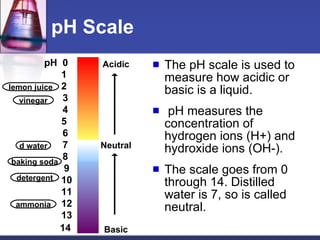
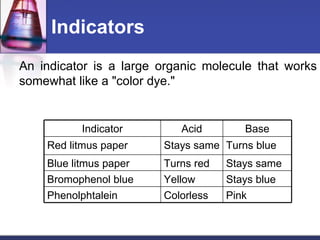
The document discusses acids and bases. It defines acids as substances that ionize to form hydrogen ions in solution, and bases as substances that ionize to form hydroxide ions. Examples of acids include HCl and H2SO4, while examples of bases include NH3 and NaOH. The pH scale is used to measure how acidic or basic a substance is. Acids and bases react with each other through neutralization reactions to form salts and water. The formation of caves is also discussed, and involves the reaction of carbonic acid with calcium carbonate bedrock.