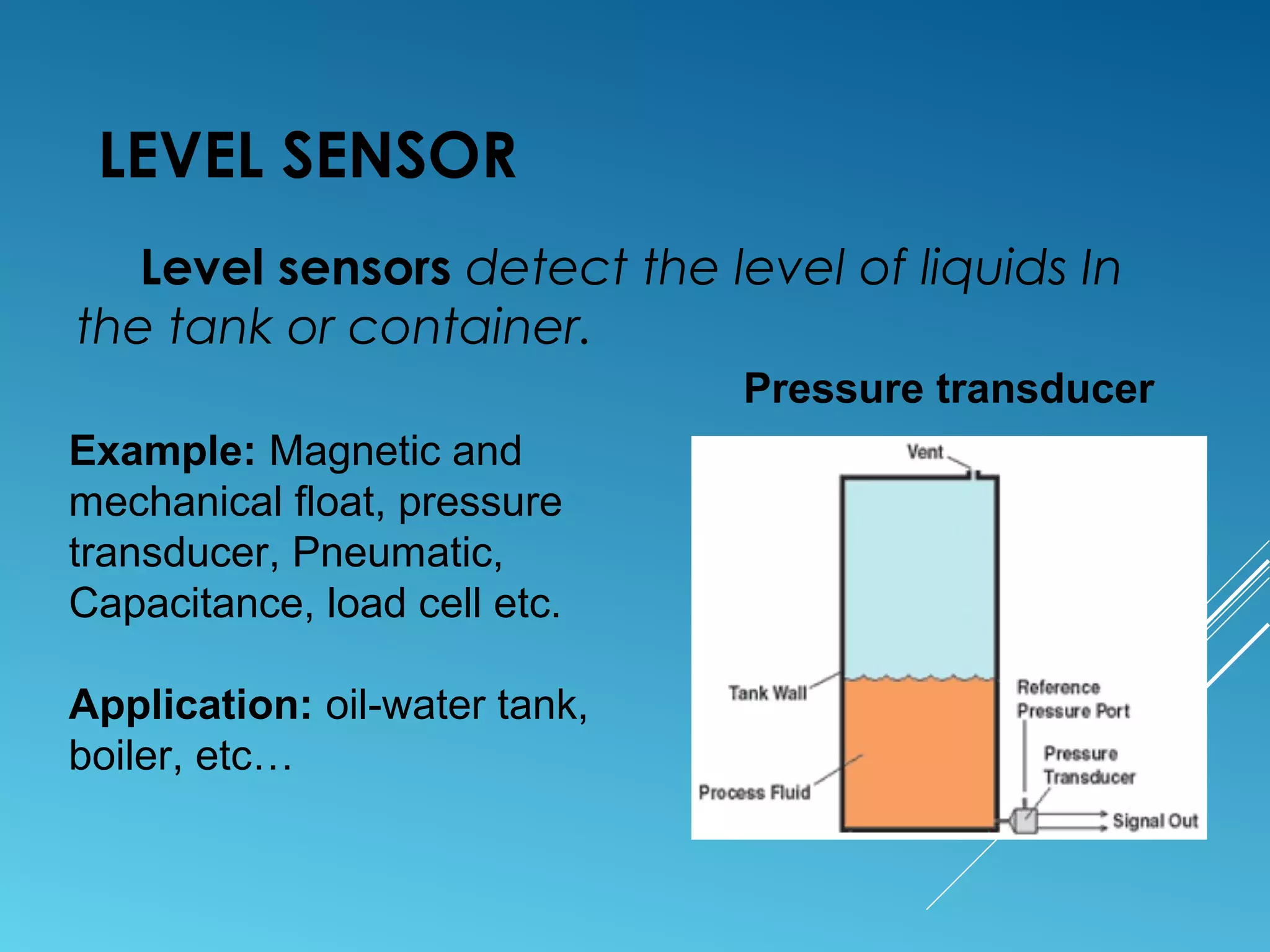
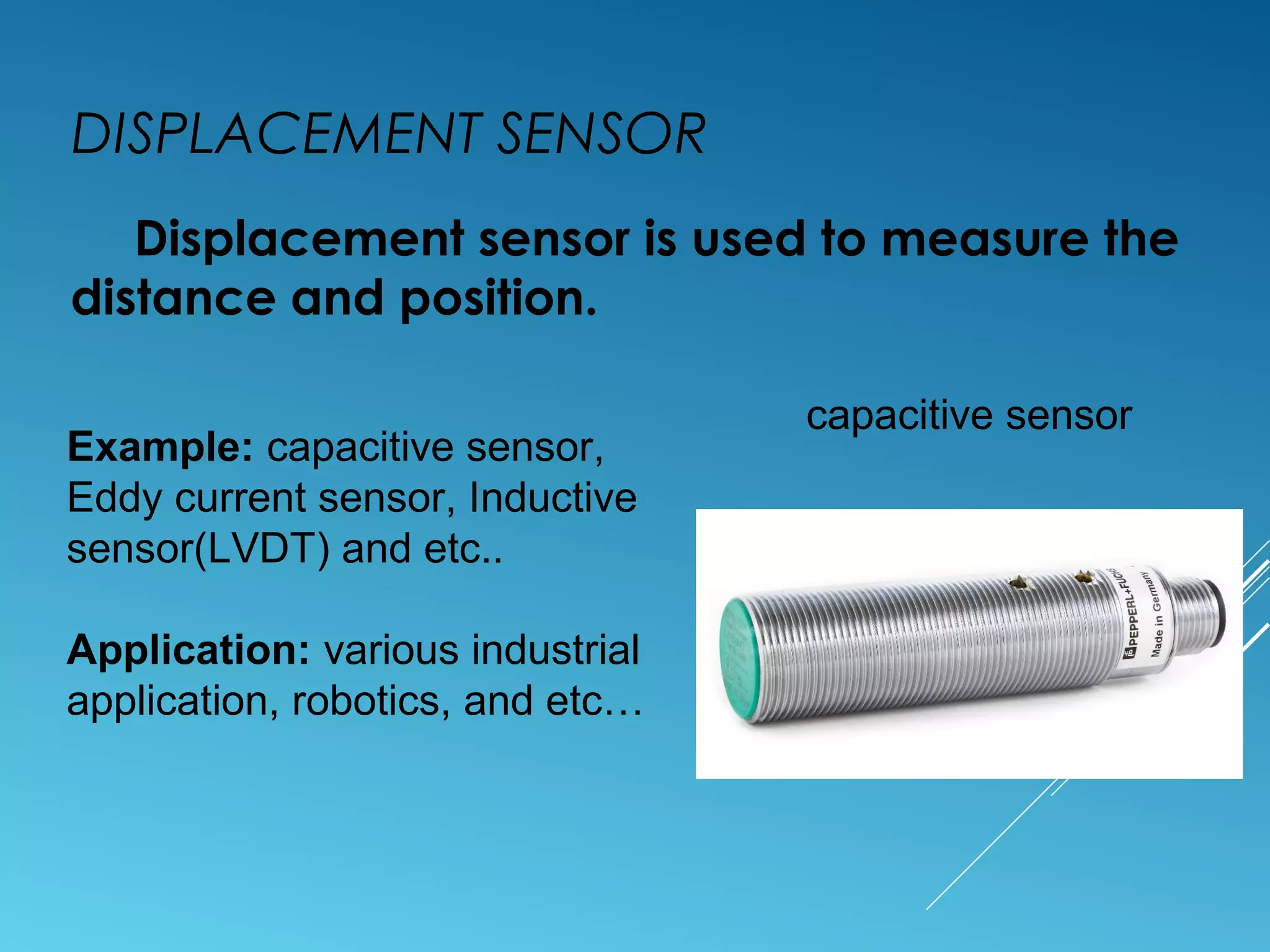
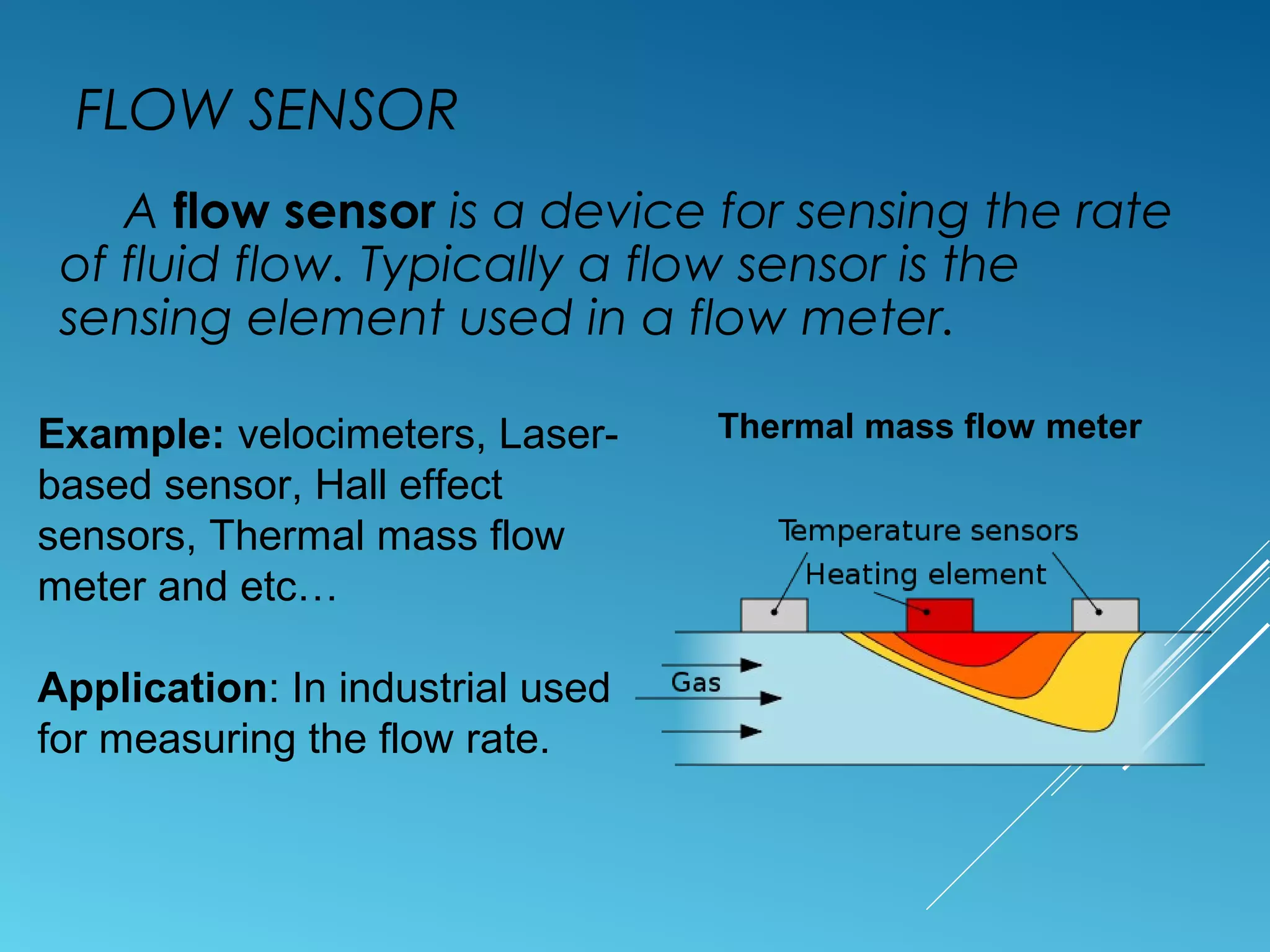
- Sensors classified by measurement objective such as temperature, pressure, level, displacement, flow, speed, and biosensors.
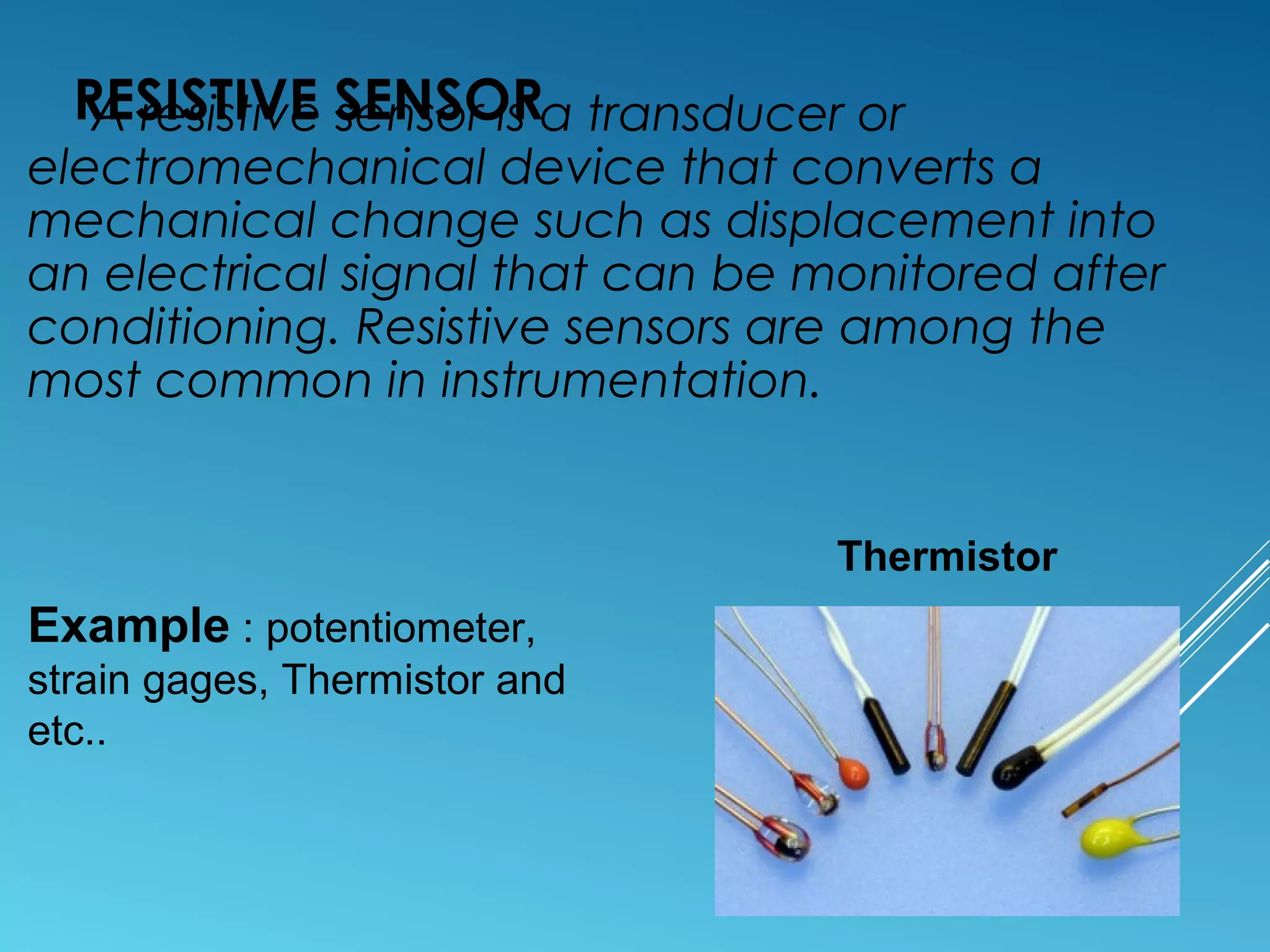
- Sensors classified by operation principle such as resistive, capacitive, inductive, and ultrasonic sensors.
- Examples are provided for each type of sensor as well as common applications. The document provides an overview of sensor fundamentals, characteristics, and applications.