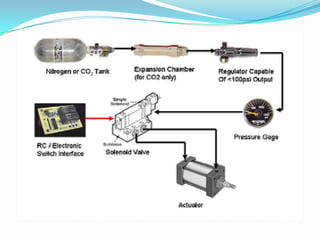
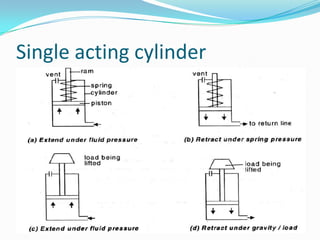
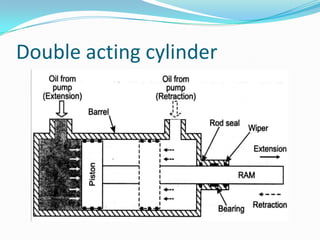
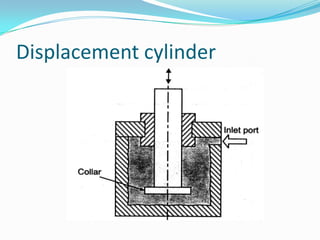
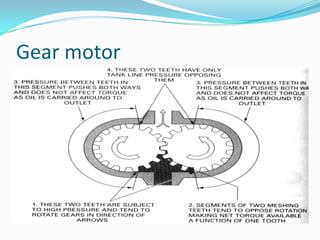
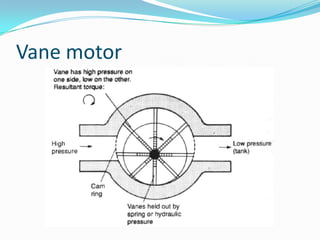
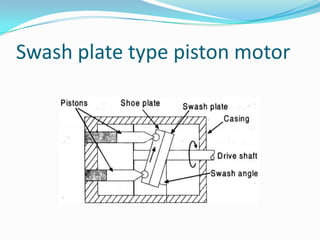
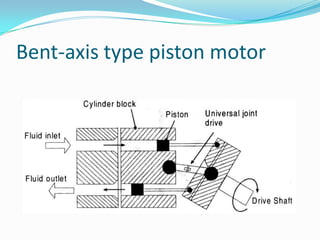
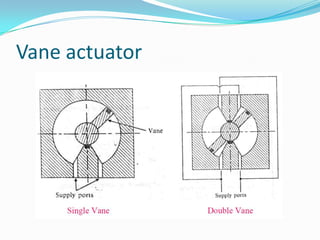
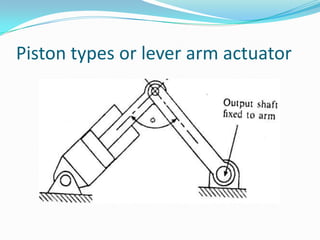
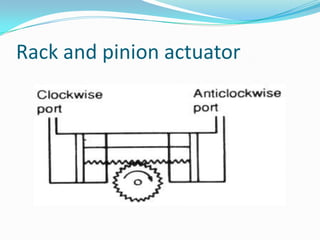
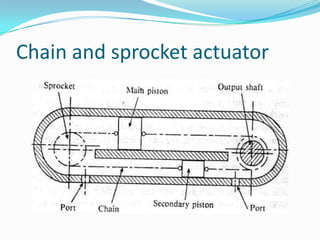
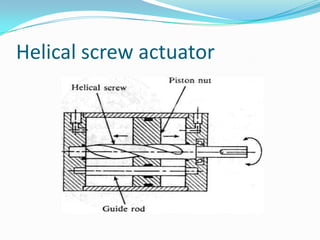
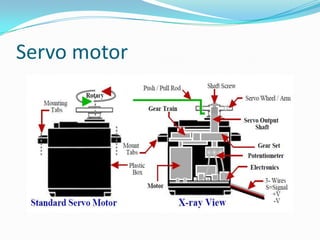
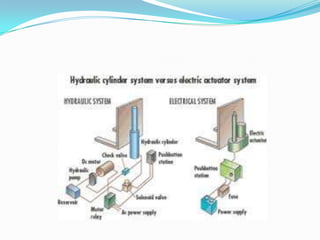
This chapter discusses different types of actuators used to control movement in robots. It describes pneumatic, hydraulic, and electrical motor systems. Pneumatic systems use compressed air and are low-cost but have limitations from air compressibility. Hydraulic systems provide greater speed and strength but require more space. Electrical motor systems like DC, AC, servo, and stepper motors offer more accuracy and repeatability than hydraulic systems. The chapter compares advantages and disadvantages of pneumatic and hydraulic actuators and describes various linear and rotary configurations for each system.