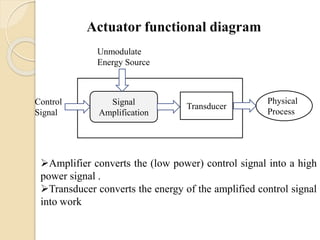
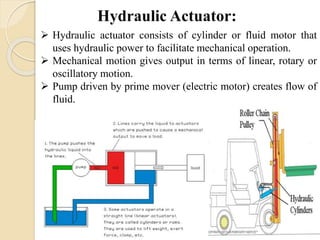
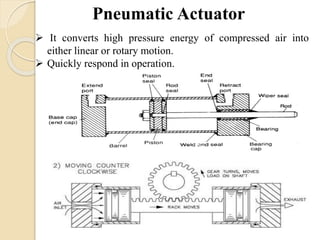
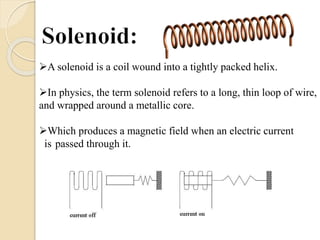
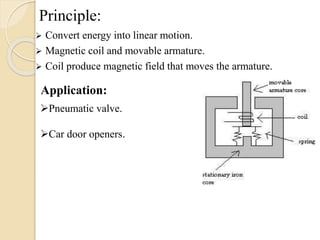
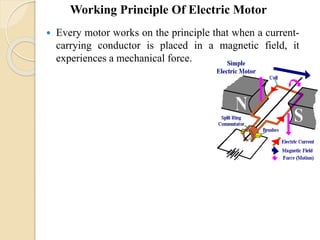
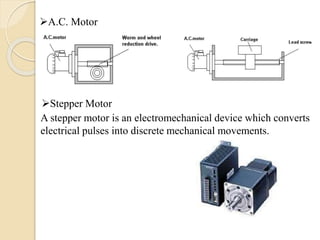
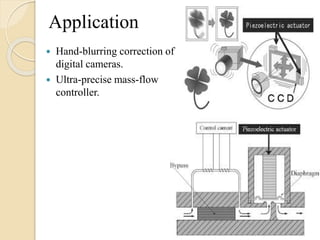
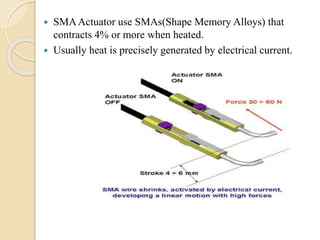
The document discusses different types of actuators. Actuators are devices that convert energy into motion. Common types include hydraulic actuators, which use fluid power to produce linear or rotational movement, pneumatic actuators, which use compressed air, and electric actuators like solenoids, motors, and piezoelectric actuators. Actuators are selected based on factors such as the required force, speed, precision, and environment. Actuators play an important role in converting control signals into physical motion in machines and devices.